Full retraining of an LLM can require dozens of GPUs and take weeks, making it impractical for most teams. LoRA reduces compute requirements and speeds up iteration by training only a small set of additional parameters.

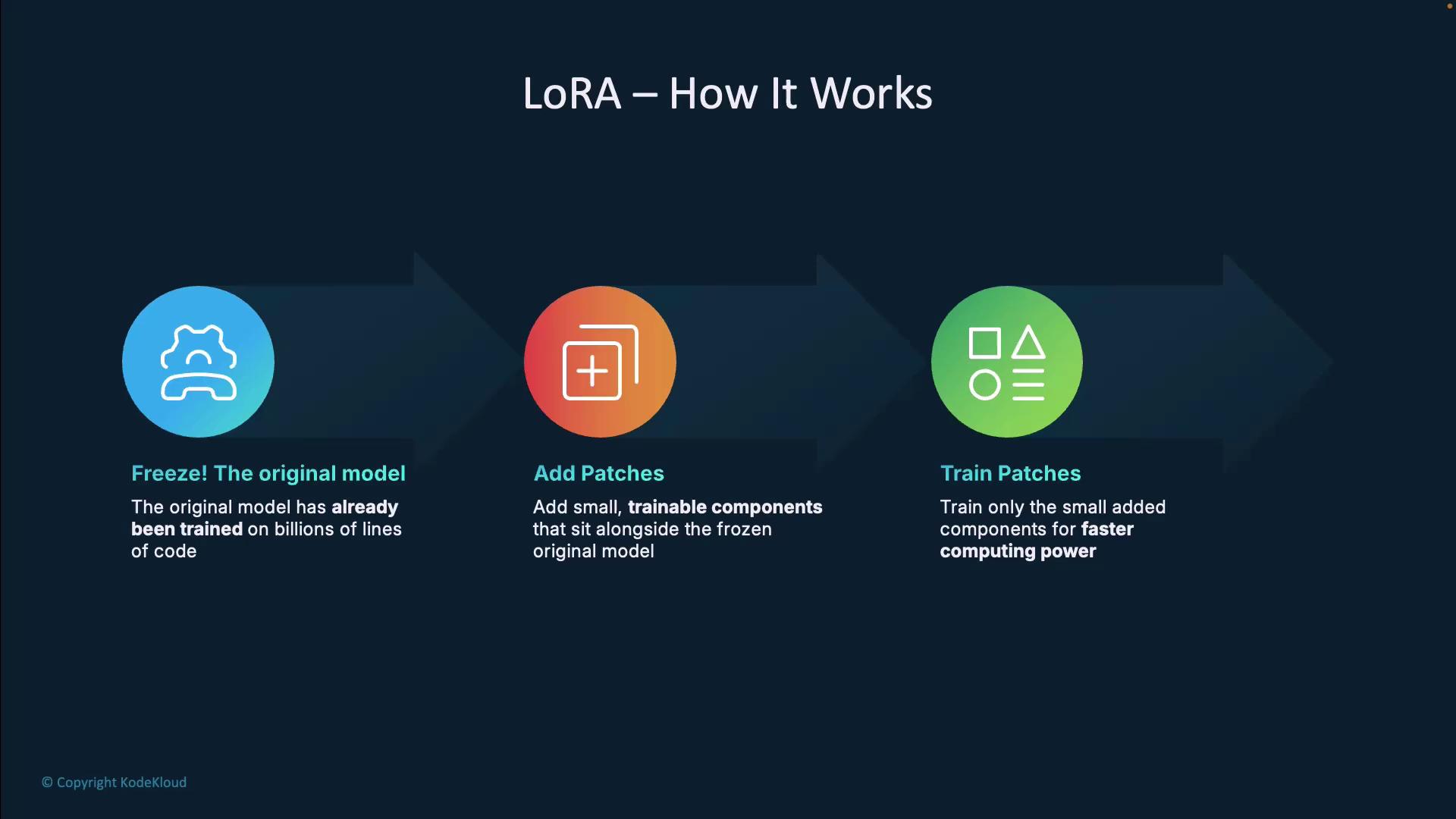
How LoRA Works
LoRA fine-tuning involves three straightforward steps:-
Freeze the Base Model
Keep the entire pre-trained LLM unchanged. This preserves its broad programming knowledge learned from billions of code examples. -
Inject Trainable Patches
Introduce small, low-rank adapters alongside existing model weights. These act like overlays on a GPS map—you keep the base map and add custom routes. -
Train Only the Adapters
Feed examples of your team’s coding style or preferences. During training, only the newly added parameters update, making the process much faster and more cost-effective.
Key Benefits of LoRA
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Lower Compute Requirements | Train and deploy on standard GPUs or even high-end laptops. |
| Faster Iteration | Go from concept to customized model in hours, not weeks. |
| High Performance | Matches full fine-tuning accuracy while drastically cutting cost and time. |

Customization Methods Compared
| Method | Compute Cost | Training Time | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Retraining | Very High | Days to Weeks | Excellent |
| Adding Extra Layers | High | Several Hours | Good |
| LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) | Low | Hours | Excellent |
Attempting full model retraining on consumer hardware can lead to out-of-memory errors and excessive cloud costs. Choose LoRA to keep budgets and timelines on track.
Key Takeaways
- Efficiency: Train small adapter modules instead of the entire model.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Achieve full fine-tuning performance on standard GPUs.
- Customization: Tailor Copilot to your team’s conventions, libraries, and architecture in hours.