Preparing Jenkins
Before proceeding, install the SAM CLI on your Jenkins server. This tool is essential for building and deploying your Lambda code to AWS, just as you would on your local machine.
Setting Up AWS Permissions
Proper AWS permissions are required for Jenkins to deploy Lambda functions. Start by creating an AWS user with the necessary permissions, and generate an access key and secret key. These credentials will be stored securely in Jenkins.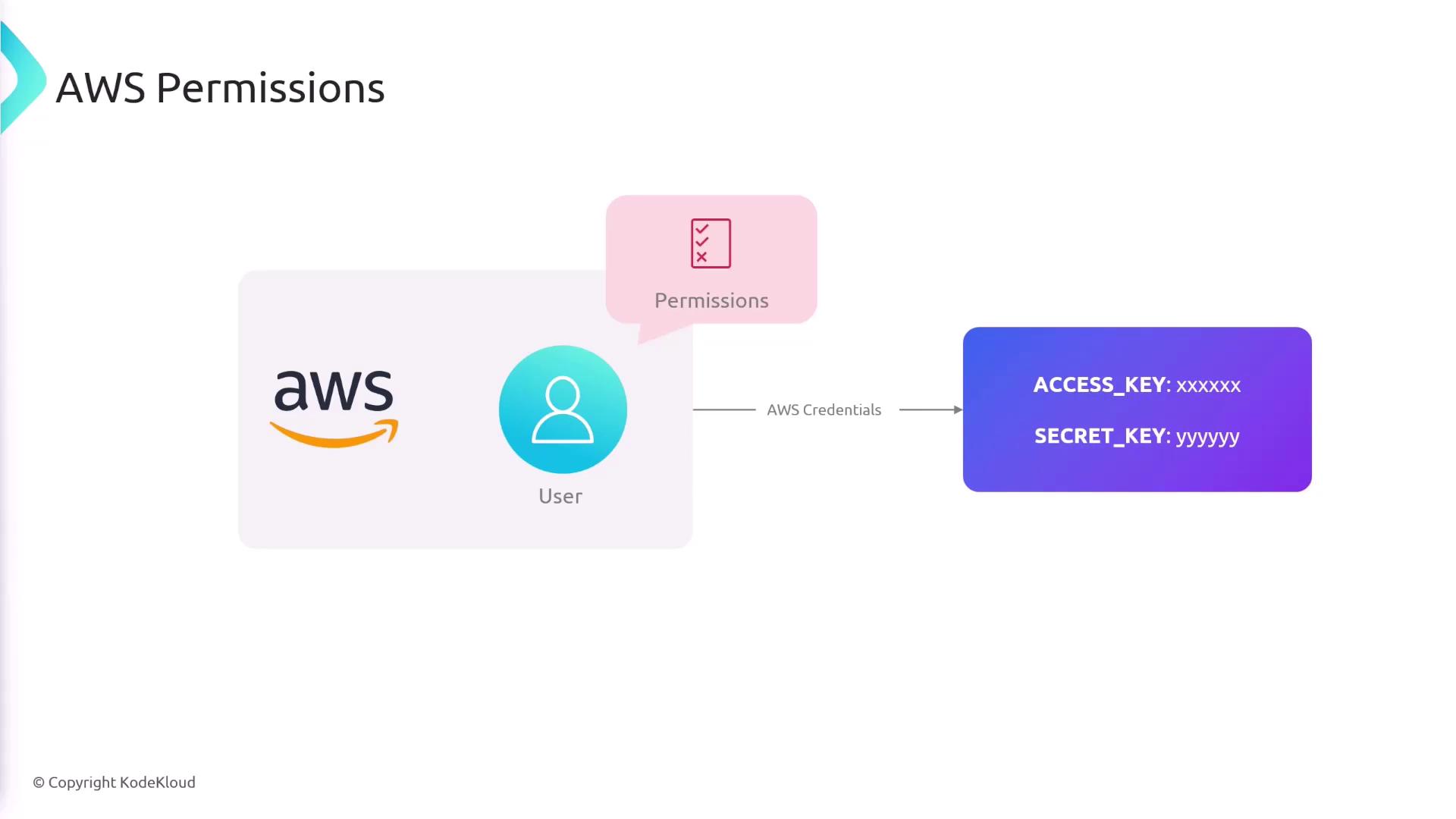
Ensure that the created AWS user has only the permissions needed for deploying Lambda functions to maintain security best practices.
