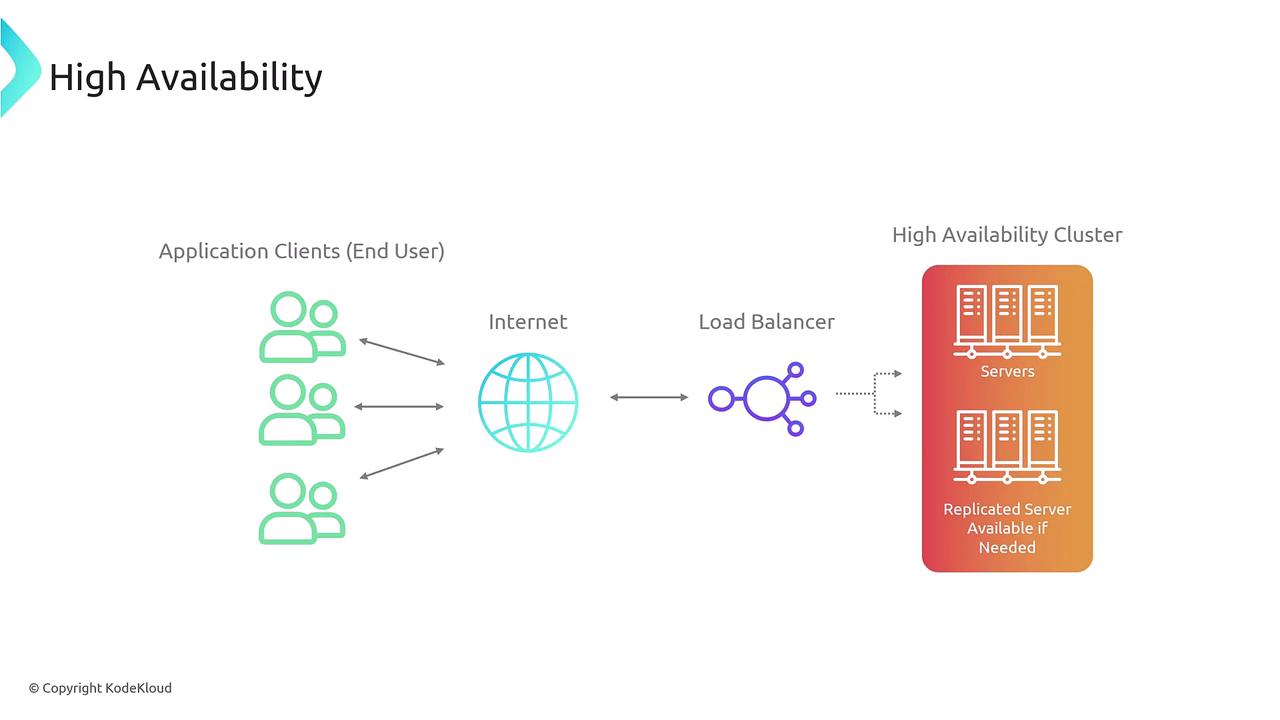
Designing for High Availability
High availability hinges on redundancy and load balancing. The use of multiple servers allows your system to scale dynamically during peak traffic periods. In AWS, an Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) abstracts the details of the underlying servers, ensuring end users experience a seamless connection. Unlike physical appliances, ELBs exist as virtual network devices that scale automatically. Several AWS services enhance high availability, including:- Amazon Route 53: Provides global traffic management.
- Amazon RDS: Supports multi-Availability Zone (AZ) deployments.
