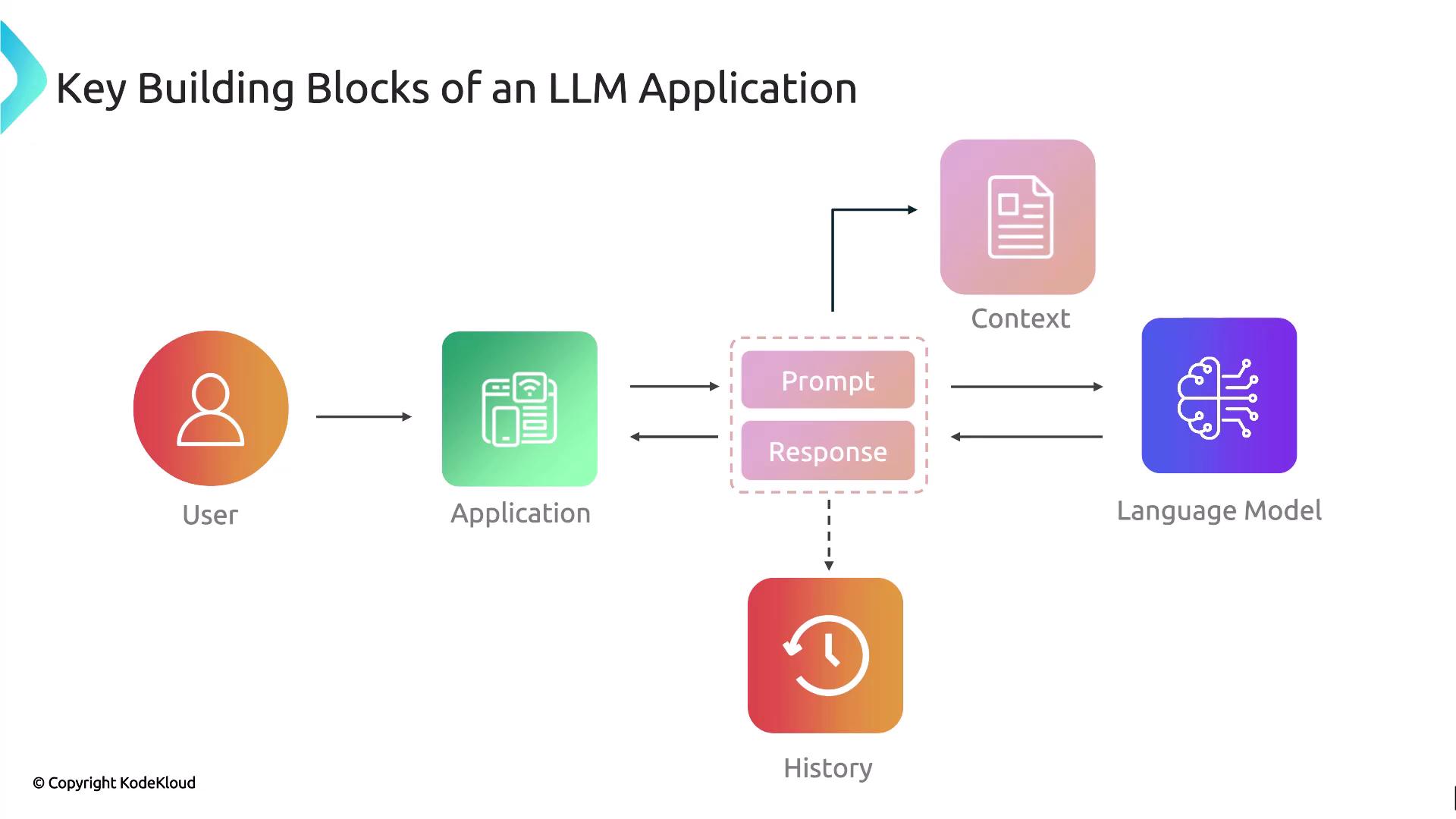
Core Components
| Component | Role | Example |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Captures input from end-users via web, mobile, or chat UI | Chat widget, web form |
| Prompt Generation | Transforms user input into a structured prompt suitable for the LLM | Template-based or dynamic prompt builder |
| Context Management | Supplies additional data—documents, user profile, or external APIs | PDF upload, database lookup |
| Language Model | Executes the prompt on an LLM (e.g., GPT-3.5, GPT-4) to generate a response | openai.ChatCompletion.create |
| Response Handling | Processes, formats, and presents the LLM output to the user | JSON parsing, HTML rendering |
| History Management | Stores and retrieves past conversations to maintain context and continuity | Database, in-memory session cache |
Providing rich, relevant context is key to minimizing hallucinations and improving answer accuracy.
