Understanding EBS Volume Types
When optimizing EBS performance, it is essential to consider both the volumes and the EC2 instances they attach to. Choosing the right volume type from the beginning can make a significant difference in performance and cost efficiency.SSD vs. HDD Storage
EBS volumes are generally split into two categories:- SSD-based Volumes: Ideal for most workloads.
- HDD-based Volumes: Generally reserved for archival data or environments that require sequential reads and writes with large chunk sizes.

Provisioned IOPS Volumes
For applications that require high I/O performance—such as intensive databases or applications with high throughput and low latency demands—the Provisioned IOPS volumes (io1 and io2) are designed to meet those needs. These volumes can achieve up to 64,000 IOPS, with the rare I/O Express option offering up to 256,000 IOPS, albeit at a higher cost.
HDD Options
For workloads requiring lower cost and high throughput in sequential operations, AWS provides two HDD options:- ST1 (Throughput Optimized HDD): Best suited for large, sequential workloads.
- SC1 (Cold HDD): Ideal for archival purposes with infrequent data access.

Quick Summary for Exam Purposes
- GP2/GP3: Standard choices for web servers, application servers, and boot volumes.
- Provisioned IOPS (io1/io2): Ideal for high-performance databases and throughput-intensive applications.
- Throughput-Optimized HDD (st1): Best for data warehousing.
- Cold HDD (sc1): Suited for backups and archival storage.
EBS-Optimized EC2 Instances
Most modern EC2 instances are EBS-optimized, meaning they have a dedicated network channel for EBS traffic that significantly improves throughput and overall performance. In fact, nearly 80% of instances come with this feature by default.
Enhancing Performance via Volume Configuration Adjustments
Volume Size Adjustments and Snapshot Pre-Warming
Modifying the volume size can also enhance performance. For example, increasing the size of a GP2 volume may lead to better performance characteristics. When restoring a volume from a snapshot, initial performance may be slow unless you use pre-warming techniques or enable fast snapshot restore. Fast snapshot restore automatically pre-initializes the volume to ensure optimal performance right from the first use.
Monitoring EBS Performance
Effective monitoring is key to performance management. Utilize Amazon CloudWatch and CloudWatch Logs to track metrics such as bytes read, total reads/writes, and total time on I/O operations. These insights help in fine-tuning your EBS performance.Leveraging RAID for Maximum I/O
For maximum I/O, consider implementing RAID 0, which stripes data across multiple drives. Note that while RAID 0 improves performance by using multiple channels, it does not offer redundancy. However, because EBS volumes are inherently redundant (AWS maintains three copies of your data), you can benefit from increased performance without compromising data availability.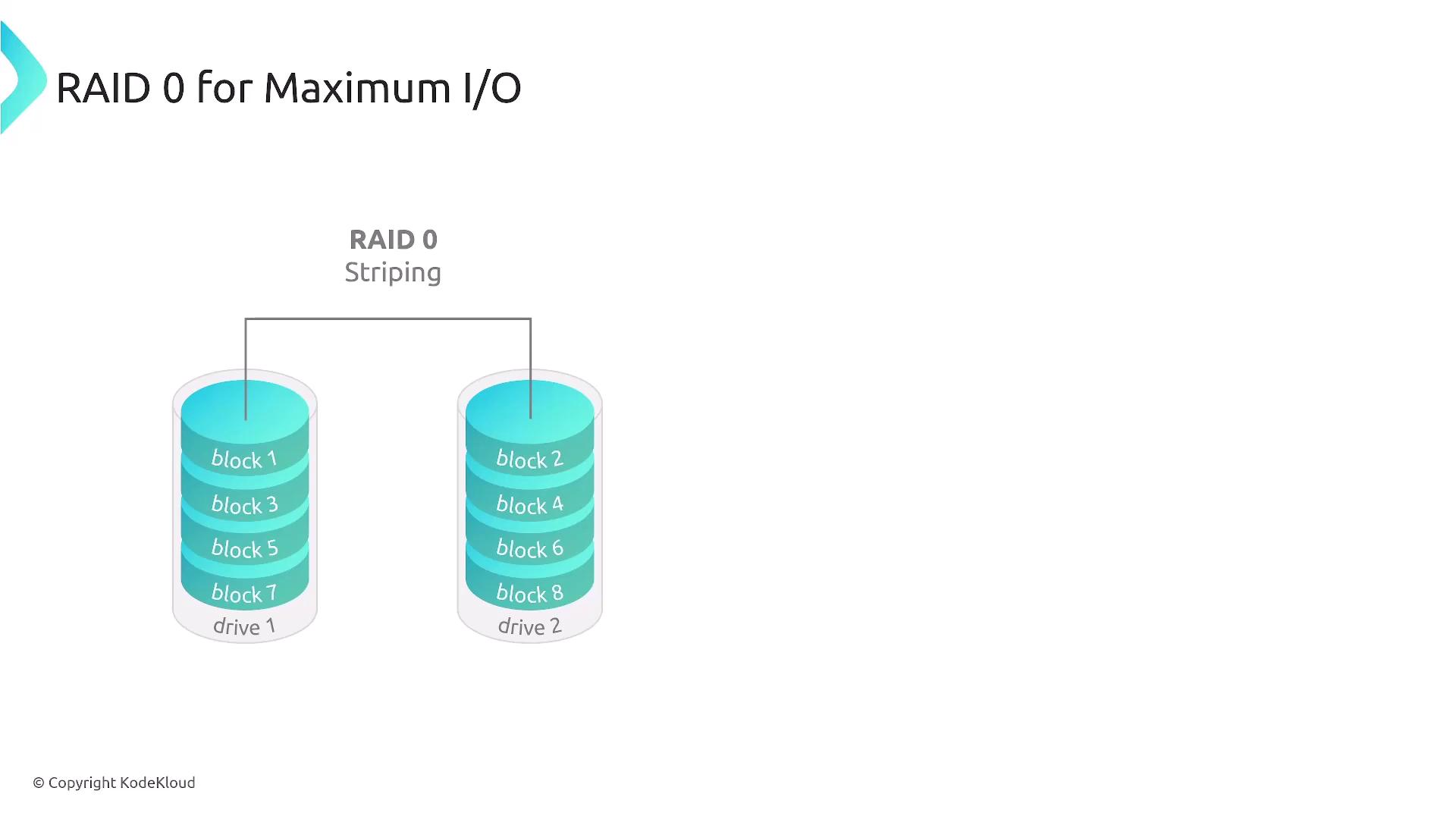
Linux Performance Tweaks
On Linux systems, adjusting the read-ahead cache can provide further performance benefits—especially for HDD volumes. For example, setting a read-ahead value of one megabyte per block can enhance performance. The following commands demonstrate how to view and adjust the read-ahead value on a Linux device:Ensure you are running a modern Linux kernel (version 3.8 or later) to benefit from the latest performance improvements and I/O monitoring capabilities.