In this lesson, we’ll cover how to manage runlevels with SysV init, configure boot targets, and perform system shutdown or reboot. Controlling which services start or stop is essential for Linux administration—whether you’re running web servers, mail daemons, or network services.
SysV init and Runlevels On SysV-based systems, /sbin/init (PID 1) manages services through predefined runlevels (0–6). Each runlevel corresponds to a different system state:
Runlevel Description 0 Halt (shutdown) 1, S Single-user mode (no networking), maintenance 2 Multi-user mode without NFS (custom on some distros) 3 Full multi-user mode with networking (console login) 4 Unused/reserved (user-defined) 5 Graphical multi-user mode (desktop environment) 6 Reboot
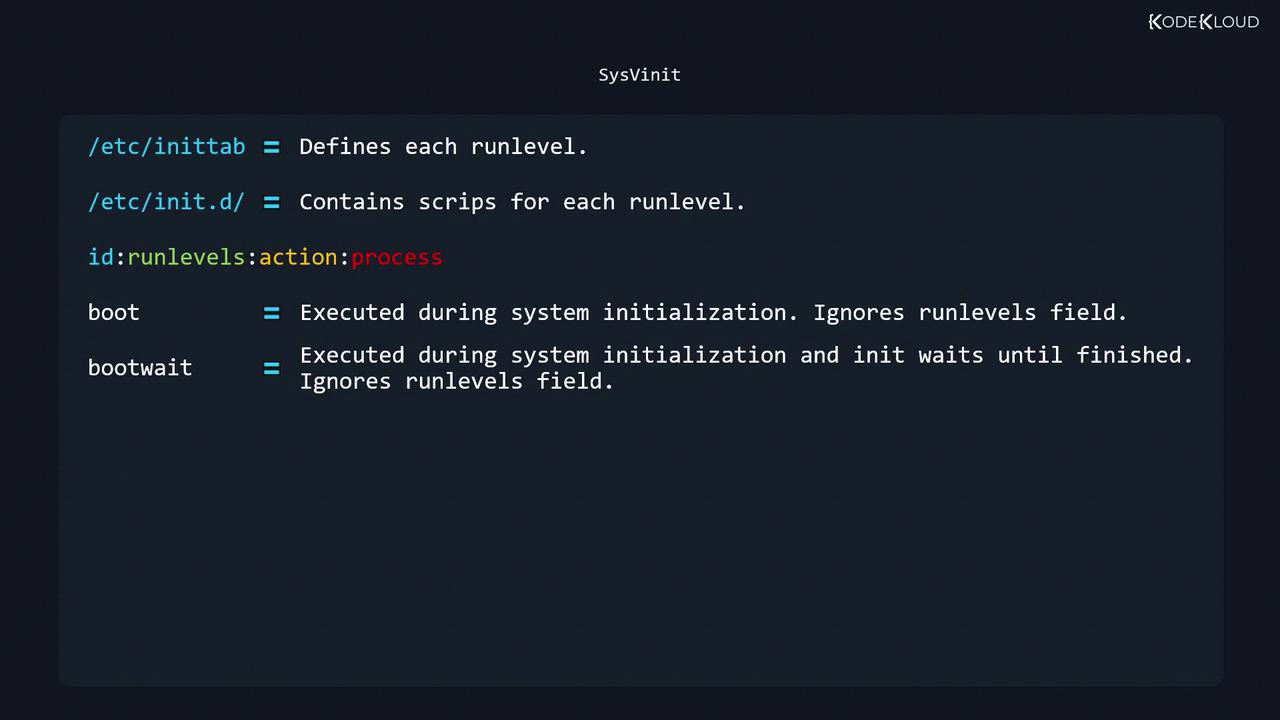
Runlevels and their associated services are defined in two places:
/etc/inittab: Specifies which scripts or processes to start at each runlevel/etc/init.d/: Contains the actual service scripts
Common /etc/inittab Actions Action Description sysinit Run once during system initialization (ignores runlevels) boot Run at boot time, but init does not wait for completion (ignores runlevels) bootwait Run at boot time—init waits until it finishes (ignores runlevels) wait Run when entering listed runlevels—init waits for it to complete respawn Always restart the process if it terminates ctrlaltdel Triggered on SIGINT (CTRL+ALT+DEL) initdefault Sets the default runlevel (values 1–5, not 0 or 6)
Editing /etc/inittab Before making changes, back up the file:
sudo cp /etc/inittab /etc/inittab.bak
Open it in your favorite editor:
A typical configuration might include:
# Set default runlevel to 3 (multi-user, console login) id:3:initdefault: # System initialization scripts si::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS # Single-user mode login ~:S:wait:/sbin/sulogin # Runlevel scripts l0:0:wait:/etc/init.d/rc 0 l1:1:wait:/etc/init.d/rc 1 l2:2:wait:/etc/init.d/rc 2 l3:3:wait:/etc/init.d/rc 3 l4:4:wait:/etc/init.d/rc 4 l5:5:wait:/etc/init.d/rc 5 l6:6:wait:/etc/init.d/rc 6 # Handle CTRL+ALT+DEL ca::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/shutdown -r now # Virtual consoles for runlevels 2 and 3 1:23:respawn:/sbin/getty tty1 VC linux 2:23:respawn:/sbin/getty tty2 VC linux # Serial console on runlevel 3 S0:3:respawn:/sbin/getty -L 9600 ttyS0 vt320
After editing /etc/inittab, reload init’s configuration without rebooting: Init Scripts and Service Directories Service scripts live in /etc/init.d/, while each runlevel directory in /etc/rc*.d/ contains symlinks:
ls /etc/rc * .d # rc0.d/ rc1.d/ rc2.d/ rc3.d/ rc4.d/ rc5.d/ rc6.d/
Within each rcN.d directory, file prefixes determine actions:
Prefix Operation Snn Start service when entering N Knn Stop service when entering N
Example for runlevel 3:
ls /etc/rc3.d # K01networking S01apache2 S02ssh ...
Checking and Changing Runlevels
Show current and previous runlevels:
Switch to single-user mode (runlevel 1):
Reboot using runlevel 6:
Halt using runlevel 0:
Switching runlevels will start or stop multiple services. Always save your work and notify other users before changing to runlevels 0, 1, or 6.
Further Reading