Table of Contents
- Standard Streams Overview
- Redirecting Output
- Appending Output
- Discarding Output
- Merging and Redirecting Both Streams
- Redirecting Input
- Here Documents and Here Strings
- Pipes and Pipelines
- Quick Reference
- Links and References
Standard Streams Overview
Linux programs communicate using three standard streams:| Descriptor | Stream Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | stdin (standard input) | Receives data (keyboard, files) |
| 1 | stdout (standard output) | Sends regular output (terminal, files) |
| 2 | stderr (standard error) | Sends error messages (terminal, files) |
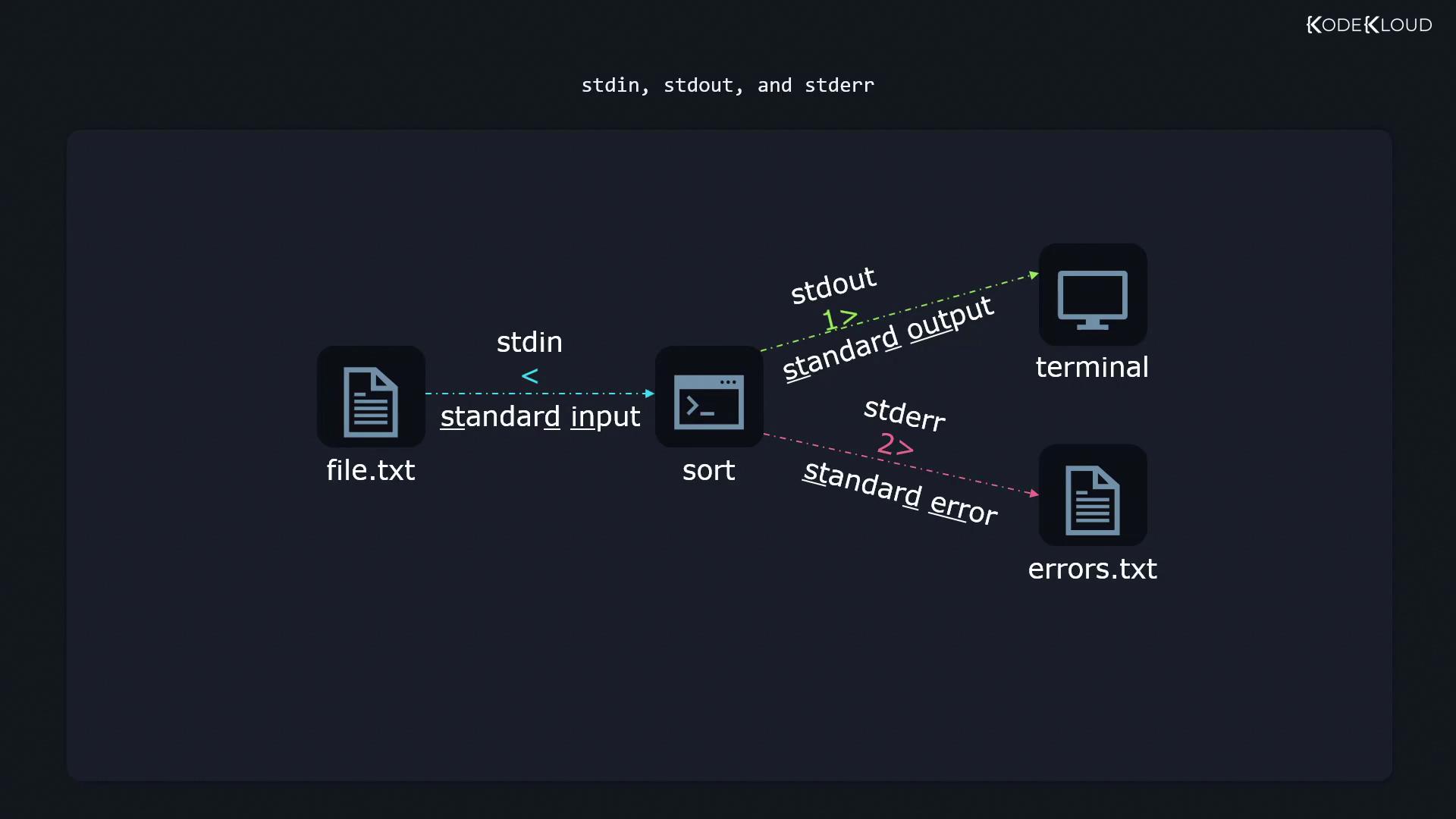
stdout and stderr appear on your terminal. You can redirect them separately:
Redirecting Output (>)
To save a command’s output to a file (creating or overwriting it), use the > operator.
-
Create a file with unsorted numbers:
-
Sort the file and write the result to
sortedfile.txt:
Using
> always overwrites the target file. You will lose previous contents!Appending Output (>>)
To add output to the end of an existing file without erasing its contents, use >>:
Discarding Output (/dev/null)
Send unwanted output or errors to /dev/null, the “black hole”:
Merging and Redirecting Both Streams
-
Redirect
stdoutandstderrto separate files: -
Append both streams:
-
Merge
stderrintostdoutand write to one file:
Order matters:
> all_output.txt 2>&1 merges error output into the same file, while reversing redirects leaves errors on the console.Redirecting Input (<)
Some commands read from stdin instead of a file argument. Redirect a file into stdin like this:
email_content.txt feed directly into sendemail.
Here Documents and Here Strings
Here Documents (<<)
Embed a block of text as input:
EOF (or any marker you choose) encloses the input region.
Here Strings (<<<)
For single-line input, here strings are concise:
Pipes and Pipelines (|)
Pipelines let you chain commands by feeding one’s stdout into the next’s stdin. Example: filter, sort, and align columns from /etc/login.defs:
grep -v '^#'removes commentssortorders linescolumn -taligns columns into a neat table
Quick Reference
| Operator | Description | Example | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
> | Redirect stdout, overwrite file | sort file.txt > sortedfile.txt | ||
>> | Redirect stdout, append to file | echo hi >> greetings.txt | ||
< | Redirect stdin from file | wc -l < file.txt | ||
2> | Redirect stderr, overwrite file | grep foo bar 2>errors.log | ||
/dev/null | Discard stream | cmd 2>/dev/null | ||
&> | Redirect both stdout and stderr | cmd &> combined.log | ||
| ` | ` | Pipe stdout into next stdin | `ls -l | grep ‘^d’` |
<<EOF | Here document (multiline input) | See Here Documents | ||
<<< | Here string (single-line input) | bc <<< "2+2" |