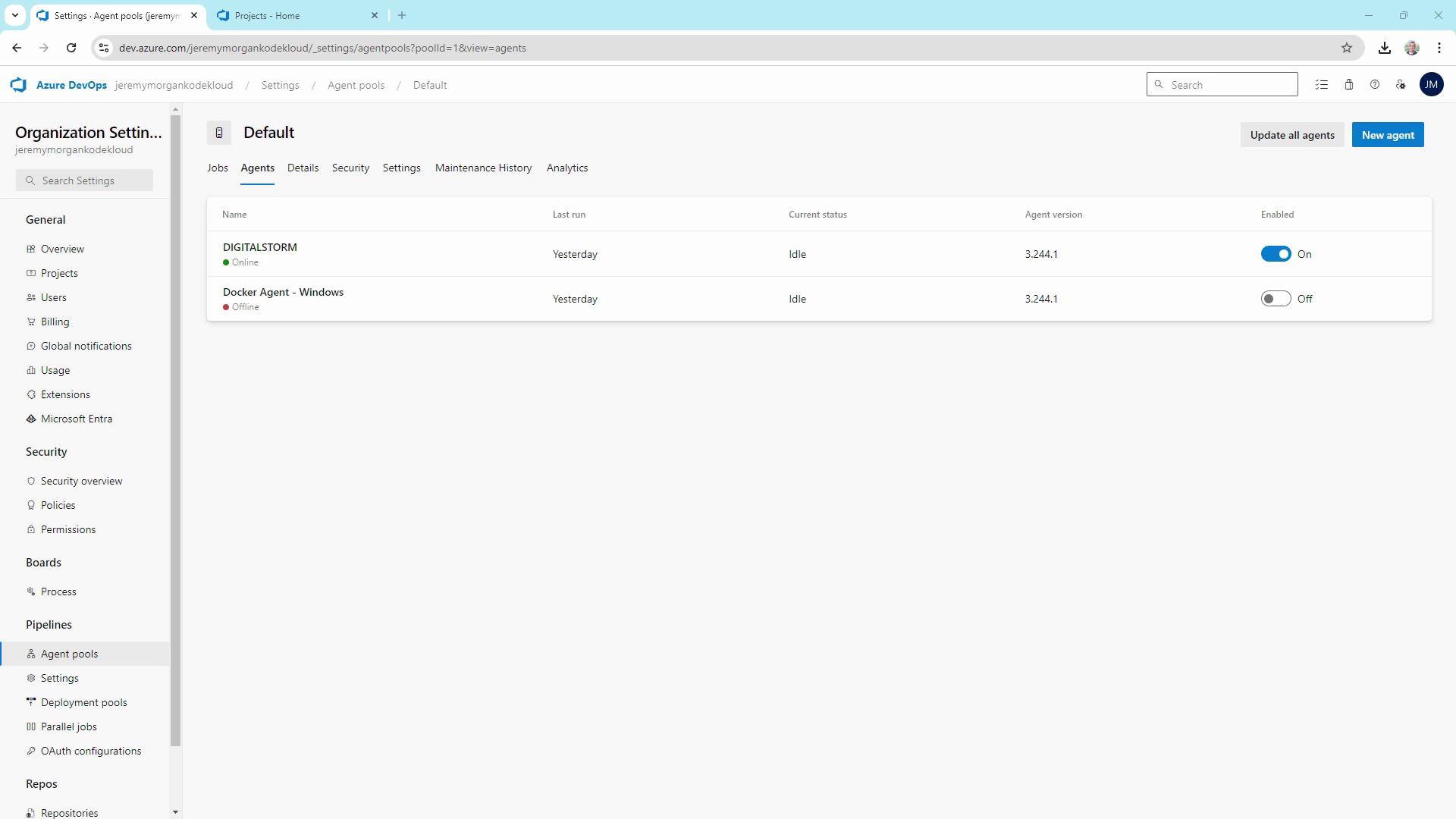
Current Agent Pools
In Azure DevOps under Organization Settings » Agent pools, you’ll typically see:| Pool Name | Type | Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Pipelines | Hosted | (Disabled when using self-hosted) |
| Default | Self-hosted (Windows) | DigitalStorm, Docker Agent - Windows |
Click Add pool, select Self-hosted, name it (e.g.,
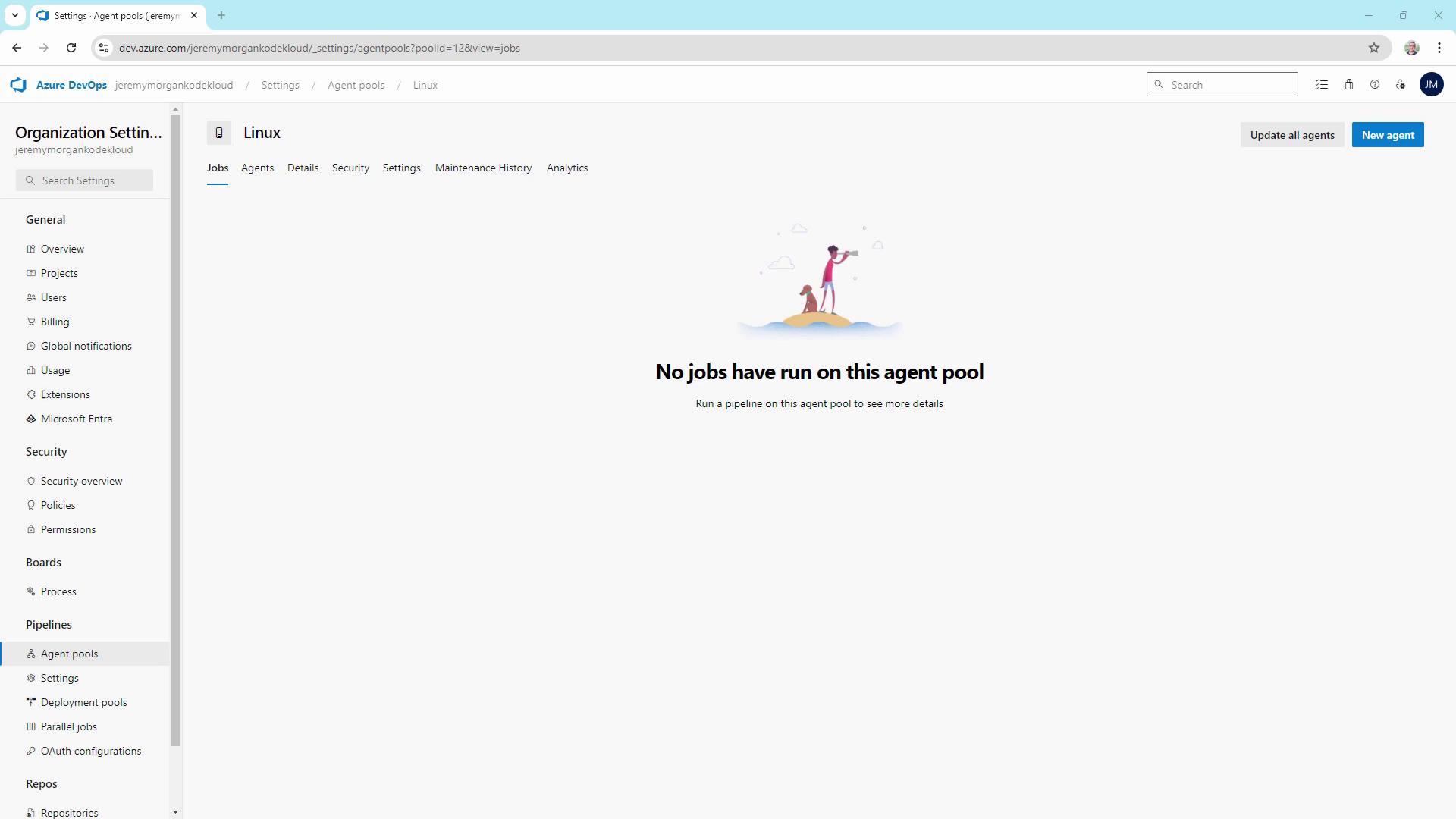
Once created, you’ll have a new Linux pool—let’s add an agent in WSL.
Linux self-hosted builders), and optionally enable Auto-provision this agent pool in all projects.Once created, you’ll have a new Linux pool—let’s add an agent in WSL.
Why Use WSL for Your Linux Agent?
WSL provides a full Linux environment on Windows without a virtual machine. Install packages, run scripts, and host a Linux build agent just like on a native Linux server.
Prerequisites
- Windows 10 (2004+) or Windows Server 2022
- WSL2 enabled with a default Linux distro
- Azure DevOps organization and a Personal Access Token (PAT) with Agent Pools scope
- Administrator access to PowerShell or Command Prompt
Installing the Linux Agent in WSL
- Download the Linux x64 agent tarball from your Azure DevOps New agent dialog.
-
In WSL, copy the file:
-
Create and navigate into the agent folder:
-
Extract the archive:
-
Run the configuration script:
Provide these details when prompted:
- Accept EULA → Y
- Server URL →
https://dev.azure.com/<yourOrganization> - Authentication → press Enter for PAT, then paste your token
- Agent pool →
Linux - Agent name →
WSL Linux Builder - Work folder → press Enter for default (
_work)
Keep your Personal Access Token secure. Do not check it into source control or share publicly.
- Start the agent:
You should see:

Final Result
On the same Windows machine, you now have:- A Windows self-hosted agent (Default pool)
- A Linux self-hosted agent (WSL Linux pool)