Accessing Jenkins
Begin by opening your Jenkins instance. If you haven’t set it up before, navigate to your Jenkins IP address on port 8080. Follow the setup instructions to configure your username and other settings. Once completed, you should see a dashboard similar to the image below:
Creating a New Pipeline
- Click on New Item.
- Provide a name for your pipeline; for this example, name it Hello World Pipeline.
- Select the Pipeline option and then click OK.
Pipeline Configuration
Scroll down to the pipeline configuration section. You will see an interface similar to the following:
- Create the pipeline script directly in Jenkins.
- Load the pipeline script from source control (e.g., via a Jenkinsfile in your repository).
Jenkins provides sample pipelines to help you get started without writing the entire script from scratch. Feel free to use these examples as a learning tool.
Sample Pipeline Script
Review the following pipeline script:Script Breakdown
- pipeline block: Encloses all instructions for the pipeline.
- agent any: Directs Jenkins to run the pipeline on any available agent. (An agent is a machine connected to the Jenkins controller for executing pipelines.)
- stages block: Groups the pipeline’s tasks into logical units (e.g., build, test, deploy).
- hello stage: Contains a
stepsblock where theecho 'hello world'command prints “hello world” to the console output.
Saving and Running the Pipeline
Once you have entered the pipeline script:- Click Save.
- To execute your pipeline, click the Build Now button.
- Click on the build number.
- Select Console Output to review the steps performed by Jenkins.
Build Interface Overview
After running your pipeline, you will encounter an interface that displays build details such as the start time, user who initiated the build, and duration metrics. Check out the build interface below: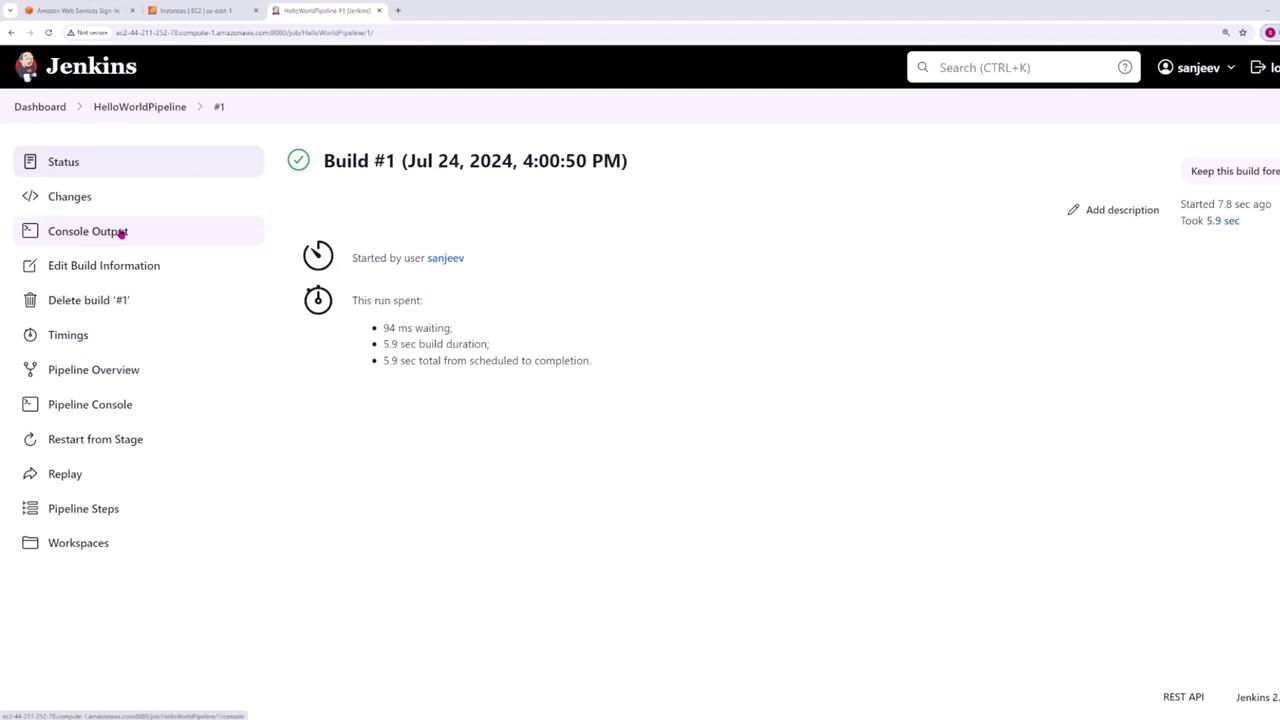
Now that you’ve successfully created and executed your first Jenkins pipeline, explore further by adding more stages or integrating additional tools to enhance your CI/CD workflow.