Pipeline Overview
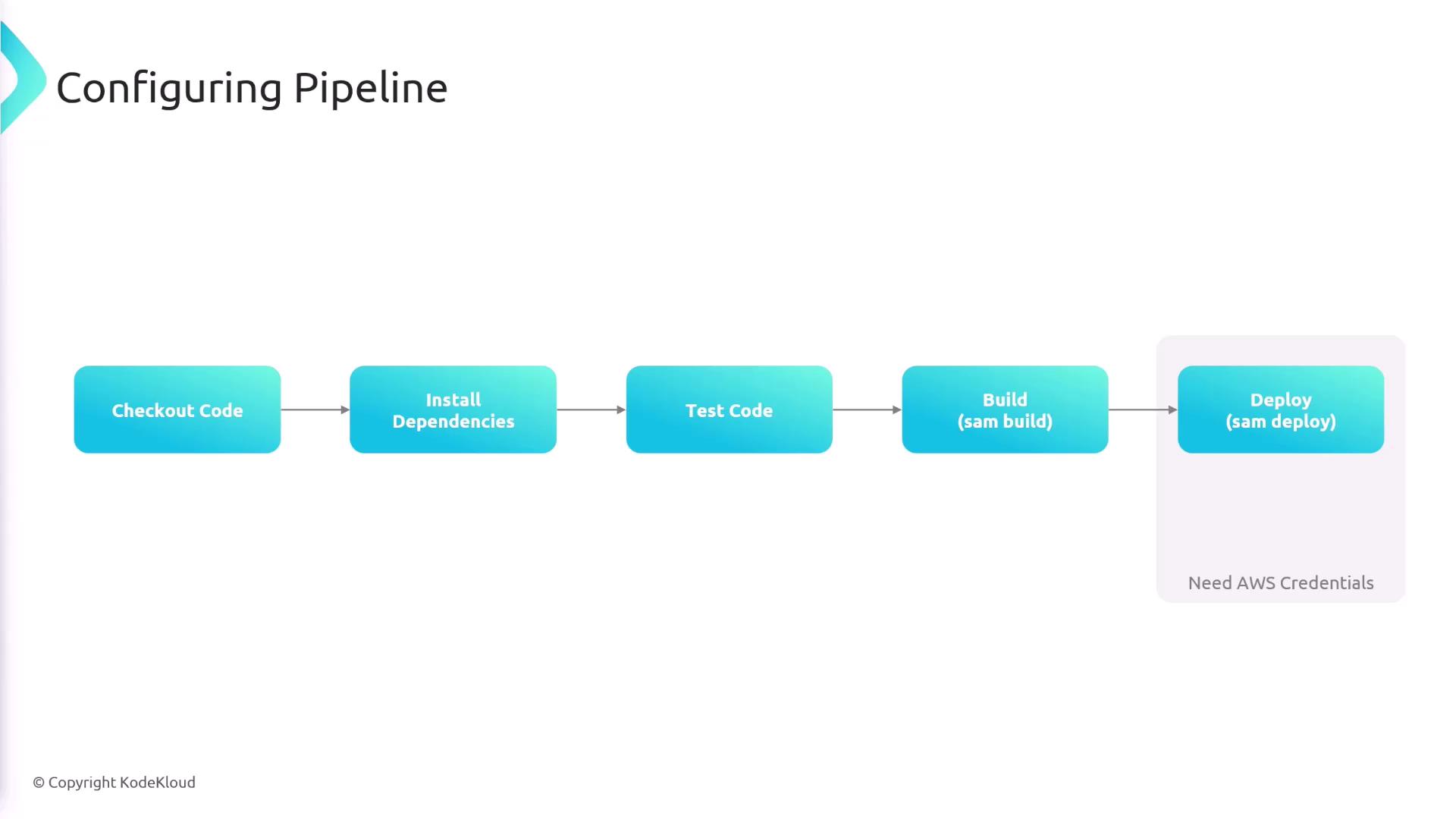
The CI/CD pipeline is designed to execute the following sequential steps:- Checkout the code from the repository.
- Install dependencies.
- Run tests.
- Build the code using the SAM CLI.
- Deploy the built application to AWS.
Jenkins Pipeline Configuration
Below is an example Jenkins pipeline configuration. Note that this project contains tworequirements.txt files. In this example, the development dependencies are installed from lambda-app/tests/requirements.txt before running tests.
Setup Stage: Installing Dependencies
Build Stage: Building the Code
With the dependencies installed and tests (if any) executed, the next step is to build the Lambda application using the SAM CLI. The command uses thelambda-app/template.yaml file to define the build parameters.
Deploy Stage: Deploying to AWS
The deploy stage includes AWS credentials provided as environment variables. These credentials are set for this stage only to enhance security. Thesam deploy command is executed with flags --no-confirm-changeset and --no-fail-on-empty-changeset to automate the deployment process without manual input.
Automating your deployment process with Jenkins ensures consistent and reproducible builds, reducing manual errors and accelerating your release cycles.