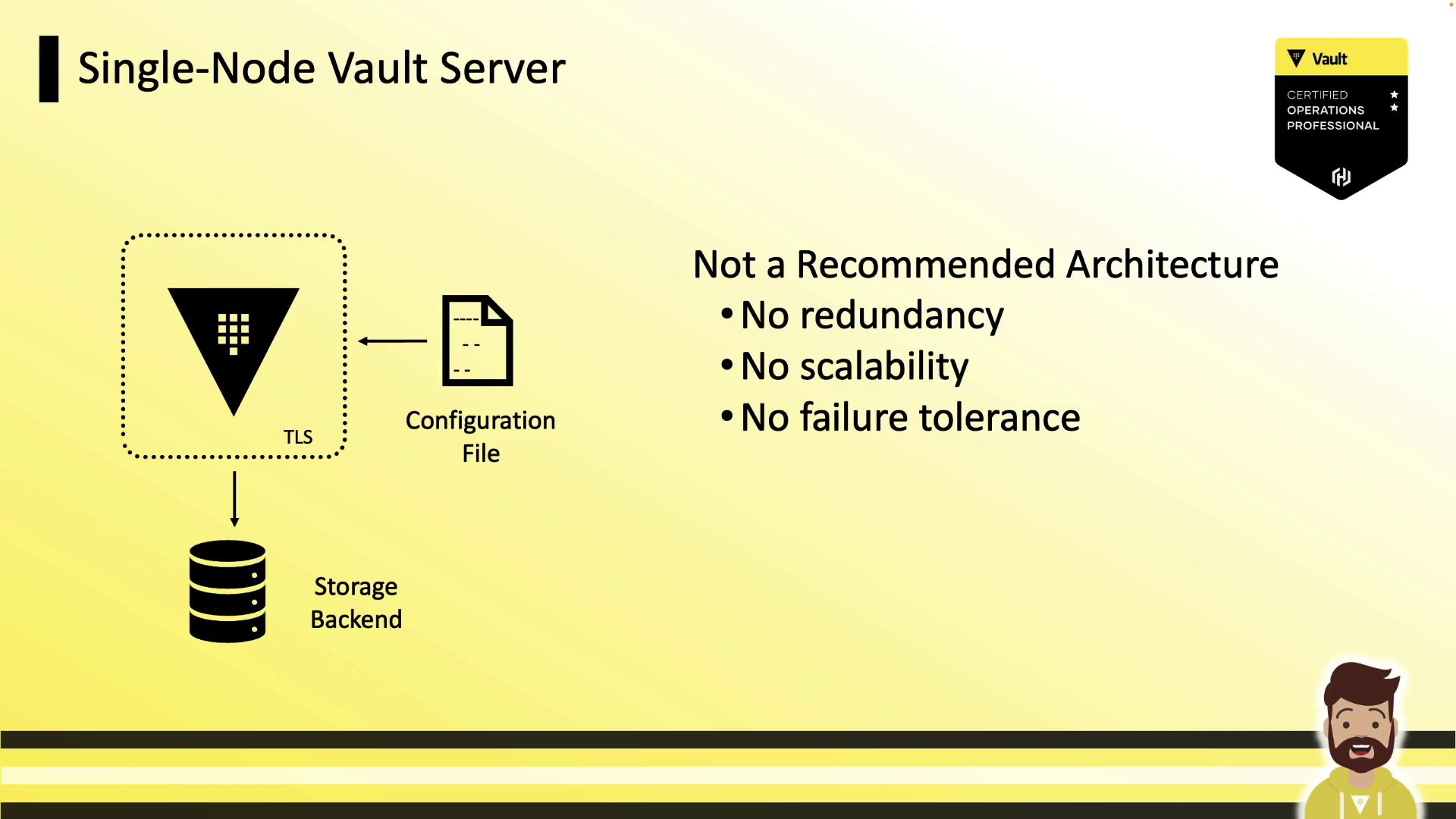
Single-Node Setup (Not Recommended)
A single-node Vault server cannot tolerate failures or scale out. If the node goes offline, Vault becomes inaccessible—acceptable only for development or testing.A single-node Vault instance has zero redundancy. Do not use this configuration in production.
Key Characteristics of an Ideal Vault Cluster
A robust, production-grade Vault cluster should:- Replicate all data across every node
- Survive one or more node failures without downtime
- Scale horizontally as application demands grow
- Maintain a fully replicated, peer-to-peer architecture

Vault Enterprise supports two storage backends: Integrated Storage (Raft) and Consul. For production, HashiCorp strongly recommends Integrated Storage (Raft). The Vault Operations Professional exam covers only Integrated Storage.
