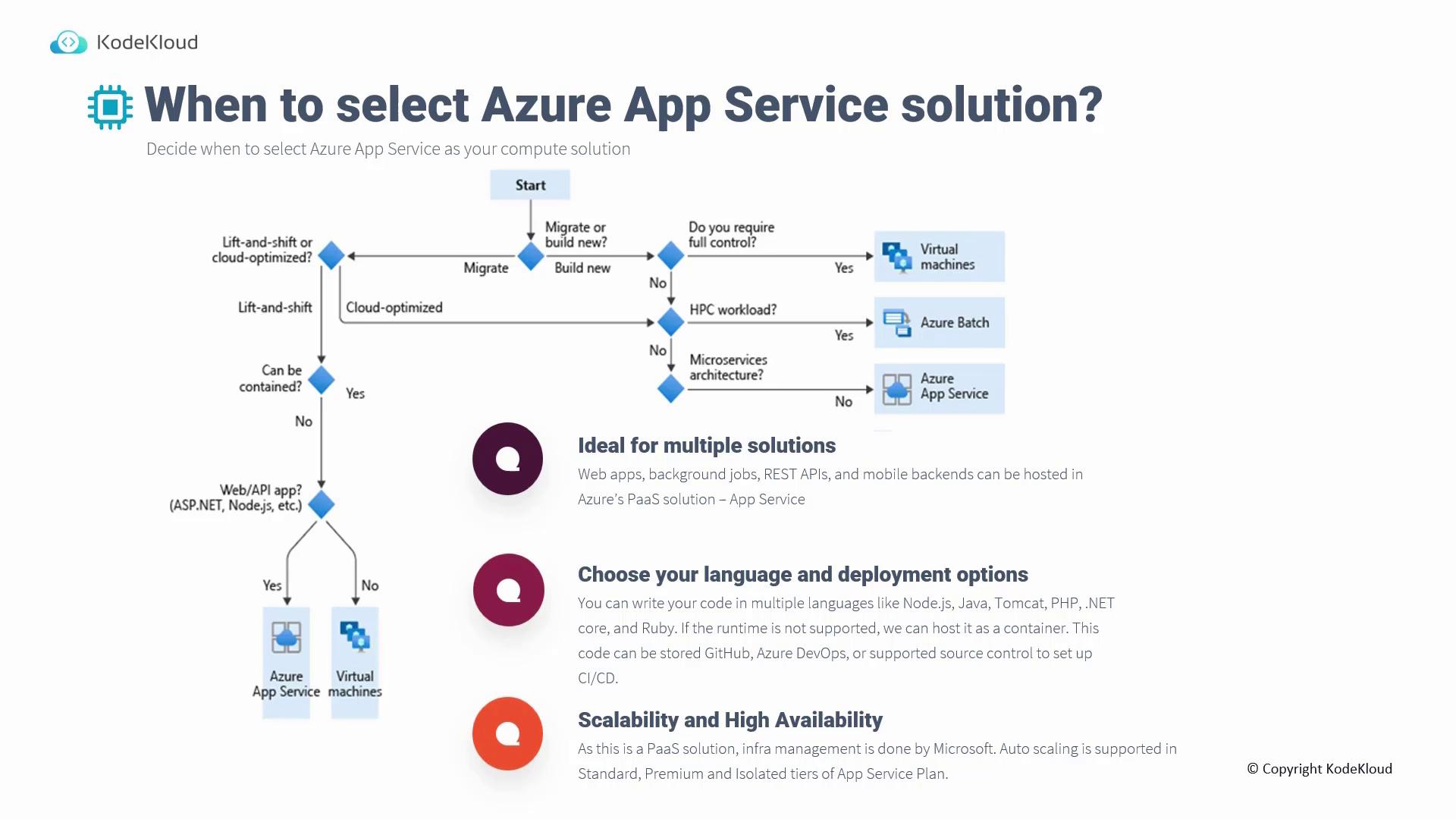
Choosing Your Development Language and Deployment Method
Azure App Service supports a wide range of programming languages, including Node.js, Java, PHP, .NET Core, Ruby, and Tomcat. For runtimes that are not directly supported, deploying your application in a container is a viable option. All your code can be stored in repositories such as GitHub, Azure DevOps, or other supported source control systems, and connected through a CI/CD pipeline for seamless deployments.Scalability and High Availability
Scalability and high availability come built-in with Azure App Service. Microsoft manages auto-scaling features across Standard, Premium, and Isolated tiers of the App Service plan. Note that the maximum number of instances you can scale to varies by tier:- Standard: up to 10 instances
- Premium: up to 30 instances
Key Considerations
1. Sizing
Evaluating the correct App Service plan tier is crucial based on cost, scaling requirements, and available features. Azure App Service plans come in various tiers ranging from Free and Shared to Basic, Standard, Premium, and Isolated. For example:- Testing: The Free tier is suitable for experimenting with an application.
- Auto-Scaling: The Standard tier is required for auto-scaling features.
- Private Endpoints: The Premium tier supports private endpoint configurations.
