Understanding EventBridge
When events are sent to an event bus, it’s essential to determine the appropriate action for each event. EventBridge rules empower you to analyze these events by matching them against defined patterns and then routing them to designated targets. Below is an overview of the standard EventBridge architecture: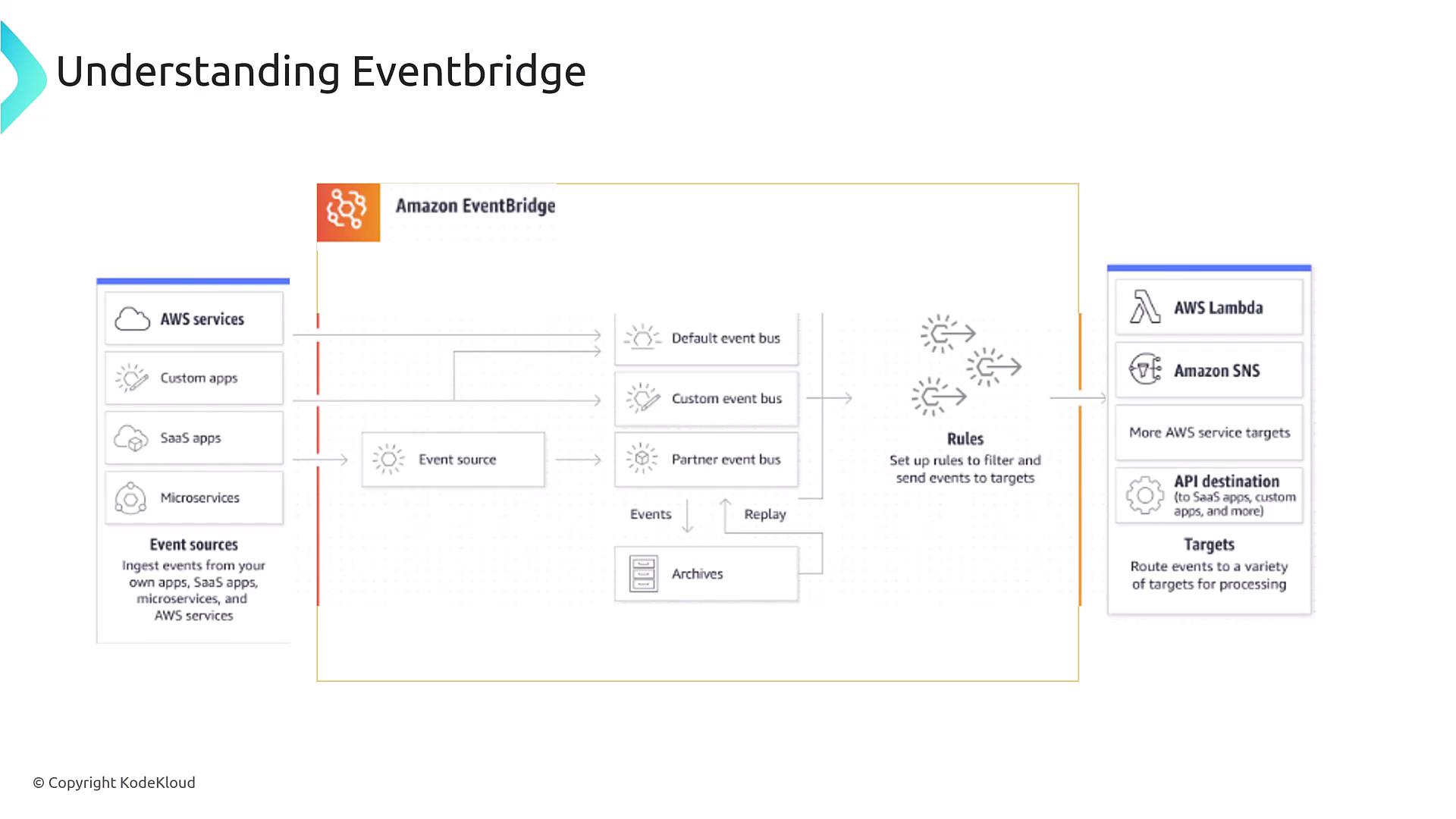
Steps to Configure an EventBridge Rule
Configuring an EventBridge rule involves a clear sequence of steps:- Define the event source: Identify the AWS service or custom application generating events.
- Specify the event pattern: Determine the criteria or pattern that an event must match to trigger the rule.
