Why Partition a Disk?
- Separate operating systems (e.g., Windows vs. Linux)
- Isolate data, swap, and boot partitions
- Use different partition table formats: MBR (DOS) vs. GPT (modern systems)
Leaving 1 MiB unallocated at the start of the disk is a best practice. Many bootloaders require this alignment for optimal performance.
1. Viewing Existing Partitions
Uselsblk to list block devices and their partitions:
part are actual partitions:
| Column | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NAME | Device name (sda, sdb, etc.) |
| SIZE | Disk or partition size |
| TYPE | disk, part, or lvm |
| MOUNTPOINT | Where it’s mounted (if applicable) |
2. Inspecting the Partition Table with fdisk
To view the partition table on/dev/sda, run:
Disklabel type: dosindicates an MBR partition table.StartandEndare measured in 512-byte sectors.
3. Creating and Modifying Partitions with cfdisk
cfdisk offers an ncurses interface for partitioning. It’s especially helpful on servers without a GUI.
Steps to Partition /dev/sdb
- Attach the disk (e.g.,
sdb) and launch: - Select a label:
- GPT for modern UEFI systems.
- DOS for legacy MBR.
- Create partitions:
- Navigate to Free Space → New → enter
8G→ Enter. - Repeat in remaining free space with
2G.
- Navigate to Free Space → New → enter
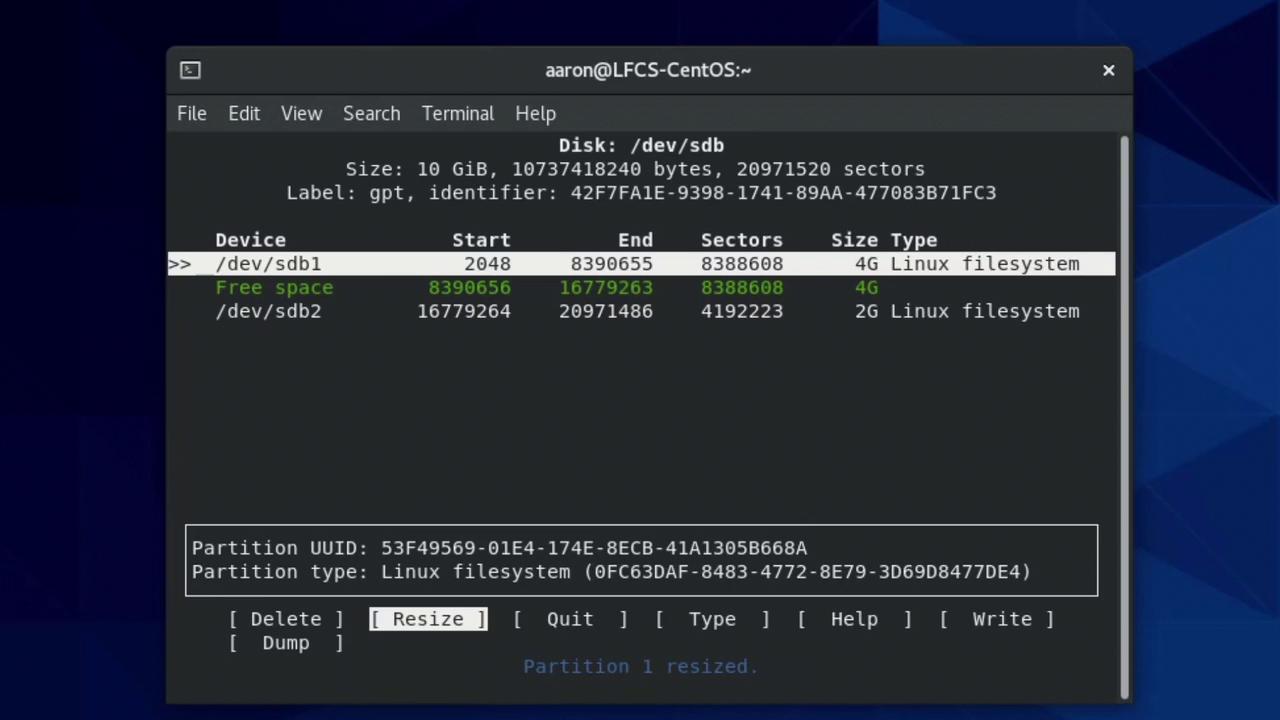
- Resize or split (optional):
- Highlight a partition → Resize → enter new size (e.g.,
4G). - Use freed space to create another partition.
