1. Create an IAM Role for EC2
- Open the AWS Console and navigate to IAM → Roles → Create role.
- Select AWS service as the trusted entity and pick EC2.
- Attach the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore policy and click Next.
- Name the role
Kafka-S3-demoand finish creation.
For production, restrict permissions to only the resources your application requires.
2. Launch an EC2 Instance
- Go to EC2 → Instances → Launch instance.
- Name it
Kafka-S3-demoand choose instance type t2.medium. - Under Key pair, select Proceed without a key pair (for demo only).
- Use the default security group.
- Increase the root volume to 16 GiB.
- In Advanced settings, attach the IAM role
Kafka-S3-demo. - Click Launch instance.
3. Connect via Session Manager
Once the instance state is running, select it and choose Connect → Session Manager → Connect.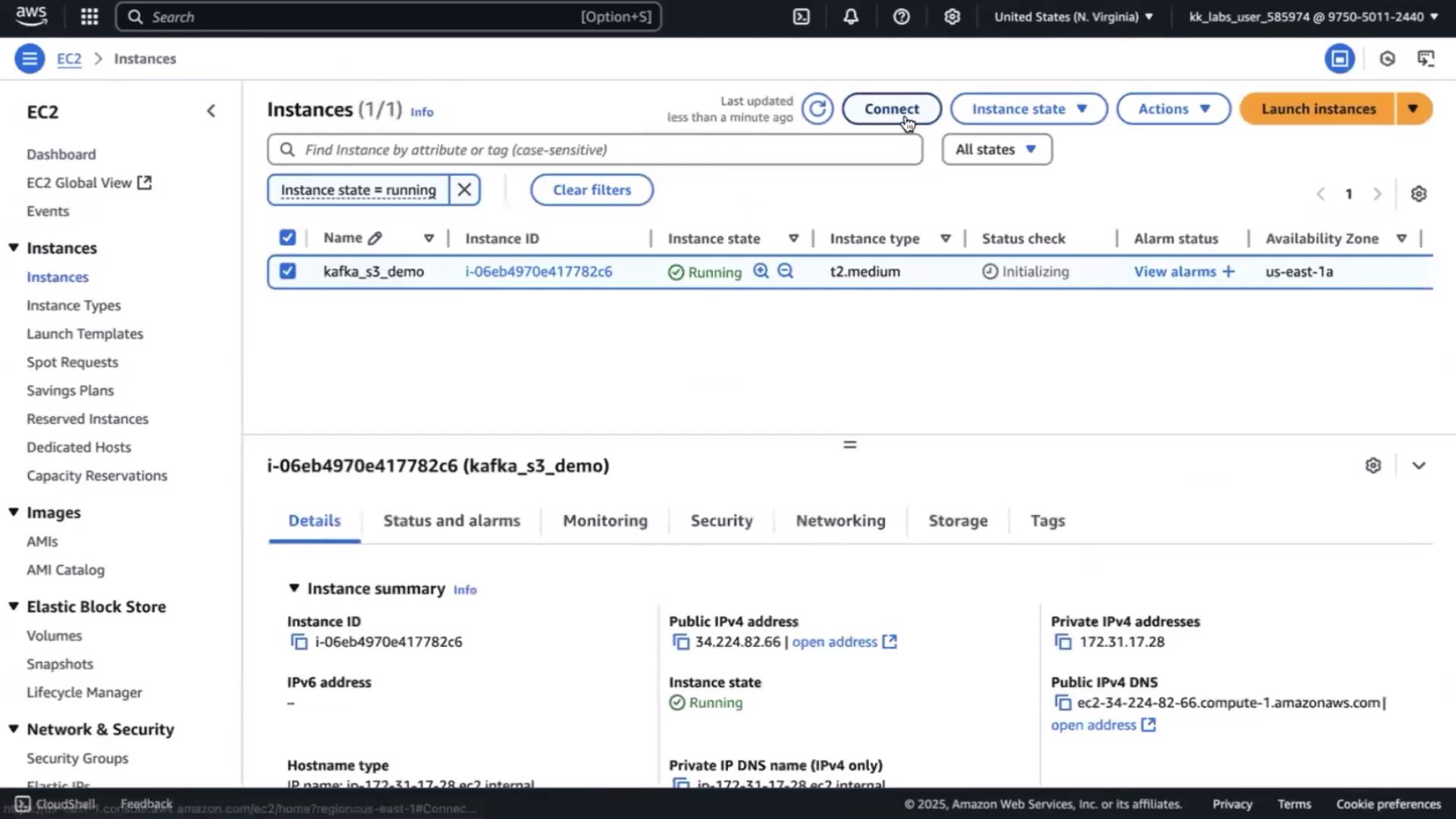
4. Download and Extract Kafka Binaries
bin, config, and libs among other folders.