- Select the target: Choose the destination where the event will be sent if it matches the pattern (e.g., AWS Lambda, API Gateway).
- Create and activate the rule: Save and enable the rule so that it begins monitoring the event bus in real time.
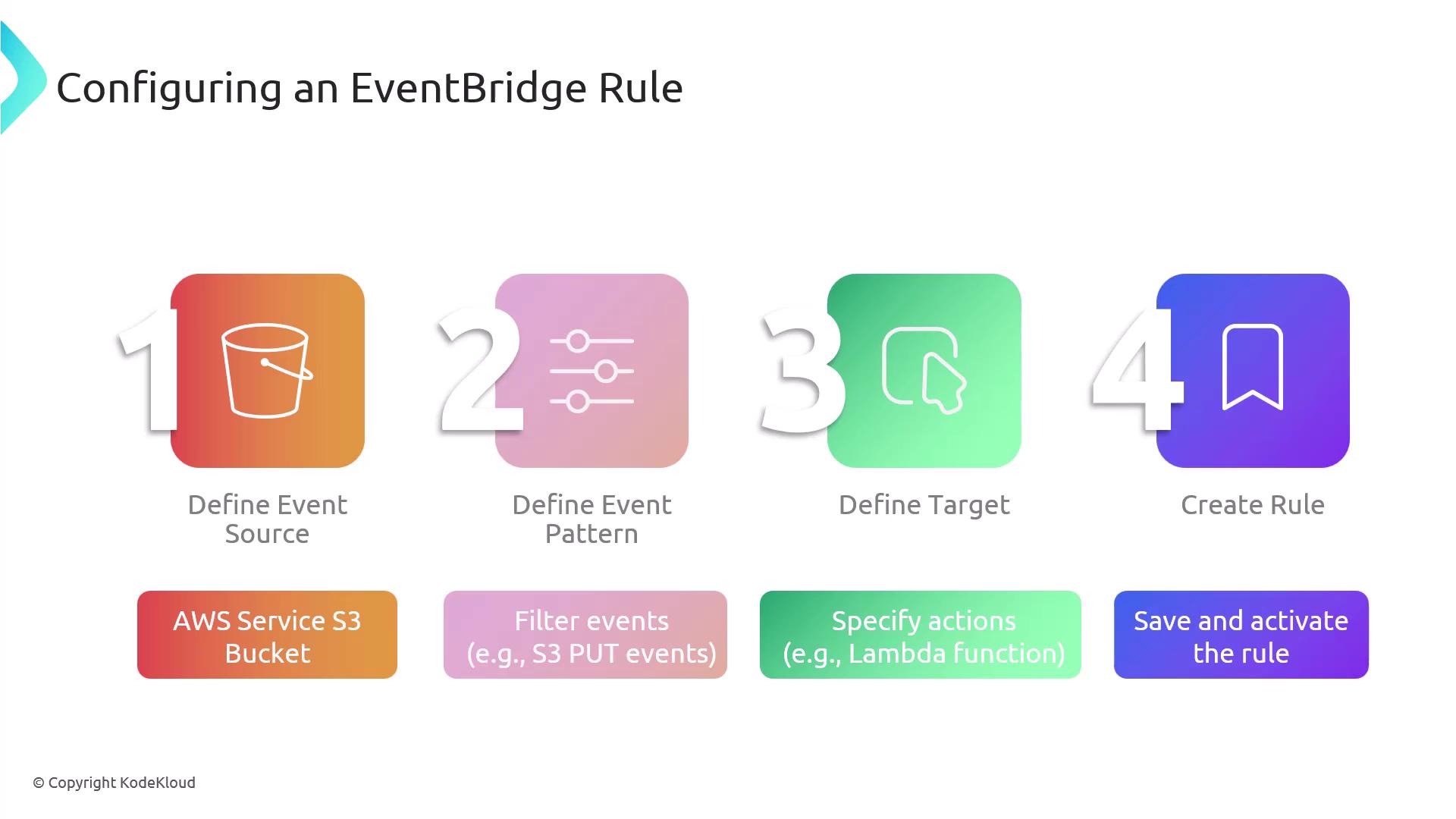
For enhanced security and reliability, ensure that all IAM roles associated with your EventBridge rules have the minimum required permissions.