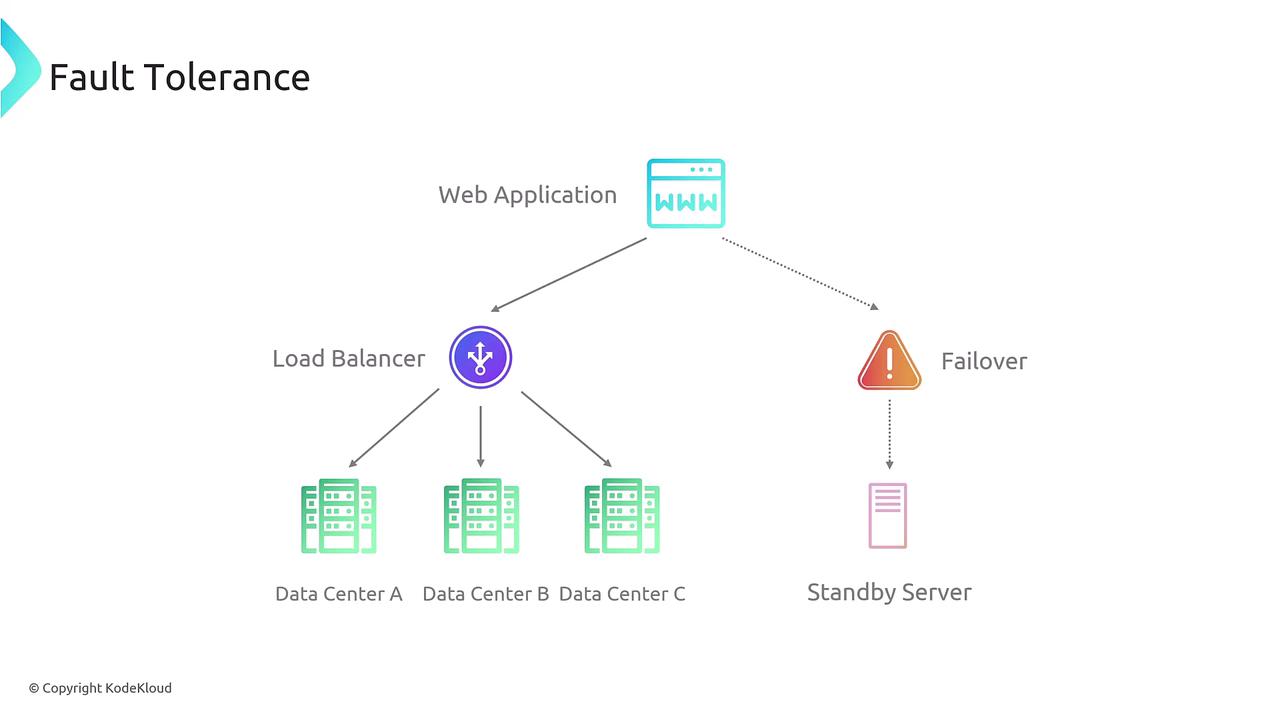
Fault Tolerance Explained
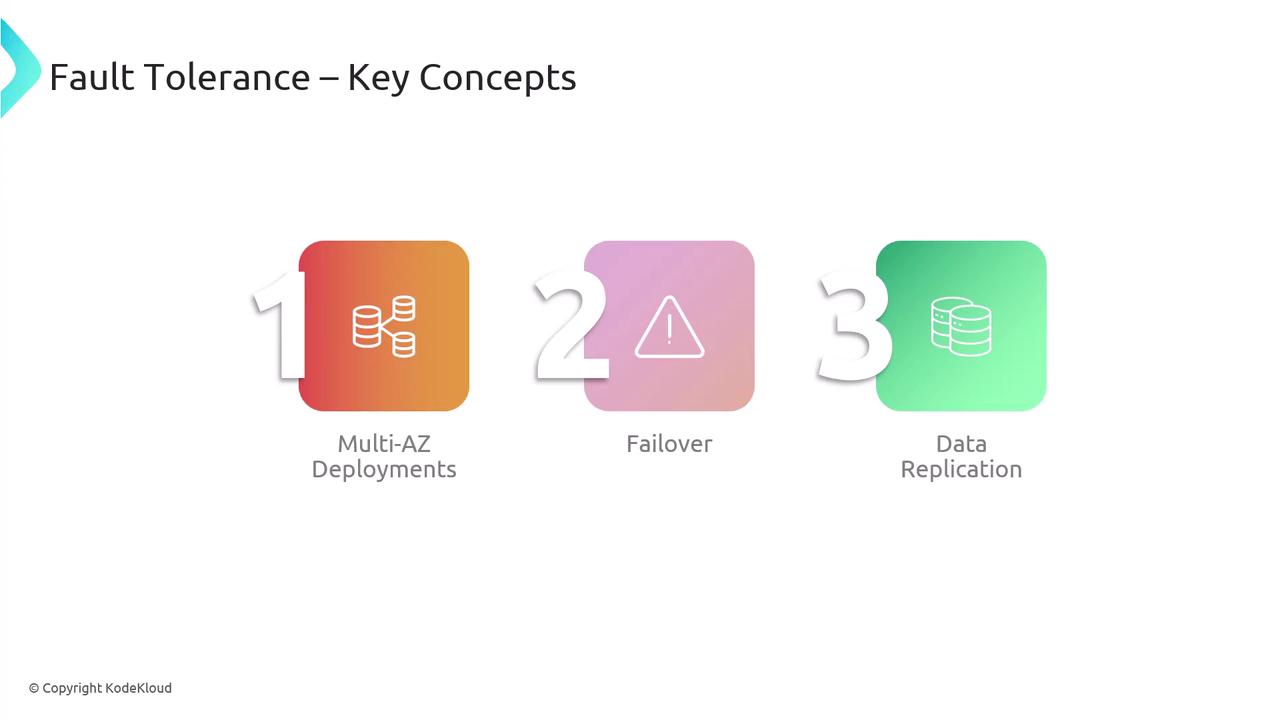
Fault tolerance ensures that your system continues to operate even when one or more components fail. In a fault-tolerant design, failures are either rapidly recovered from or mitigated through redundancy, ensuring minimal disruption in service.- Multi-AZ deployments with automatic failover.
