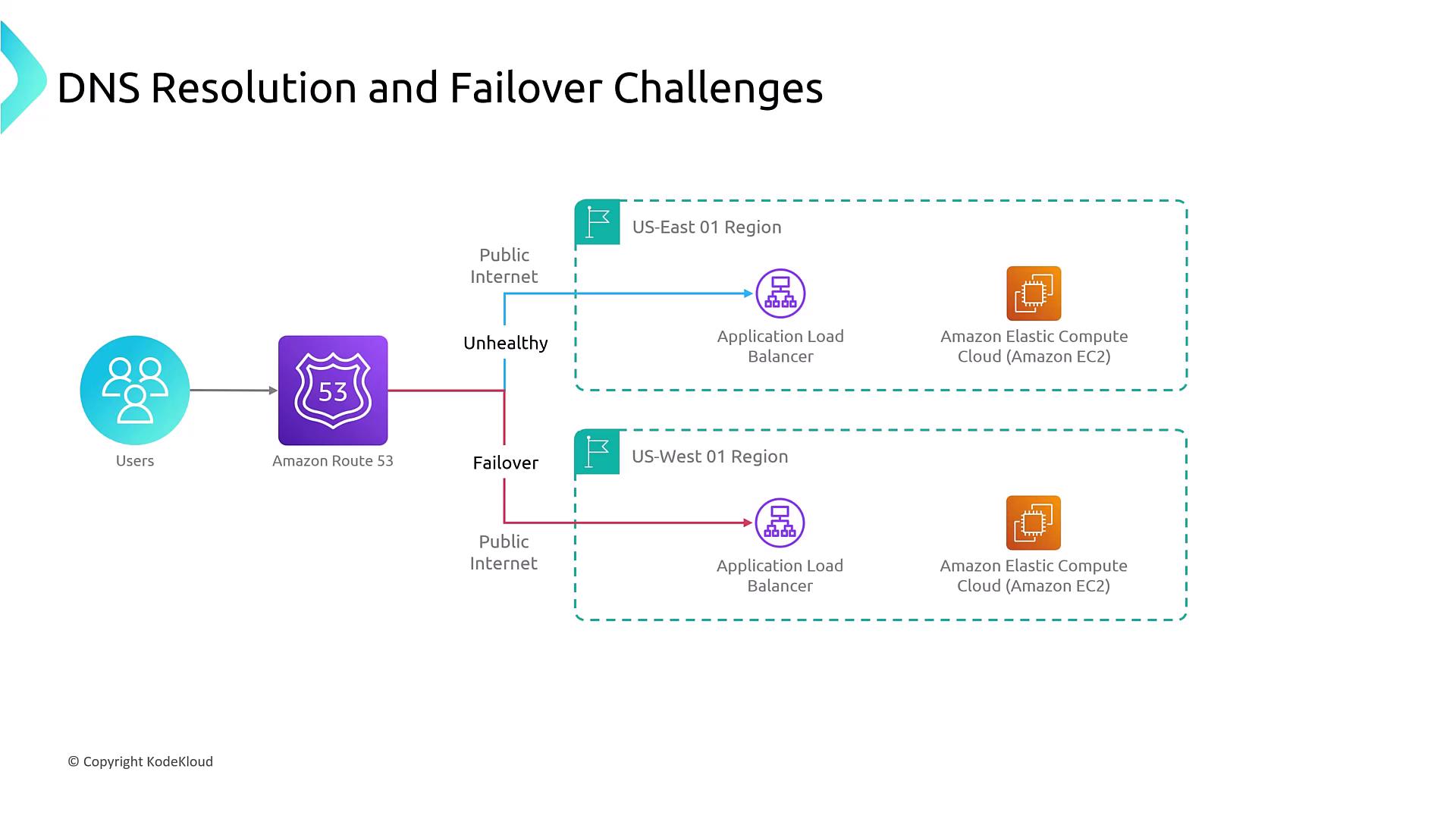
Traditional DNS-Based Load Balancing
Traditionally, load balancing for applications is managed through DNS services such as Amazon Route 53. In such setups, DNS routes user requests to publicly accessible endpoints, which can include multiple ELBs across different regions (for example, in an active-active configuration). This design supports regional failover by redirecting traffic if a particular region becomes unhealthy. However, the DNS resolution process involves multiple steps:- A user’s device requests the domain name resolution (e.g., www.example.com).
- The request travels through local DNS servers, the ISP’s DNS cache, root name servers, and finally the authoritative name server.
- The resolved IP address is cached across multiple network points.
Be aware that caching behavior can complicate timely failover, as different caching layers may honor different TTL (time-to-live) values. This could lead to outdated DNS records persisting for minutes, or even hours, and potentially route traffic to unhealthy endpoints.
- TTL values set to 30 seconds may be exceeded by longer caching durations at upstream servers.
- Cached DNS responses might result in delayed failover during regional outages.
- Limited control over external DNS caches across ISPs and third parties.