ChatGPT Interface Example
The following diagram shows how ChatGPT ties all the building blocks together in a real-world user interface: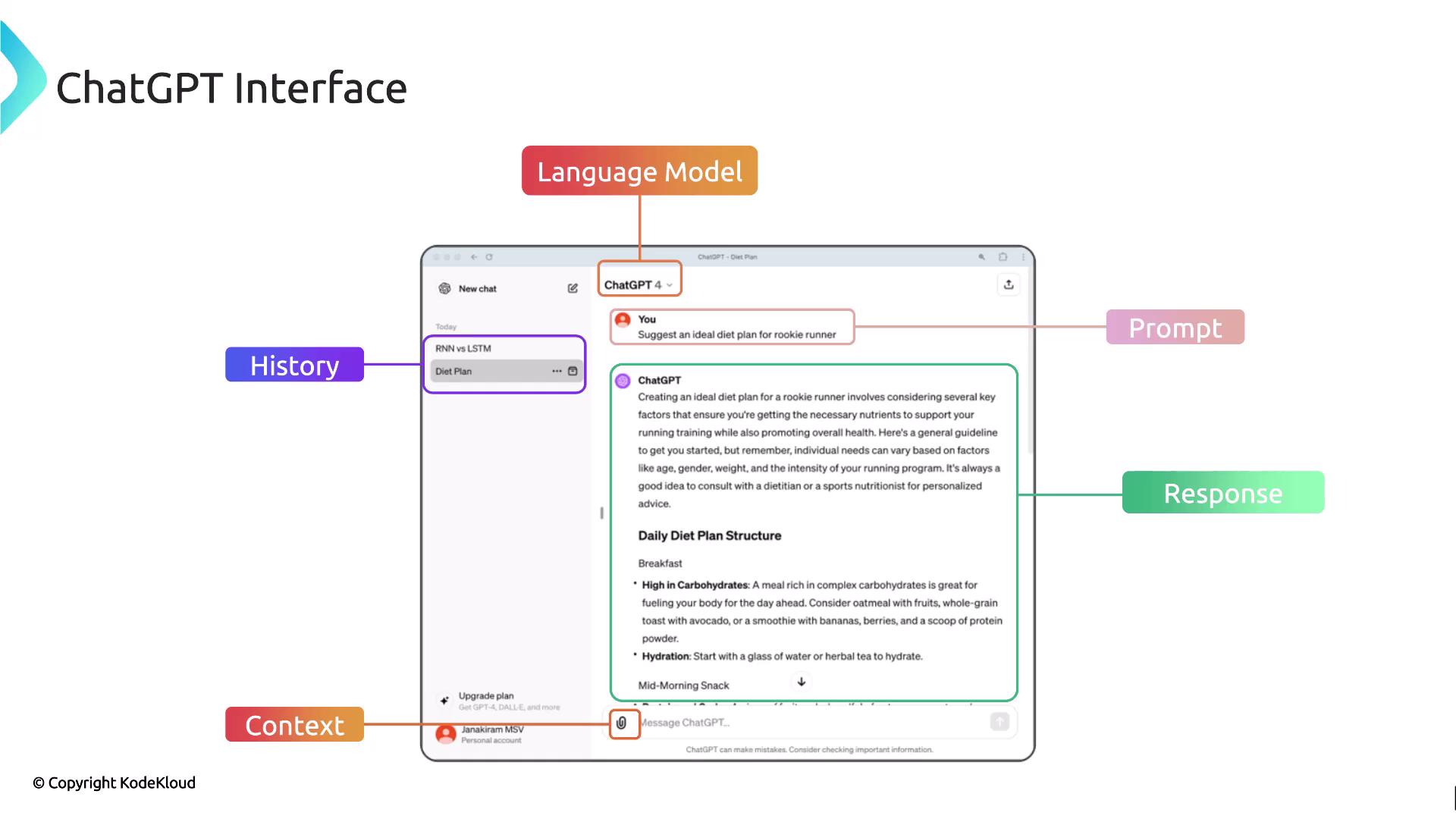
| UI Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Language Model Selector | Switch between GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 |
| Prompt Input | Enter queries like “Suggested ideal diet plan for a rookie runner.” |
| Context Upload | Attach files—PDFs, CSVs—to refine model output |
| Response Panel | Displays the generated answer |
| History Sidebar | Shows previous conversations for continuity |
Always handle user data securely and comply with GDPR, CCPA, or other regional regulations when storing conversation history.
Sample Code Snippet
Below is a simple example using LangChain and OpenAI’s Python API to create a chat completion:What’s Next
In the upcoming sections, we’ll dive deeper into each component:- Prompt engineering best practices
- Incorporating external knowledge sources
- Advanced context management patterns
- State persistence and session orchestration