1. Define your team structure
Start by mapping out which team members need access and the level of control they require. Common permission levels in GitHub include:| Role | Permission Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Read | read | View code, issues, and pull requests |
| Triage | triage | Manage issues and pull requests |
| Write | write | Push to non-protected branches |
| Maintain | maintain | Manage repository settings, branches, and keys |
| Admin | admin | Full control over the repository and settings |
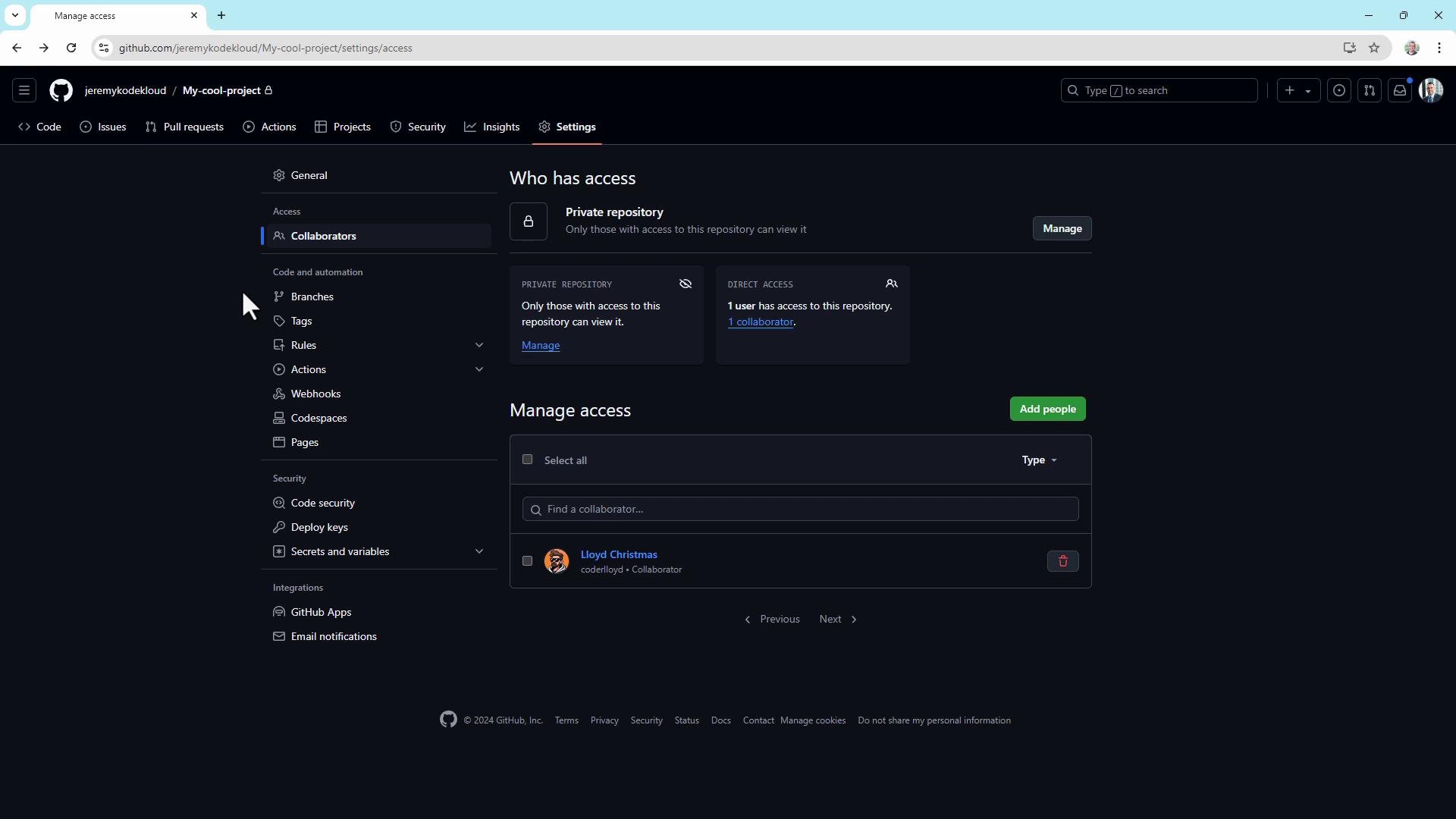
2. Add collaborators
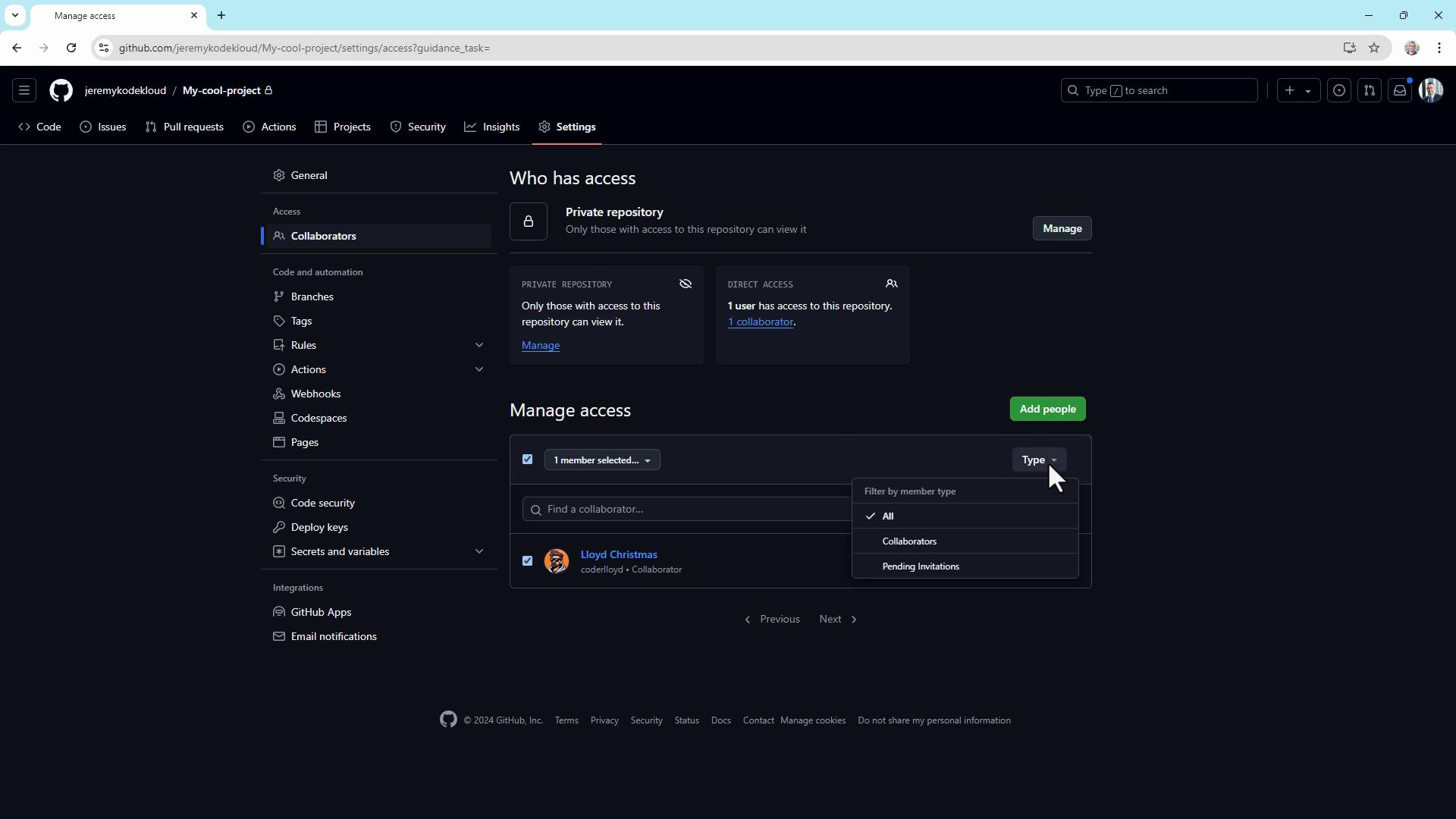
To grant someone access to your repository:- Go to Settings (click the gear icon).