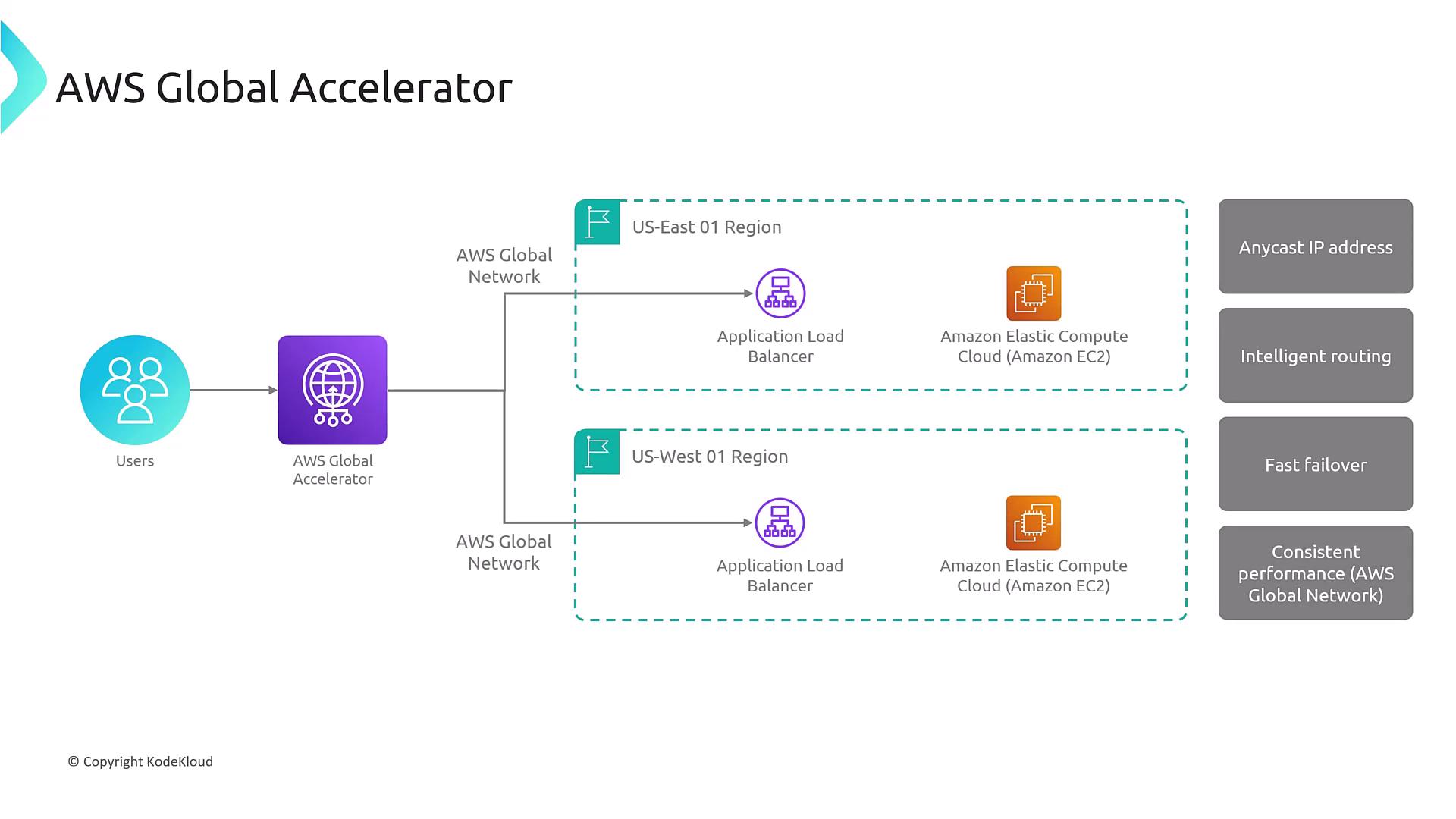
Global Accelerator: A Robust Global Load Balancer
To address the shortcomings of DNS-based load balancing, AWS Global Accelerator provides a powerful alternative. It offers a static, anycast IP address that remains unchanged, serving as a fixed global entry point to your application. Key benefits of Global Accelerator include:- Static Global Endpoint: Just as with a regional load balancer, Global Accelerator provides a constant anycast IP, making client configurations simpler and more reliable.
- Intelligent, Real-Time Routing: It directs traffic dynamically to the optimal regional application load balancer based on the health and performance of the endpoints, without needing to wait for DNS propagation.
- Flexible Traffic Distribution: Control traffic routing with:
- Percentage-based allocations (e.g., 20% to US-East-1 and 80% to US-West-1).
- Numerical weight settings on a scale from 0 to 255 (default weight is 128).
- Fast Failover: Quickly detects endpoint issues and reroutes traffic immediately, avoiding delays due to DNS caching.
- Enhanced Global Performance: Utilizes AWS’s global network to maintain fast, secure, and scalable performance even under DDoS attacks or other network disruptions.
