Benefits of Using Jenkins Credentials
Using Jenkins credentials provides several key advantages:- Enhanced Security: Sensitive data is stored securely, reducing the risk of exposure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Keeps your organization in line with regulatory requirements that prohibit storing sensitive information in plain text.
- Process Efficiency: Automating secure access to secrets improves overall pipeline reliability.
- Global: The credential can be used by all jobs in the pipeline.
- System: Access is restricted to the Jenkins system and background tasks; jobs and pipelines cannot access these credentials.
- User: The credential is specific to an individual Jenkins user, used for personal access.
Always adhere to the principle of least privilege. Grant only the necessary permissions to the users, jobs, or plugins that require access to a credential. Regular audits and credential rotations are also recommended for maintaining security.
Creating a Credential in Jenkins
To add a new credential, navigate to the Jenkins dashboard, click on Manage Jenkins, then access the credentials section. The image below illustrates the Jenkins dashboard interface where you can configure credentials: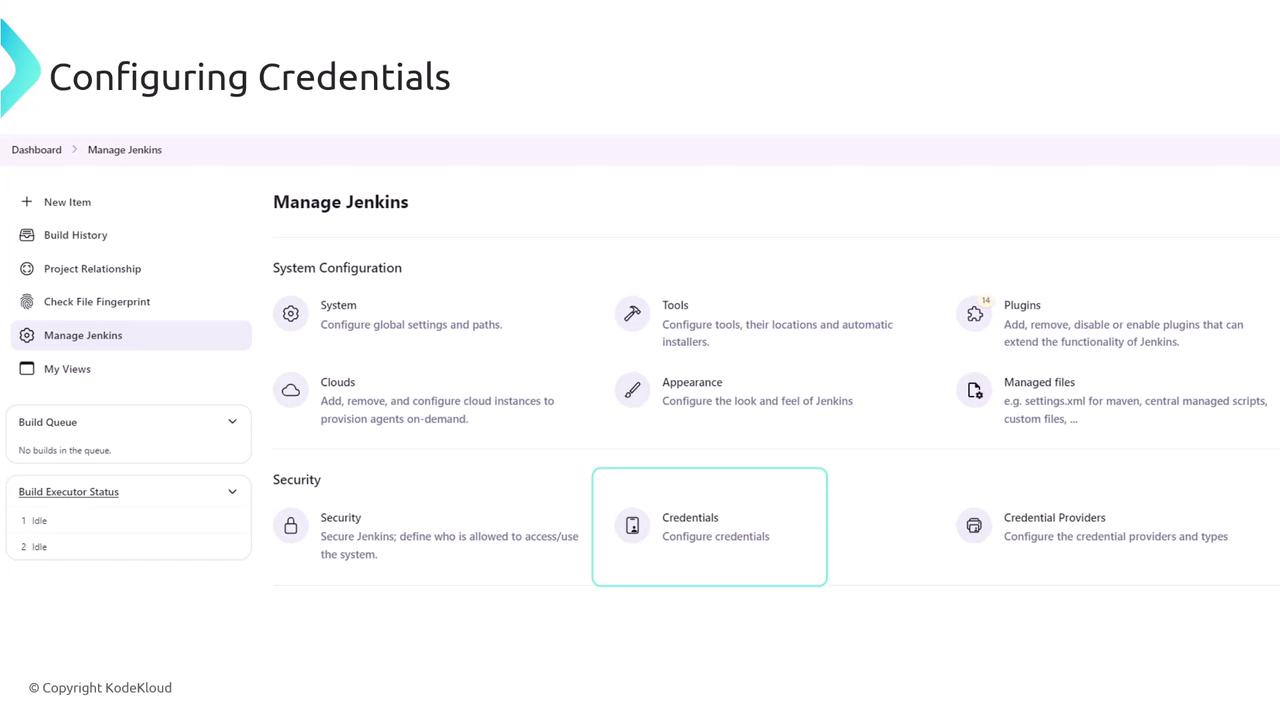
Accessing Credentials in a Pipeline
One effective method for using Jenkins credentials is by binding them to environment variables. For example, after creating a credential (named “prod-server”) via the GUI, you can reference it in your pipeline script with the following approach:Avoid printing sensitive information using commands like
echo. Although Jenkins masks secret values in the console output, displaying sensitive data can be risky. For more details, refer to Jenkins Groovy String Interpolation.Using the Credentials Binding Plugin
For a more secure alternative, utilize the credentials binding plugin. This method restricts the exposure of credentials to a specific block of code. The following example shows how to use a username/password credential securely with the plugin:withCredentials block, the environment variables mypassword and myusername are available for secure use within your shell commands.
Binding an SSH Key Credential
Jenkins credentials also support SSH keys. By configuring an SSH key credential, you can bind it to an environment variable and use it in your SSH commands. Consider the following example:MY_SSH_KEY, while the username is retrieved from the corresponding credential.
By implementing these techniques and examples, you can securely manage and utilize credentials in your Jenkins pipelines, improving both security and efficiency.