5. Install Java Runtime
Verify Java is present:6. Format Storage for KRaft
Generate a unique ID and format the combined logs directory:7. Configure Kafka for KRaft Mode
Open the KRaft properties:<EC2_PUBLIC_IP> with your instance’s public IPv4):
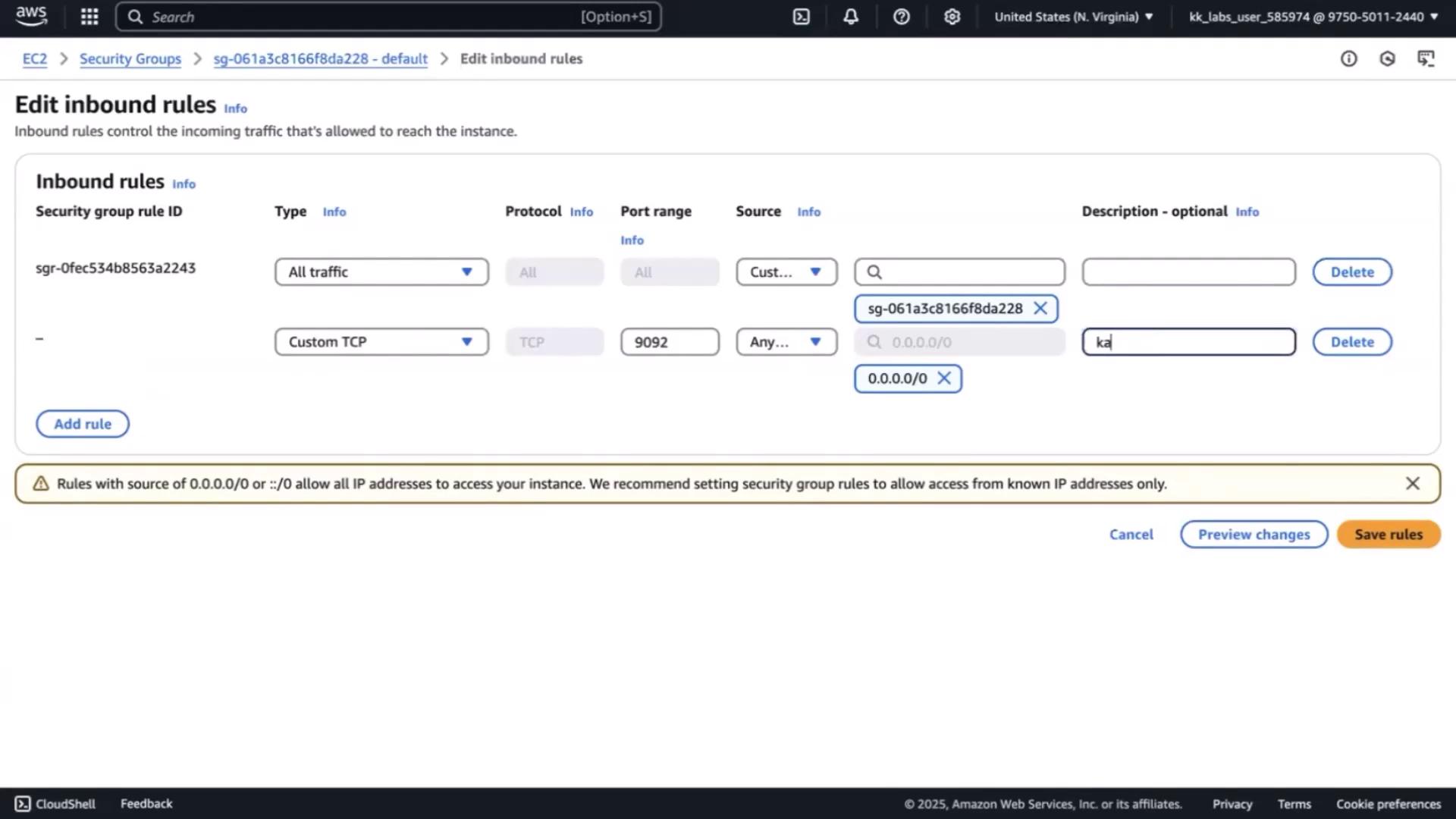
8. Open Port 9092 in Your Security Group
- In the EC2 Console, select Security Groups for your instance.
- Click Edit inbound rules.
- Add a Custom TCP rule for port 9092 from 0.0.0.0/0 (demo only).
- Description:
Kafka Brokers. - Save changes.
Allowing 0.0.0.0/0 exposes your broker to the internet. Restrict this in production.
| Port | Protocol | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 9092 | PLAINTEXT | Client–broker communication |
| 9093 | CONTROLLER | Controller quorum and internal API |
9. Start Kafka in KRaft Mode
Launch the broker and controller together:Next Steps
With your KRaft broker running, proceed to:- Download the Kafka S3 Connector plugin.
- Configure
connect-standalone.propertiesands3-sink.properties. - Launch the connector to start syncing topic data to Amazon S3.