Key Stages & Tools
Below is a high-level overview of the major phases in a secure CI/CD pipeline. Each component plays a critical role in enforcing security policies and maintaining compliance from code commit to production.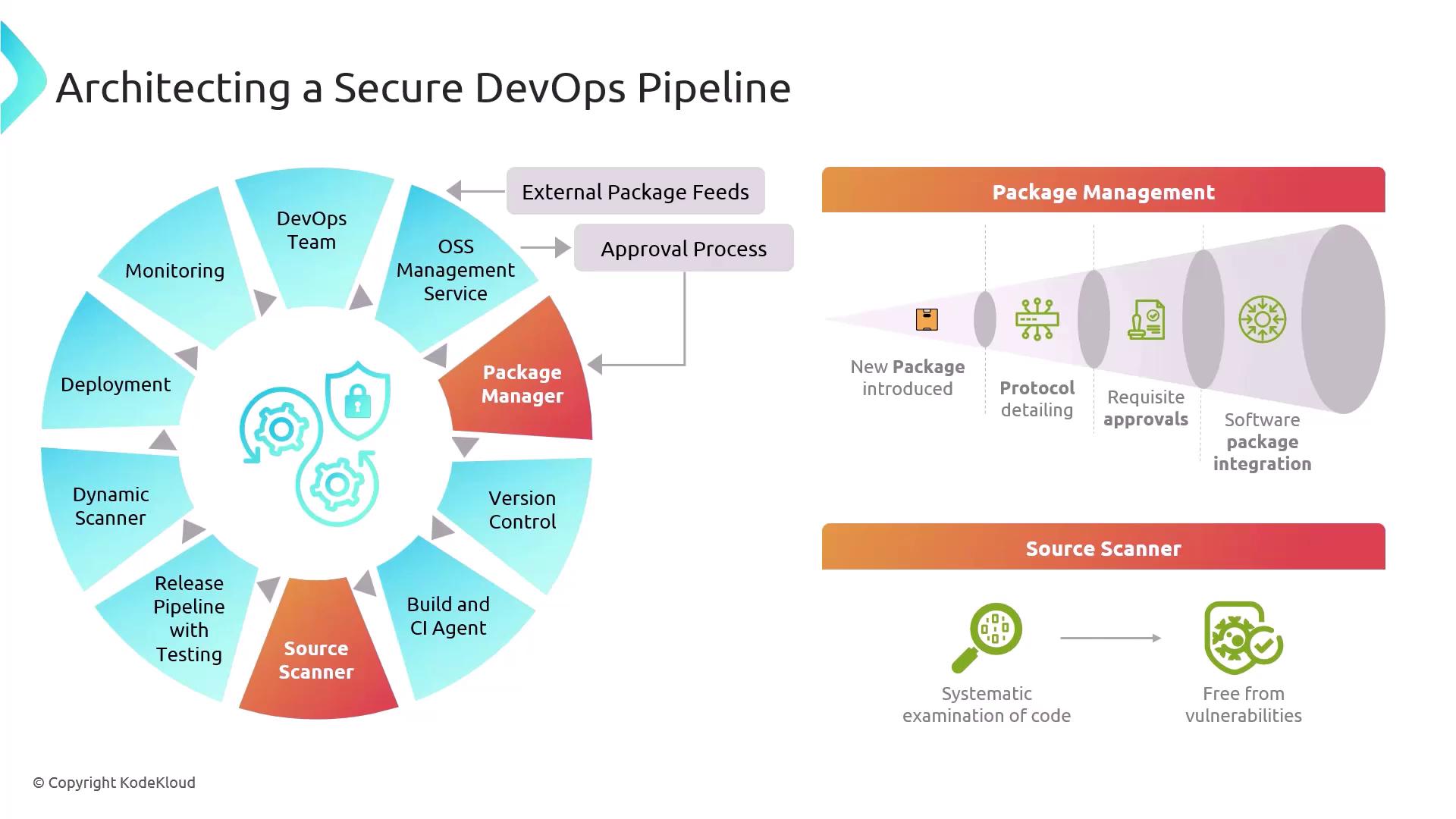
1. Problem Area: External Package Feeds
Open source libraries are invaluable, but they can introduce risks if packages aren’t properly vetted. A single compromised dependency can cascade into a serious breach.Malicious or vulnerable open source packages can introduce critical security flaws if not vetted properly.
- Implement an approval workflow for any new package before it’s consumed.
- Use an OSS management service to track versions, licenses, and known CVEs.
- Maintain a curated feed of trusted packages to prevent unauthorized or unsafe dependencies.
2. Focus Area 1: Package Management Best Practices
Centralizing package control ensures that only approved artifacts enter your pipeline. Automate governance with these key policies:| Policy | Description | Tool Support |
|---|---|---|
| Source Whitelisting | Restrict feeds to vetted registries | Azure Artifacts, GitHub Packages |
| Version Pinning | Approve and pin specific package versions | npm, NuGet, PyPI` |
| Role-Based Access | Limit publish/update rights to authorized personnel | Azure AD, GitHub Teams |
Centralizing package governance helps maintain consistency and auditability across all teams.
3. Focus Area 2: Source Scanning
Automated scanning tools catch vulnerabilities early—long before they reach production. Integrate these scans as part of your CI/CD workflow:| Scan Type | Trigger | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Static Code Analysis | Pull Request | Detailed report on code weaknesses |
| Dependency Scanning | Every Build | License checks & CVE alerts |
| Secrets Detection | Continuous | Blocks commits containing credentials |