- Select Collaborators under “Access”.
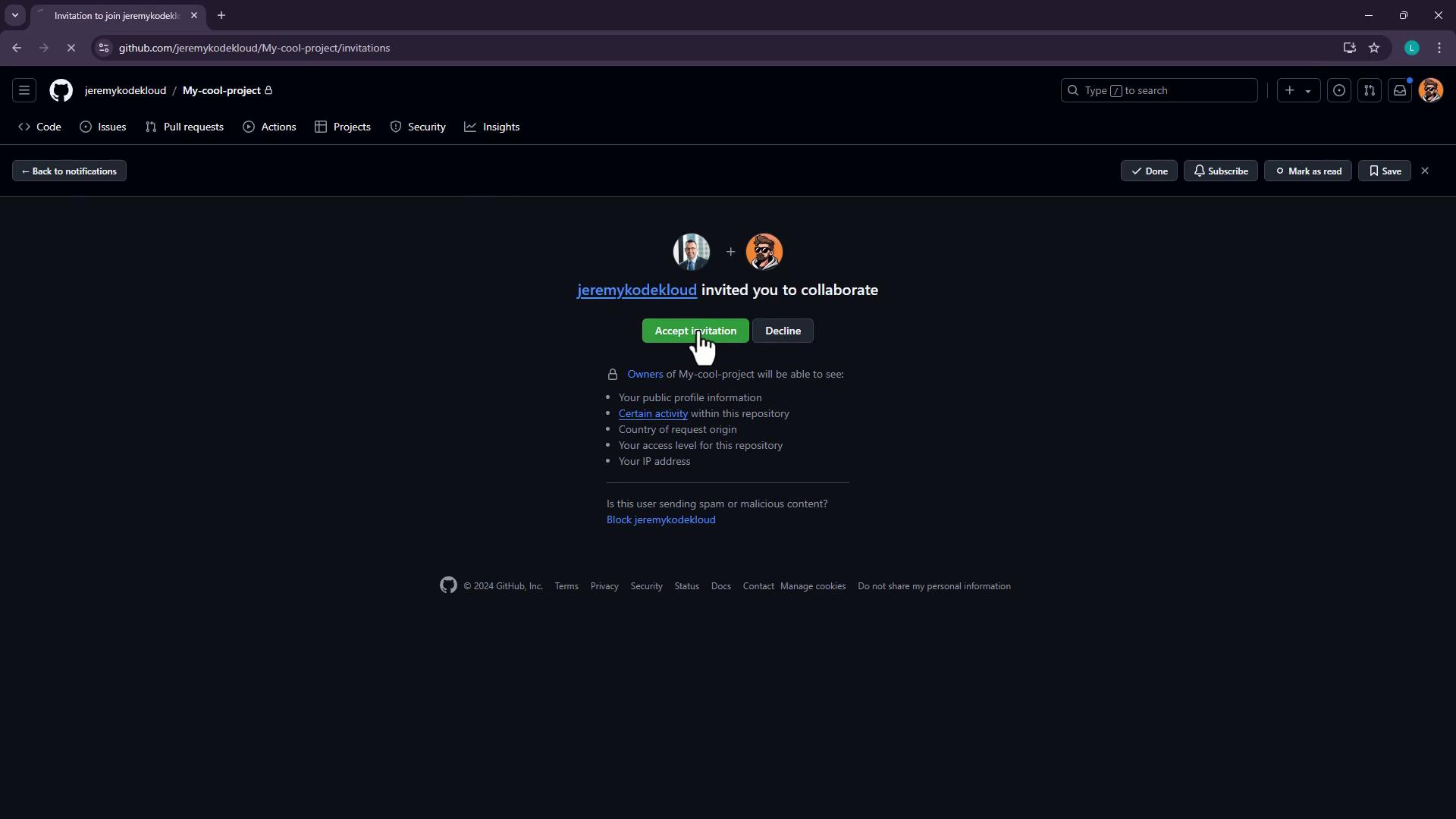
- Click Add people, enter the GitHub username, and send the invitation.