- Highlight a partition → Resize → enter new size (e.g.,
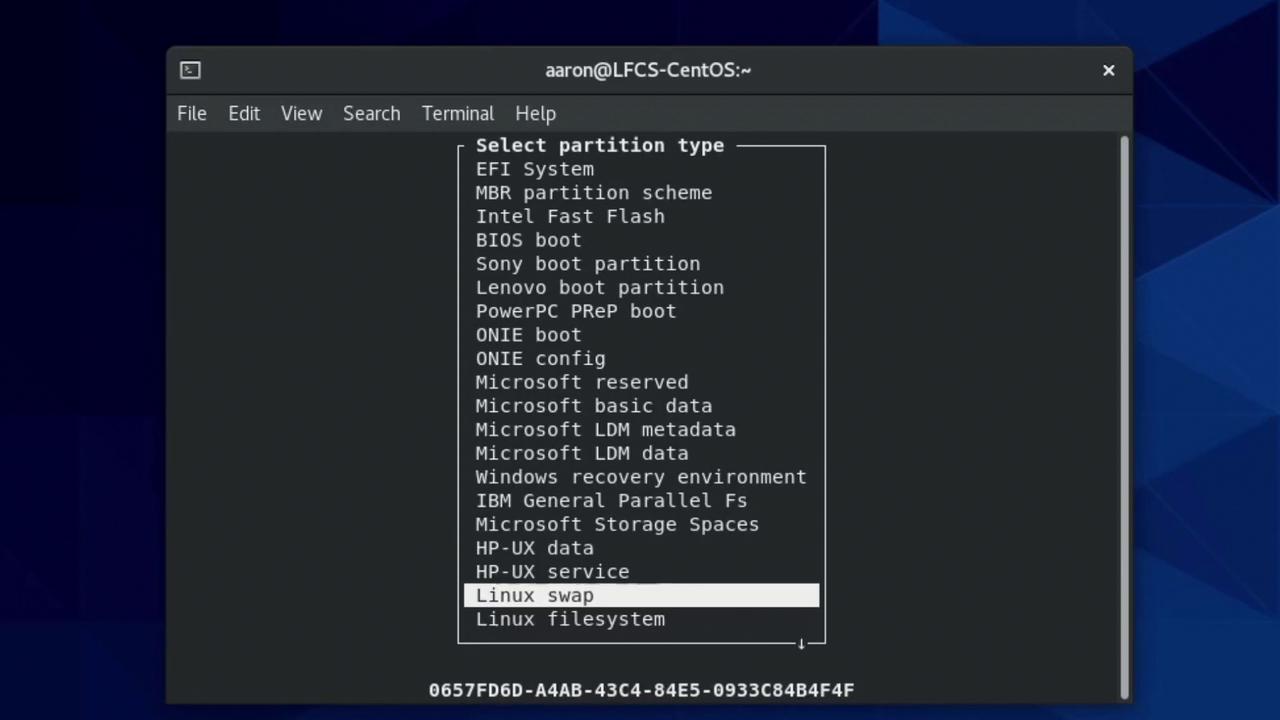
3.1 Setting a Partition Type
The default type is “Linux filesystem.” To mark/dev/sdb3 as swap:
- Highlight sdb3 → Type → select Linux swap → Enter.

When you Write changes in
cfdisk, all partition modifications become permanent. Double-check before confirming.3.2 Writing and Quitting
- Select Write, type
yes, and press Enter. - Select Quit to exit
cfdisk.
4. Verifying the New Partitions
Back in the shell, confirm withlsblk:
/dev/sdb has three partitions: two 4 GiB data partitions and one 2 GiB swap.
Summary of Common Commands
| Command | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| lsblk | List block devices and partitions | lsblk |
| sudo fdisk —list /dev/sdX | Show partition table | sudo fdisk -l /dev/sda |
| sudo cfdisk /dev/sdX | Interactive disk partitioning | sudo cfdisk /dev/sdb |