Integrated Storage Overview
Integrated Storage (Raft) leverages the Raft consensus protocol to replicate data across Vault nodes. Every node retains a full copy of the data. The leader handles writes and streams updates to follower nodes. If the leader goes down, followers elect a new leader almost immediately.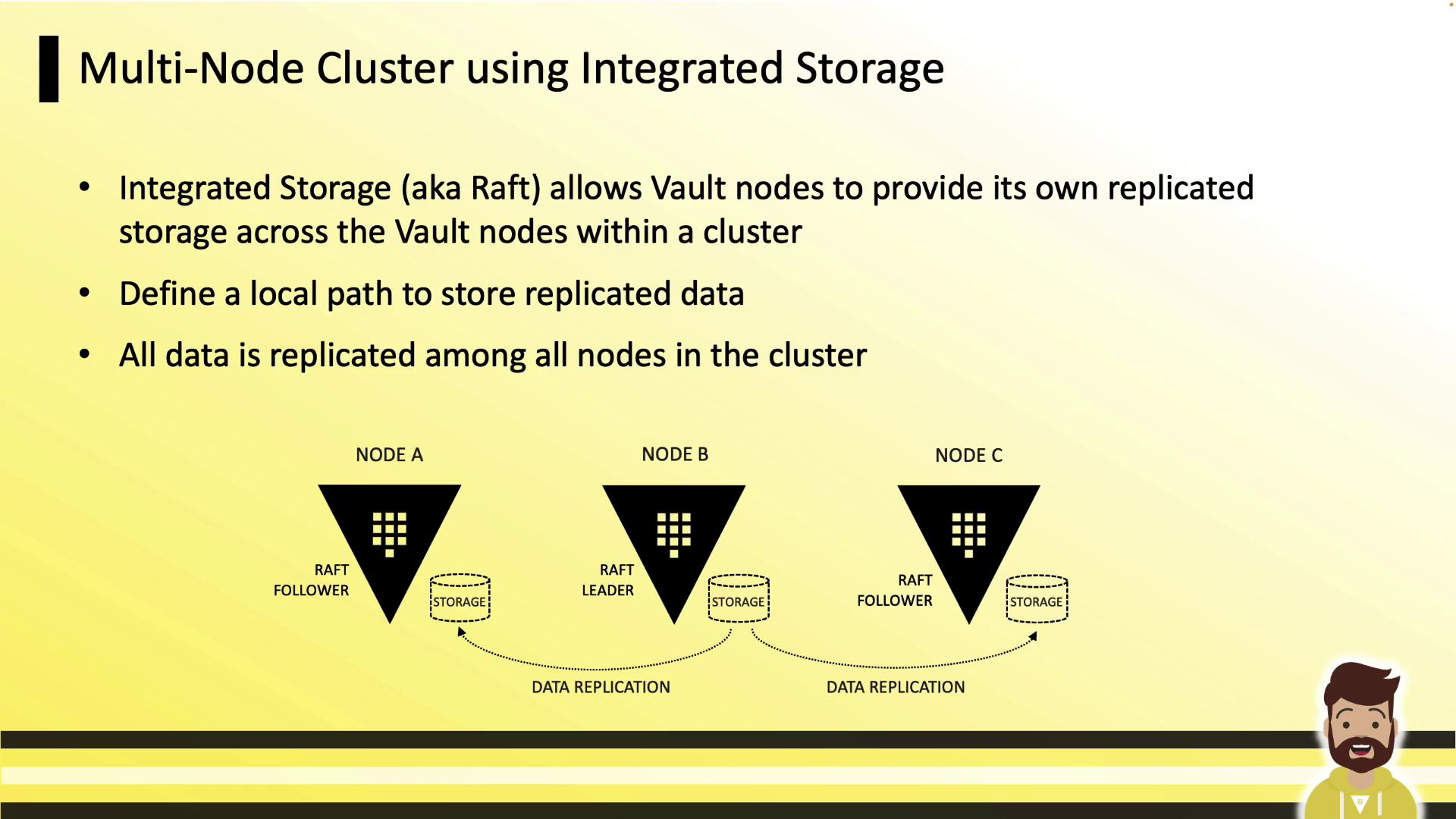
Configuring Integrated Storage
Add astorage "raft" block to your Vault HCL configuration (config.hcl), then define your listener and seal settings:
path
Local filesystem path for Raft data. Must be identical on every node.node_id
Unique identifier for each Vault instance.retry_join
Automates cluster formation. You can use cloud provider tags or explicit host addresses.
Explicit Retry Join Hosts
If you prefer manually listing each peer:CLI Management for Integrated Storage

vault operator raft subcommands to manage your cluster:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
vault operator raft list-peers | List current cluster members and their roles |
vault operator raft join <leader> | Add a new follower to the Raft cluster |
vault operator raft remove-peer <id> | Remove a node gracefully from the cluster |
vault operator raft snapshot | Create or restore a cluster snapshot |
Manual Cluster Workflow
- Initialize and unseal the leader (node A):
- On each follower (nodes B, C, …), join the cluster:
- If manual unseal is in use:
With auto-unseal (e.g., AWS KMS), Vault nodes unseal themselves after joining.
- Repeat steps 2–3 for each node until all peers have joined.
Viewing and Removing Peers
Log in and inspect your Raft peers:| Node | Address | State | Voter |
|---|---|---|---|
| node-a | 10.0.101.22:8201 | leader | true |
| node-b | 10.0.101.23:8201 | follower | true |
| node-c | 10.0.101.24:8201 | follower | true |
| node-d | 10.0.101.25:8201 | follower | true |
| node-e | 10.0.101.26:8201 | follower | true |
vault operator raft list-peers to confirm.
A hands-on lab will walk you through both manual and automated cluster formation.