- Risk Management: Contain failures and reduce blast radius.
- Improved Uptime: Roll out updates in stages to avoid downtime.
- Continuous Delivery: Deploy features more frequently with confidence.

Table of Contents
- Blue/Green Deployments
- Canary Releases
- Ring Deployments
- Progressive Exposure
- Feature Flags
- A/B Testing
Blue/Green Deployments
Blue/Green deployments use two identical production environments to achieve near-zero downtime and instant rollback capabilities.- Build and validate version B in the blue environment.
- Switch the router or load balancer so all traffic flows to blue.
- Monitor metrics; if issues occur, revert traffic to green immediately.
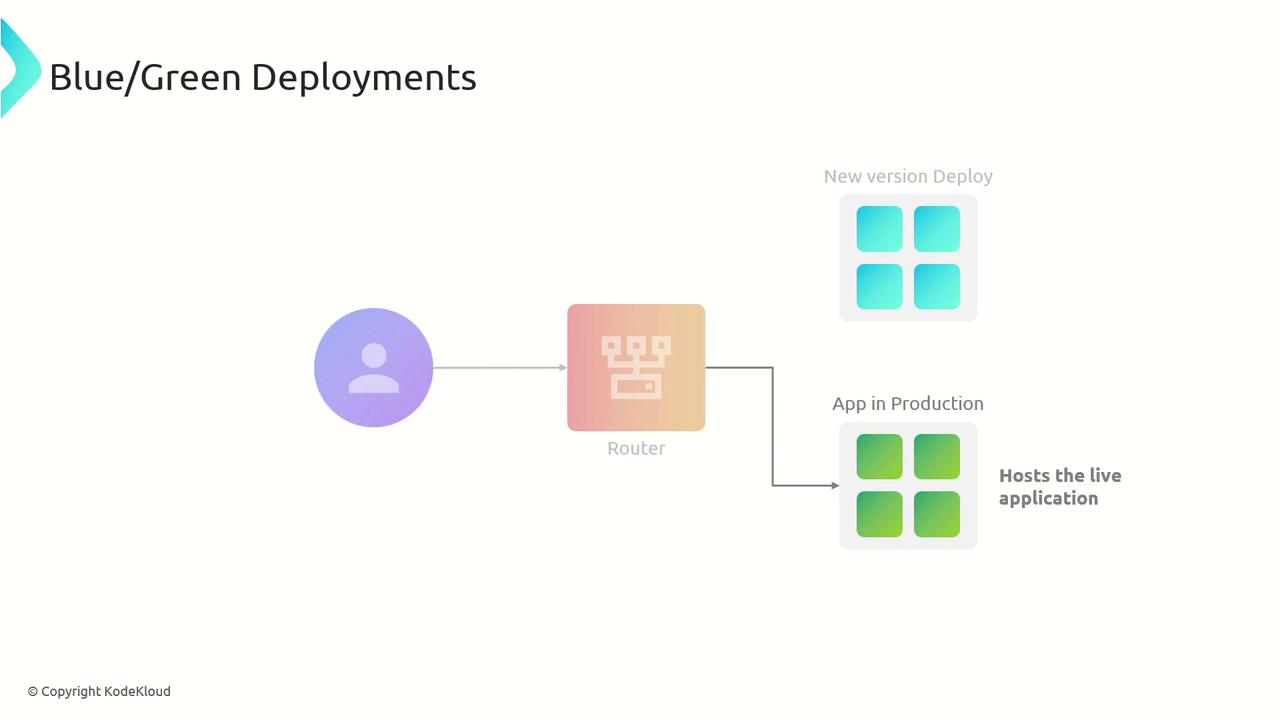
Blue/Green is ideal when you need a fast rollback plan and zero interruption for end users.