3. Configure repository settings
Under Settings > Options, customize repository behavior:- Require sign-off on web commits
Enforce contributor attestations for commits made via the web editor. - Wikis
Enable or disable wikis for collaborative documentation. - Merge options
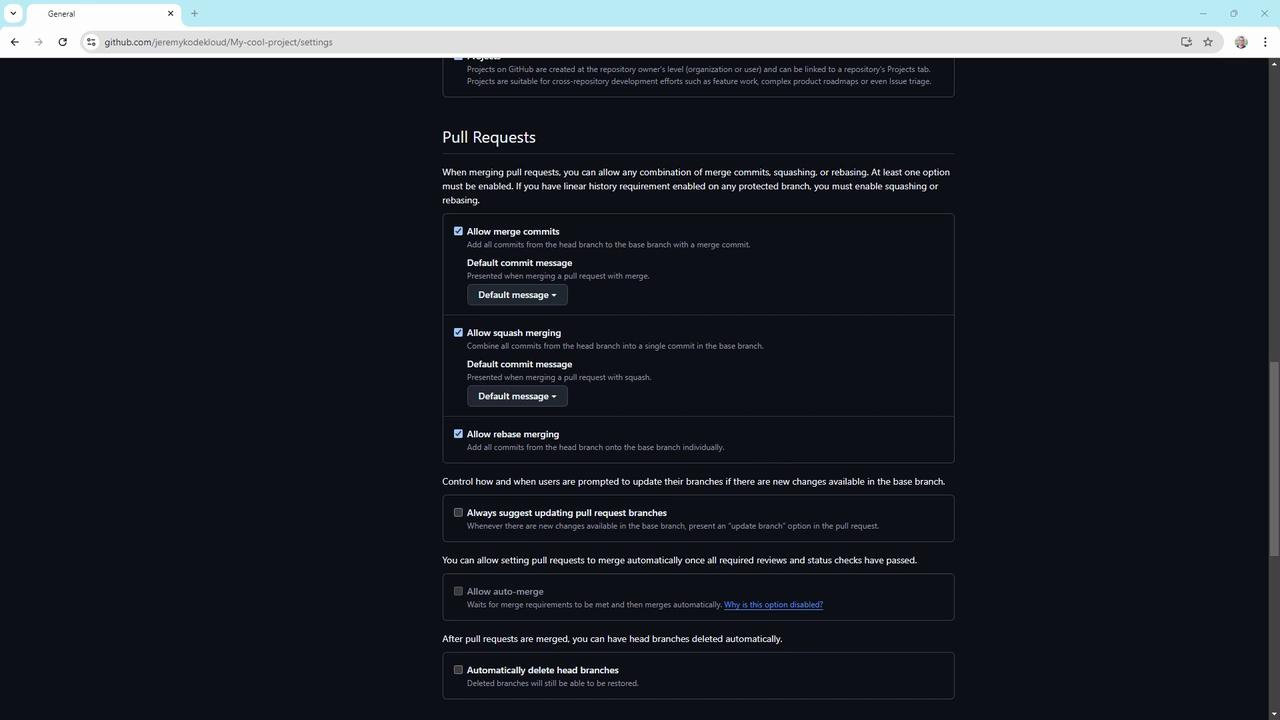
Under Settings > Pull requests, choose to allow or block:- Merge commits
- Squash merging
- Rebase merging
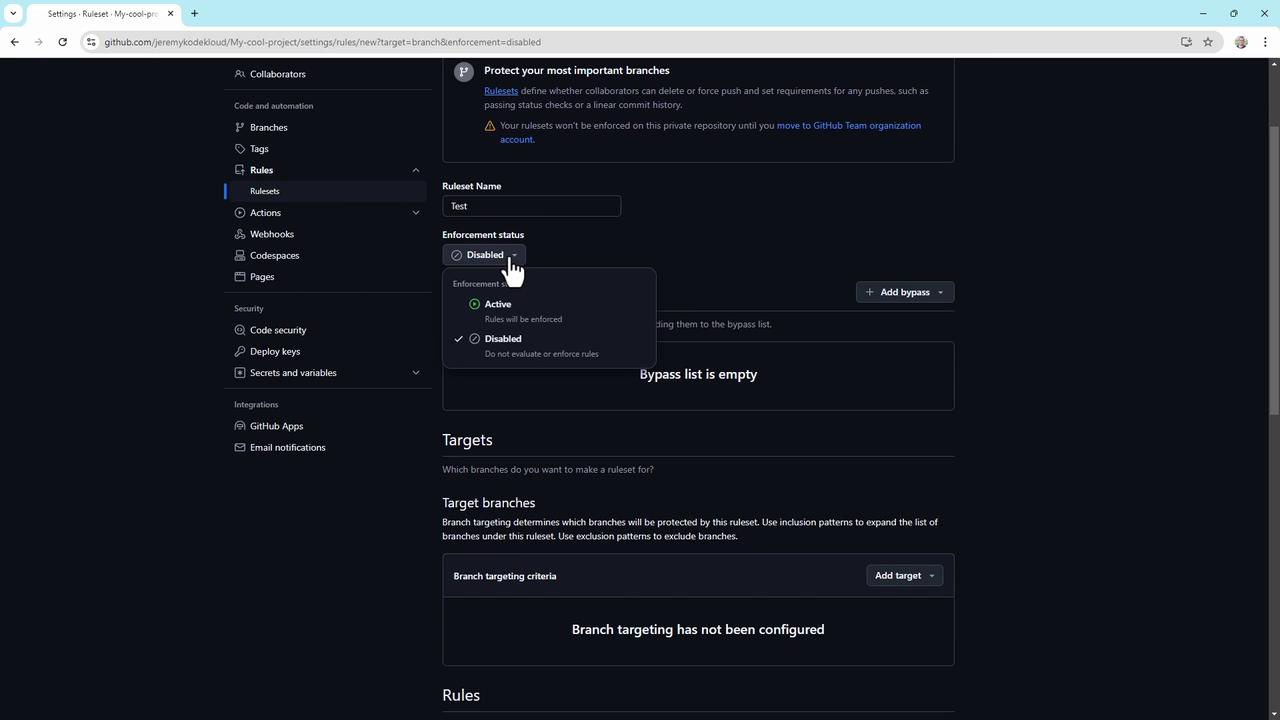
4. Create branch protection rules