2. Built-in Authentication
Azure App Service offers seamless integration with popular identity providers like Microsoft, Google, and Facebook. Unlike virtual machines that often require additional SDKs or code modules to manage authentication for languages such as .NET, Java, or Python, App Service allows you to directly choose and configure an identity provider for your application.3. Deployment Slots
Deployment slots allow you to promote staging code to production and provide a simple rollback mechanism if issues arise. Available from the Standard plan onward, deployment slots enable developers to test code in a staging environment before swapping with the production slot, ensuring a smooth transition and quick recovery if needed.4. App Type
Azure App Service accommodates a diverse range of application types, including web apps, API apps, web jobs, and mobile app backends. Whether you are deploying an app written in ASP.NET, Java, Ruby, PHP, or Python, you can choose between Windows or Linux hosting. Additionally, web jobs allow you to run scripts or programs (e.g., Node.js, PHP, Python, Java) using command shell scripts, batch files, PowerShell, or bash for both scheduled and triggered tasks.5. CI/CD Integration
Modern app development relies on Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) practices. Azure App Service integrates with popular source control providers like GitHub, Azure DevOps, Bitbucket, or even manual methods via Dropbox or OneDrive, allowing you to set up automated deployment pipelines with ease.Summary of Considerations for App Service as a Compute Solution
Below is an infographic summarizing the critical considerations for utilizing Azure App Service as your compute solution. The infographic covers aspects such as sizing, authentication, deployment slots, application type, and CI/CD integration.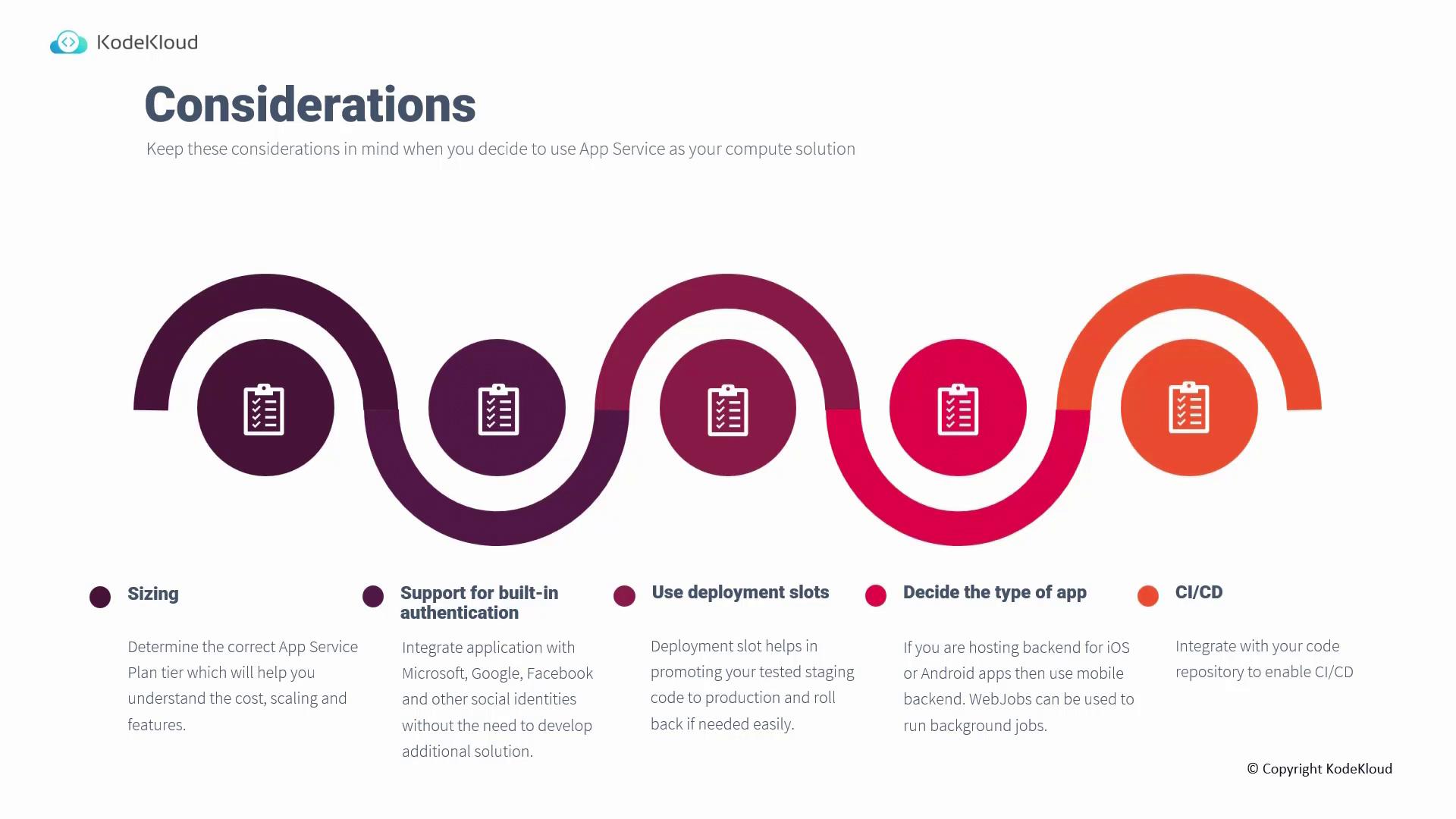
For a detailed exploration of Azure App Service, including live deployment demonstrations, please refer to our AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator course.