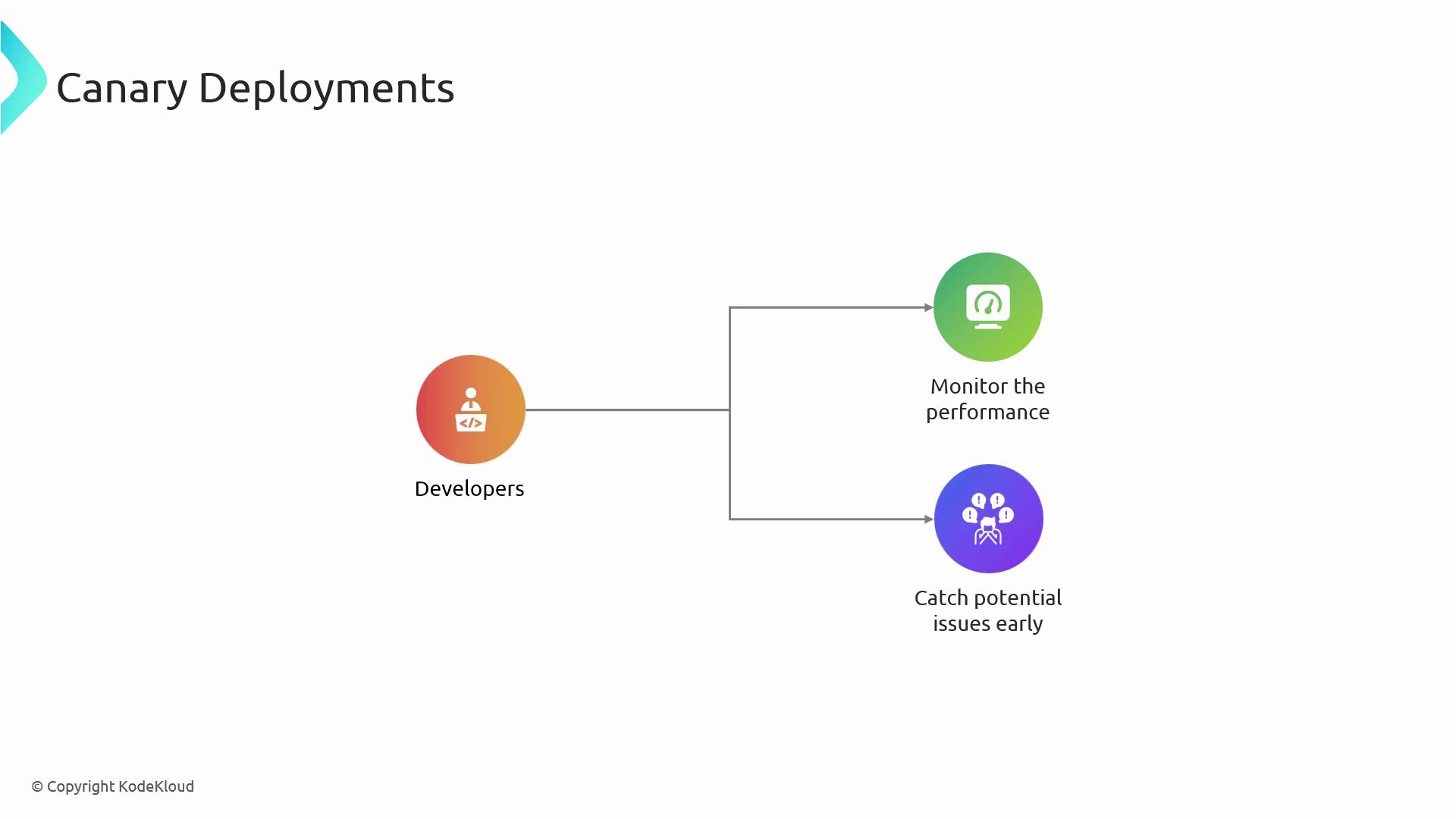
Canary Releases
Canary deployments roll out new features to a small subset of users, enabling early detection of performance regressions before a full release.- Deploy the new version to a limited group of servers or users.
- Collect metrics, logs, and user feedback.
- Gradually increase traffic to the canary cohort if all health checks pass.