Branch protection rules help enforce workflow policies. To set up:- Navigate to Settings > Branch rulesets.
- Click New branch rule set, name it (e.g.,
ReleaseProtection). - Set Enforcement status to Enabled.
- Define a Bypass list for organization or repository admins, if needed.
- Specify target branches by name or pattern (e.g.,
main,release/*).
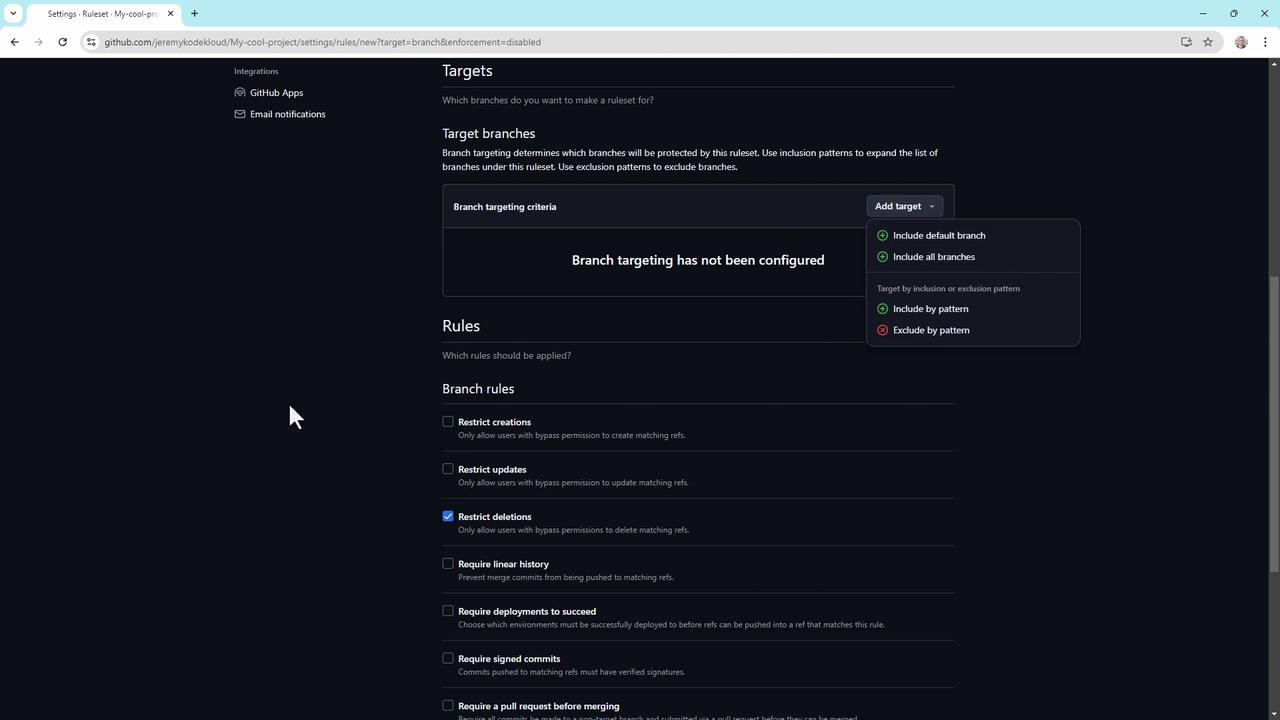
- Restrict branch creation, updates, and deletions
- Require a linear commit history
- Enforce successful CI builds or staging deployments