Practical Example: S3 Bucket Trigger
Consider an example where an object is uploaded to an S3 bucket. Here’s how the process unfolds:- An event is generated when the S3 bucket detects a PUT operation (i.e., an object upload).
- The configured EventBridge rule, which is set to monitor this specific event pattern, routes the event to an AWS Lambda function.
- The Lambda function processes the uploaded object—for instance, generating thumbnails for images.
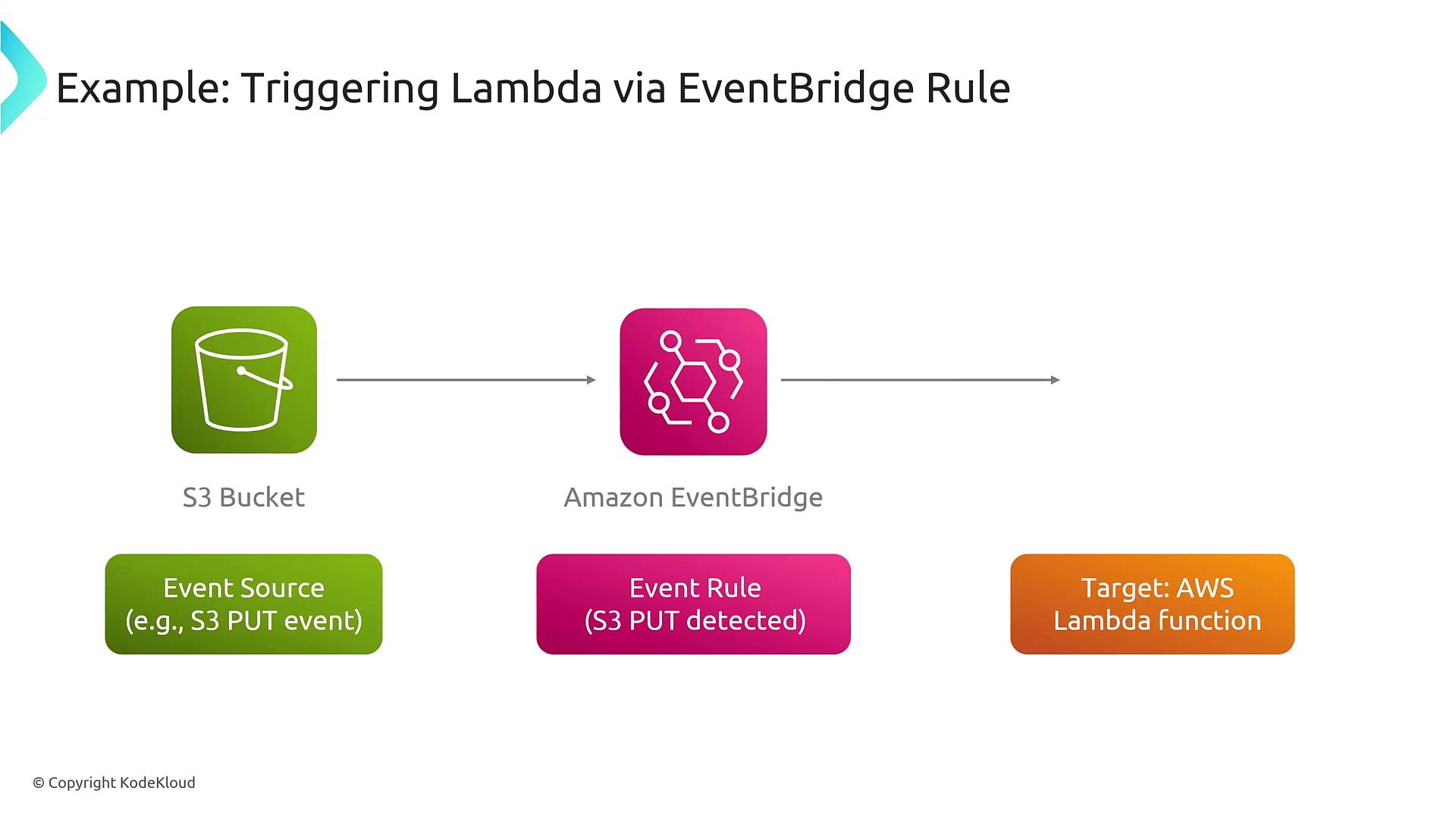
Remember, while this example uses Lambda as the target, EventBridge supports over 200 AWS services and third-party integrations, providing significant flexibility to suit your application’s requirements.