#!) directive affects script execution and portability. You will learn to:
- Remove the shebang from a script and analyze its behavior.
- Trace system calls with
straceto observe kernel execution. - Demonstrate shebangs across different shells (e.g., Bash, C shell).
- Adopt a modern, portable shebang and avoid common pitfalls.
The Shebang Analogy
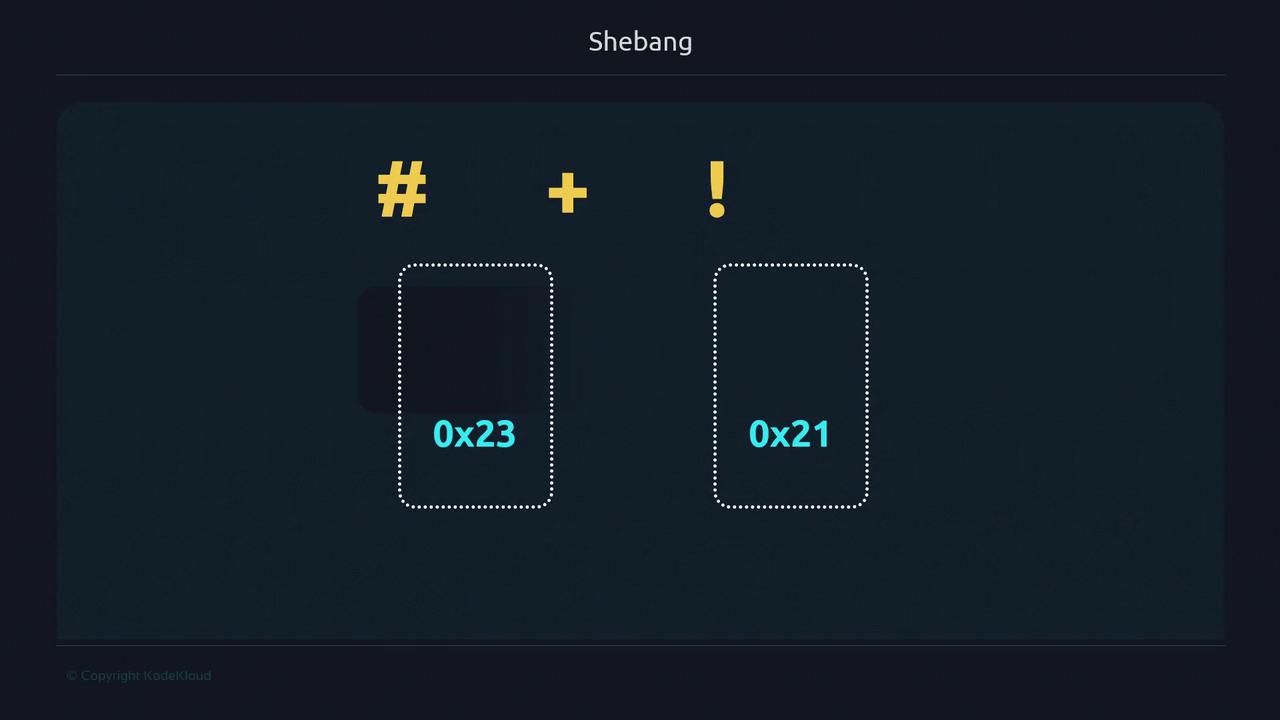
Think of yourself as a polyglot translator facing an ancient manuscript. Each dialect (shell) has subtle differences. A shebang acts like a translator’s guide, ensuring your script is read by the intended interpreter. Without it, your login shell takes over, which may lead to unexpected behavior and portability issues. Example of a classic shebang:#, 0x23) with “bang” (!, 0x21), sometimes pronounced “shbang.”
What Happens Without a Shebang?
Createnoshebang.sh without a shebang:
/bin/sh, which lacks Bash-specific features.
Tracing Kernel Execution with strace
Compare a script without and with a shebang:$$) in the background:
#! followed by a valid interpreter, it invokes that program directly.
Using a Different Shell: C Shell Example
C shell (csh) syntax is distinct. Running a C shell script under Bash without a shebang will fail:
Modern, Portable Shebang
Hardcoding interpreter paths can break across systems. Instead, use:env to locate bash via your PATH, enhancing cross-platform compatibility.
Using
#!/usr/bin/env bash avoids assumptions about interpreter locations, but it relies on env being in /usr/bin.| Shebang Line | Description | Pros & Cons |
|---|---|---|
| #!/bin/bash | Direct path to Bash | Fast invocation, but not portable if Bash is installed elsewhere. |
| #!/usr/bin/env bash | Finds Bash in PATH via env | Portable across environments, depends on a correct PATH. |
Demo: Bash Version Features
Createbash_versions.sh:
PATH:
#!/usr/bin/env bash, you automatically use the most appropriate Bash installed on your system.
Caveats & Recommendations
-
Minimal environments (e.g., BusyBox) may not include
bash. Verify available interpreters in/etc/shells:
If
/usr/bin/env or your chosen shell isn’t available, scripts will fail. Always confirm interpreter paths before deployment.- Select a shebang that aligns with your target environment and installed shells.