- Require signed commits
- Enforce pull request reviews (up to 10 required approvals)
- Require conversation resolution before merging
- Block force pushes
- Require status checks (e.g., code scanning results)
Organization and repository administrators can always bypass branch protection rules unless explicitly restricted by policy.
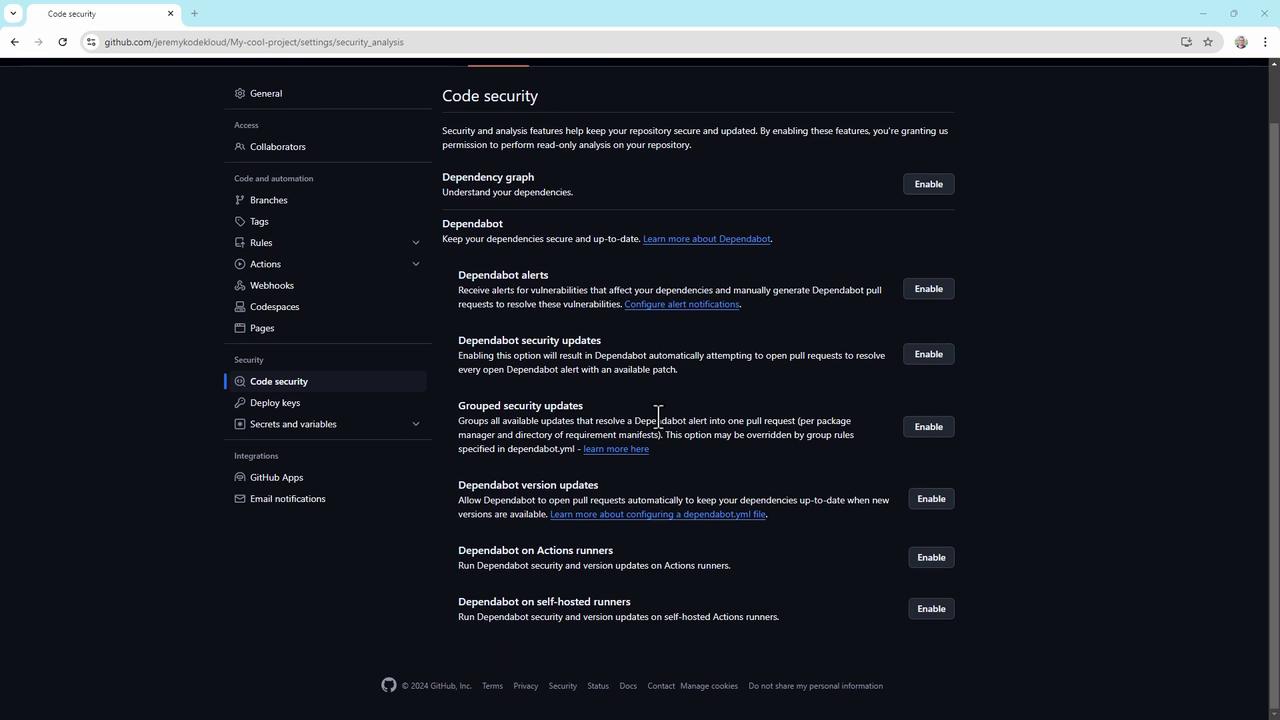
5. Enable code security features
GitHub’s built-in security tools let you detect and fix vulnerabilities early. In Settings > Code security, toggle on:- Dependabot alerts