Ring Deployments
Ring deployments build on canary by defining multiple user “rings” that receive updates in succession. Rings are often organized by geography, device type, or user role.- Insiders: Internal team or trusted testers.
- Pilot: Small subset of external users.
- Targeted: Larger user segment.
- Broad: All remaining users.
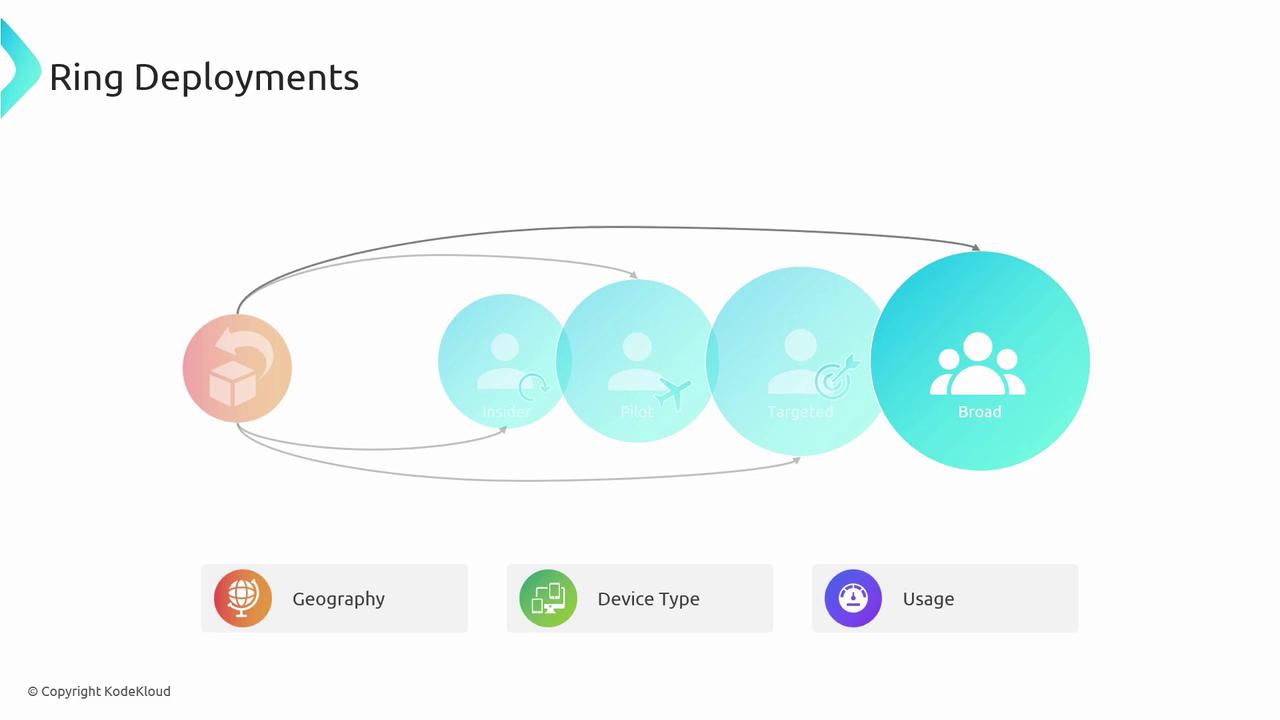
Managing multiple rings introduces complexity in monitoring and coordination—plan your automation carefully.
Progressive Exposure
Progressive exposure combines canary and ring patterns by advancing through well-defined stages based on real-time metrics. This method works well for large-scale features that require validation under varying loads.
- Canary: Initial validation with minimal users.
- Pilot Customers: Trusted external testers.
- Light-Load Regions: Early geographic rollout.
- Medium-Load Regions: Expanded coverage upon successful metrics.
Feature Flags
Feature flags (also known as feature toggles) decouple code deployment from feature release, granting granular control over who sees new functionality.- Turn features on/off at runtime without redeploying.
- Perform dark launches by toggling visibility.