Global Accelerator with ELB Integration
AWS Global Accelerator works in perfect harmony with Elastic Load Balancers. When users access the static anycast IP provided by Global Accelerator, the traffic is efficiently forwarded to an appropriate ELB within the target region. The ELB then distributes incoming requests across one or more back-end instances (such as EC2 instances). This integration enhances real-time failover, global performance, and overall availability by minimizing dependency on public DNS caching. The diagram below shows how AWS Global Accelerator interacts with ELB instances across various regions: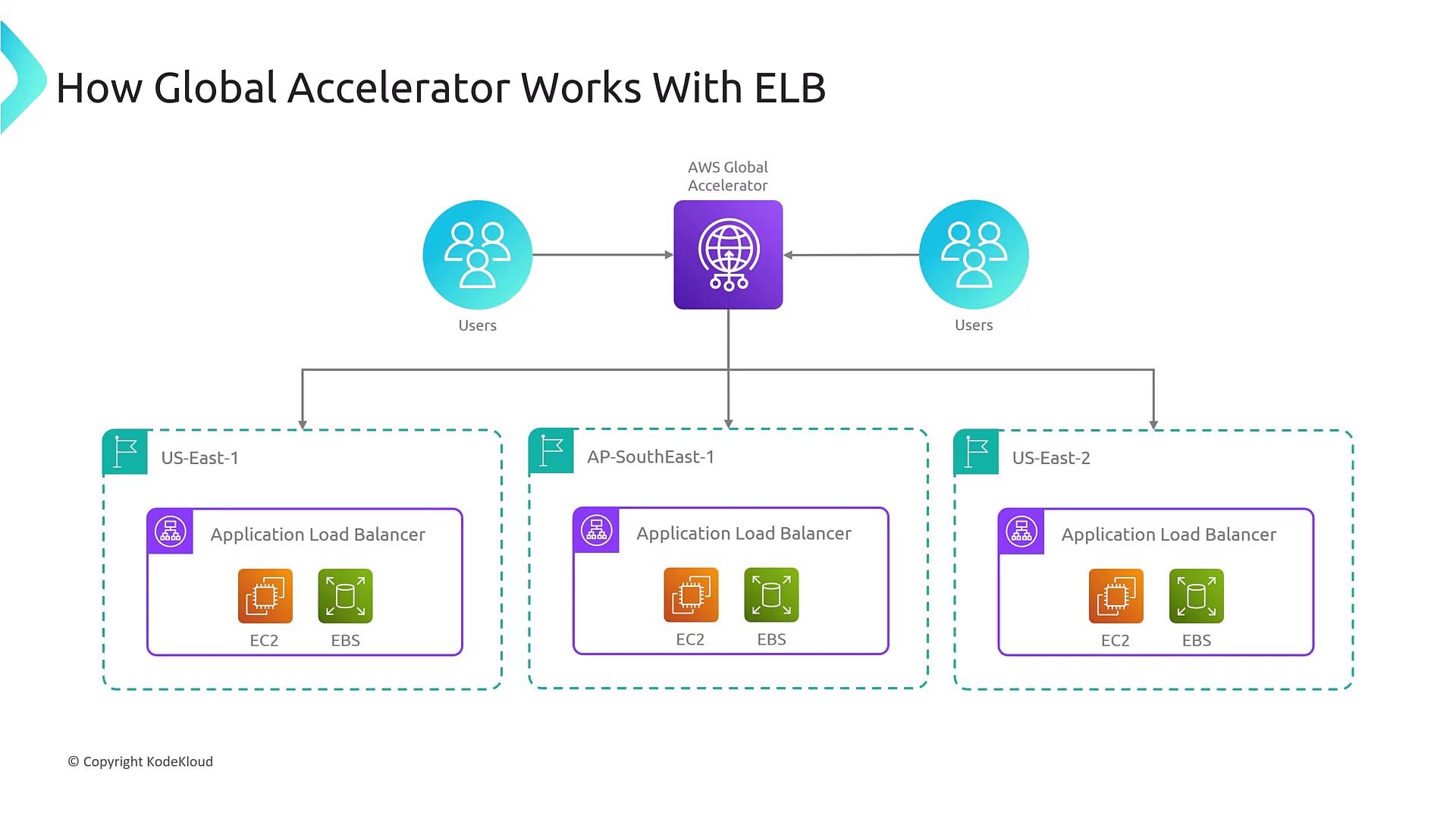

Summary
In summary, AWS Global Accelerator offers a significant upgrade over traditional DNS-based load balancing. Its key advantages include:- A static, anycast IP address that establishes a consistent global entry point.
- Intelligent, real-time routing that bypasses DNS caching, ensuring rapid failover.
- Flexible traffic management using percentage-based distribution or numerical weighting.
- Integration with ELB for streamlined backend traffic distribution.
- Enhanced global performance, improved availability, and strengthened security.