- Dependabot security updates
- Group security updates
6. Set up a security policy and Dependabot alerts
- Under Security > Security policy, click Start setup to create a
SECURITY.mdfile.- Supported versions: List the versions you actively maintain.
- Reporting guidelines: Explain how to disclose vulnerabilities, expected response times, and required information.
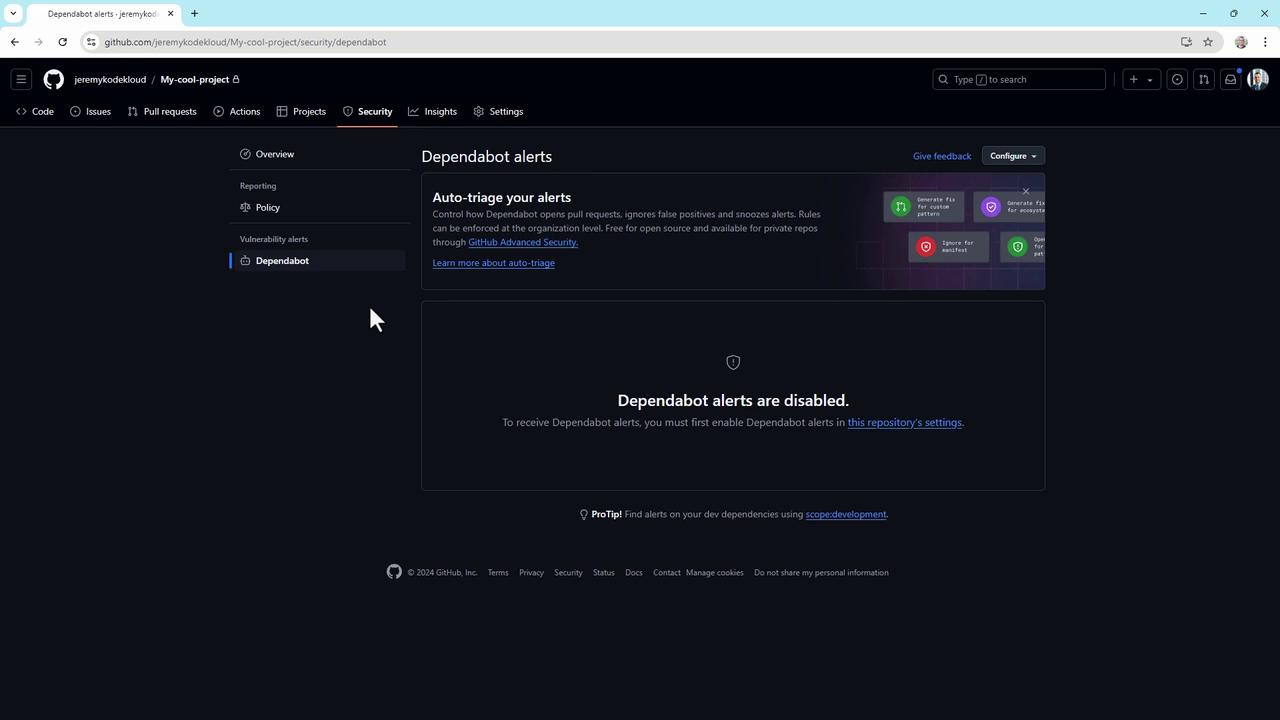
- Go to Security > Dependabot alerts and enable alerts to get real-time notifications.