- Enable canary or phased rollouts by flagging select user segments.
- Instantly disable problematic features to avoid full rollback.
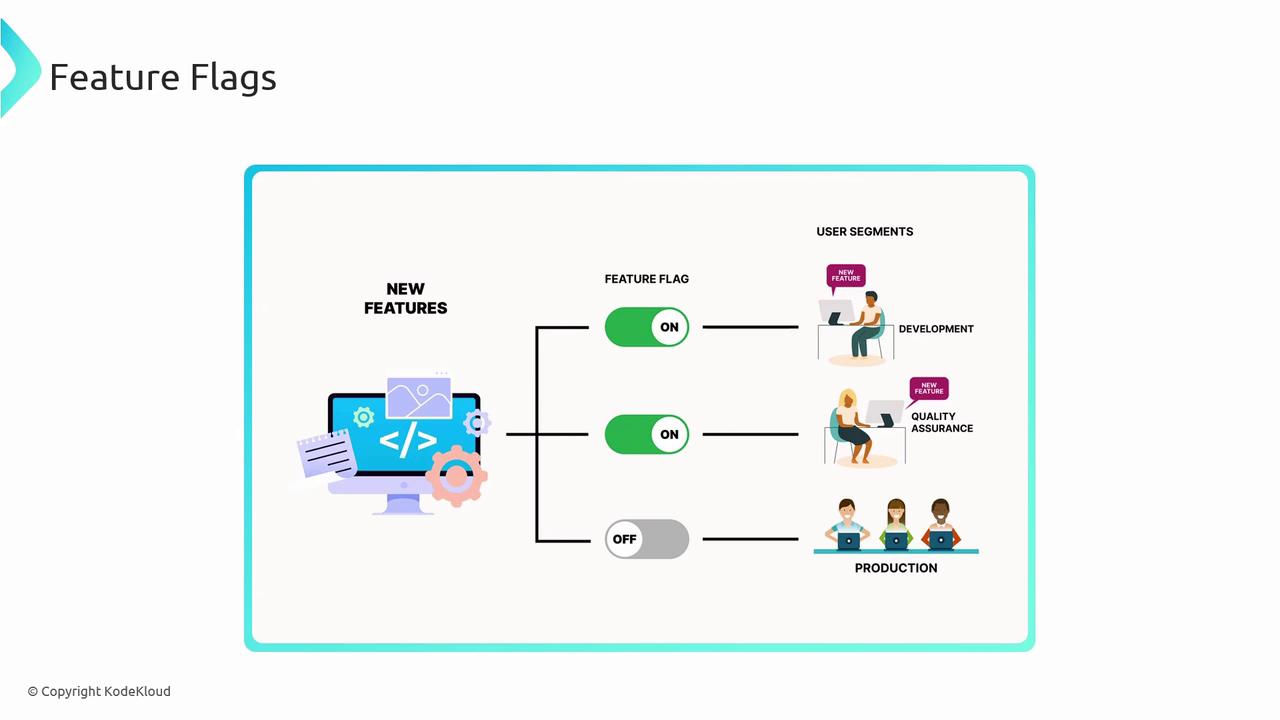
Use a centralized flag management service to avoid flag sprawl and technical debt.
A/B Testing
A/B testing (split testing) helps you compare two or more variants of a feature to identify which one best meets your key performance indicators (KPIs).- Serve version A to one cohort and version B to another.
- Collect behavioral data (e.g., click-through rates, conversions).
- Analyze results statistically and roll out the winning variant.
Strategy Comparison
| Strategy | Key Benefit | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Blue/Green | Instant rollback, zero downtime | Major version upgrades |
| Canary | Early anomaly detection | High-risk features, backend services |
| Ring | Controlled phased release | Large user bases with varied geographies |
| Progressive Exposure | Multi-stage validation | Complex features requiring load-specific testing |
| Feature Flags | Runtime control, dark launches | Incremental feature releases, quick disablement |
| A/B Testing | Data-driven UX improvements | UI/UX experiments, marketing campaigns |