- Database replication (across S3, RDS, Aurora, or DynamoDB) to maintain continuous operation.
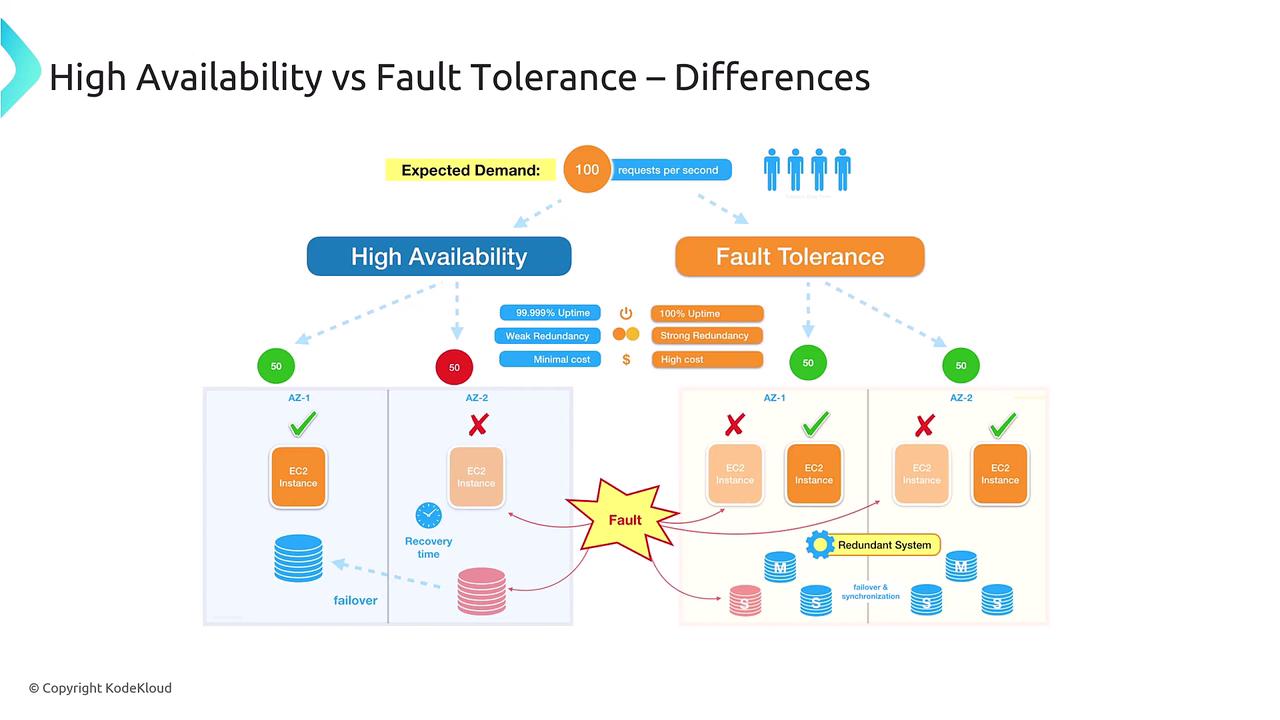
Comparing High Availability and Fault Tolerance
Although both high availability and fault tolerance strive for continuous operation, they differ significantly in their approach:| Approach | Key Focus | Example Scenario | Cost Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Availability | Minimizing downtime with minimal recovery lag | A server failure triggers a quick failover resulting in a short interruption | Lower due to less redundancy |
| Fault Tolerance | Eliminating downtime through immediate failover | Active-active configuration where redundant components instantly take over | Higher due to full replication |
Summary
In summary, high availability involves designing systems with redundant resources to minimize downtime during failures, while fault tolerance goes a step further to ensure continuous operation even when components fail. AWS implements these concepts using a variety of services such as Elastic Load Balancing, Route 53, multi-AZ RDS deployments, and several serverless options.Both high availability and fault tolerance are integral to building robust and scalable AWS architectures, making them crucial topics for those preparing for the AWS SysOps certification.
For more AWS resources, refer to the AWS Documentation.