7. The Danger Zone
At the bottom of Settings > Collaborators, you’ll find critical operations under the Danger Zone:- Change repository visibility (private ↔ public)
- Disable branch protection rules
- Transfer repository ownership
- Archive or delete the repository
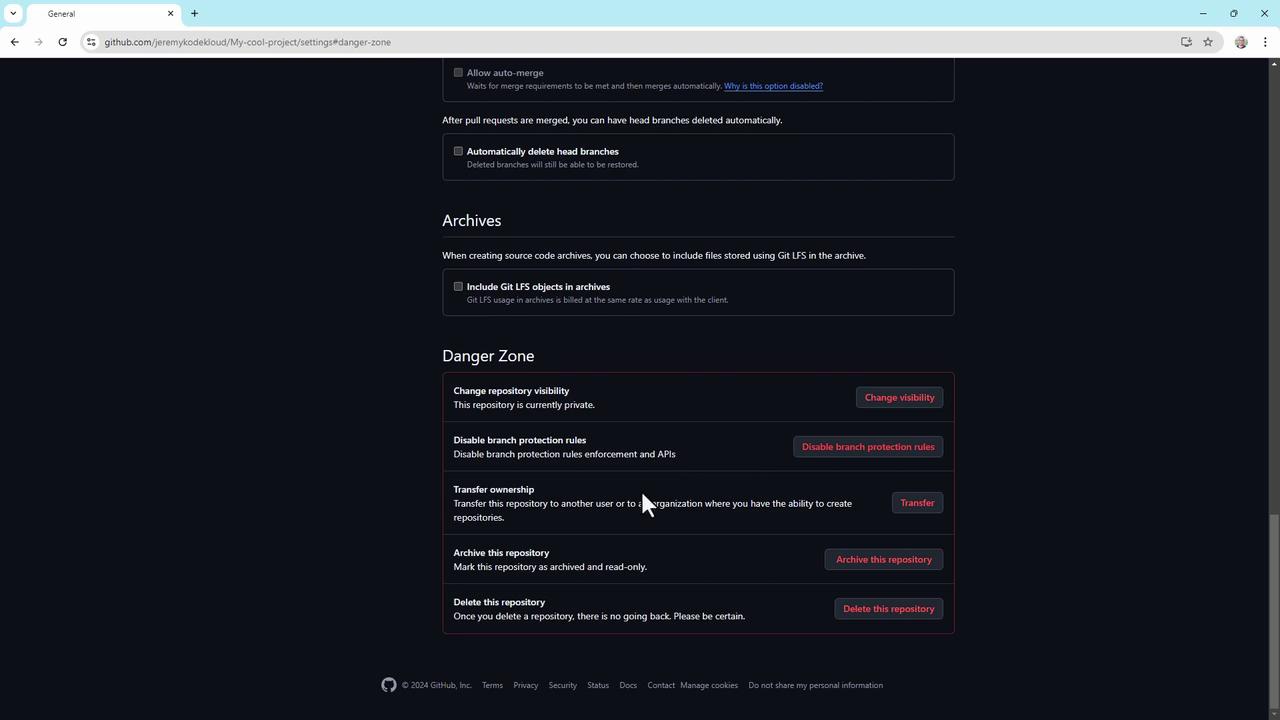
Actions in the Danger Zone are irreversible. Double-check permissions and backups before proceeding.
Conclusion
These best practices apply to standard GitHub repositories, though GitHub Enterprise Cloud offers advanced controls. For deeper dives, visit GitHub’s official documentation.