Deploying with the Official Helm Chart
To install Vault using Helm:my-vault-values.yaml to enable mlock, non-root execution, and other hardening options.
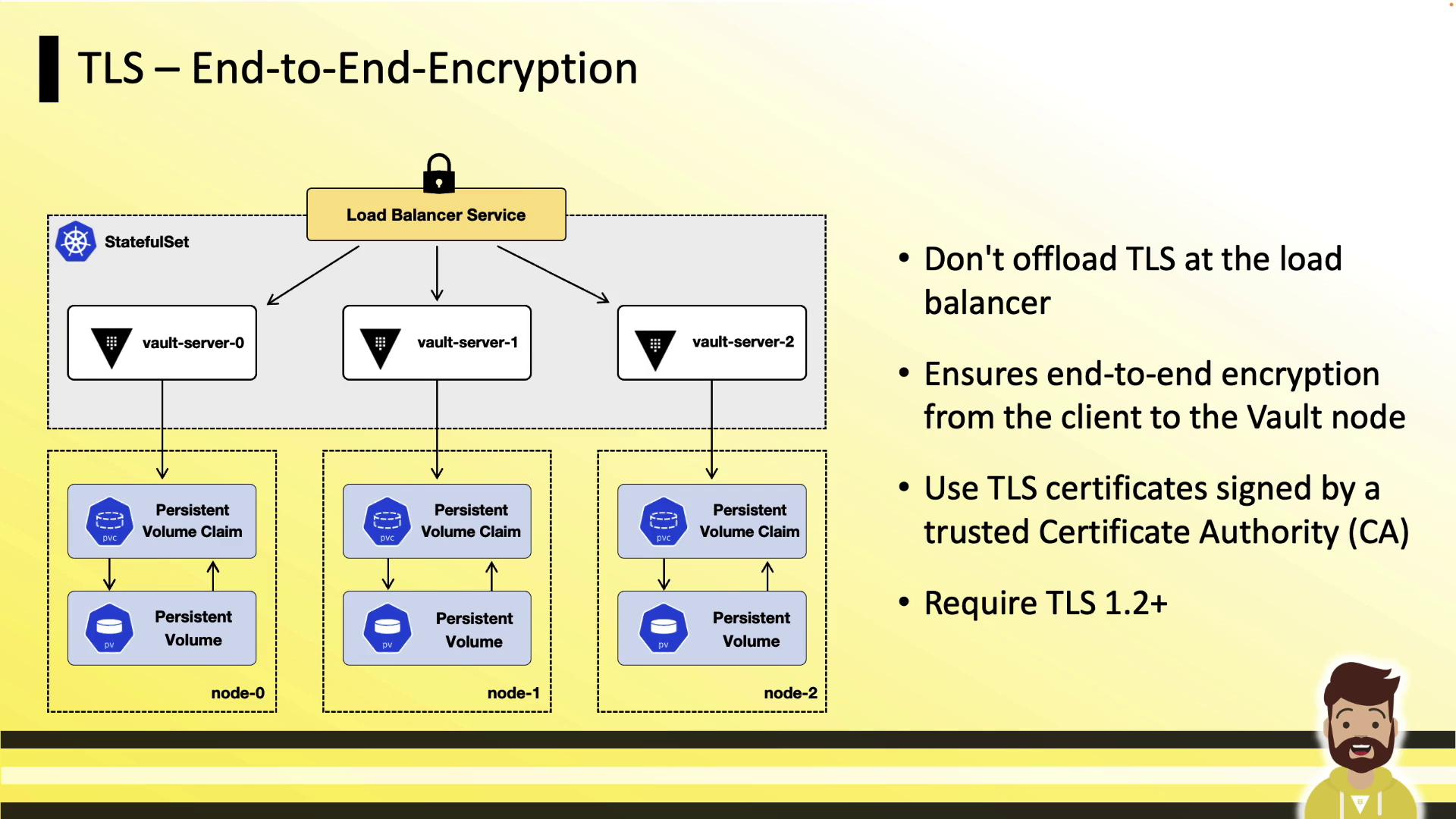
TLS End-to-End Encryption
Ensure that all traffic between clients, load balancers, and Vault pods is encrypted with TLS 1.2 or higher. Do not terminate TLS at the load balancer; instead, use TLS passthrough so that Vault pods handle the certificate handshake.Configure your cloud load balancer for TCP passthrough to maintain end-to-end encryption. This prevents cleartext traffic from ever reaching your Vault pods.
Secret and a PersistentVolumeClaim.
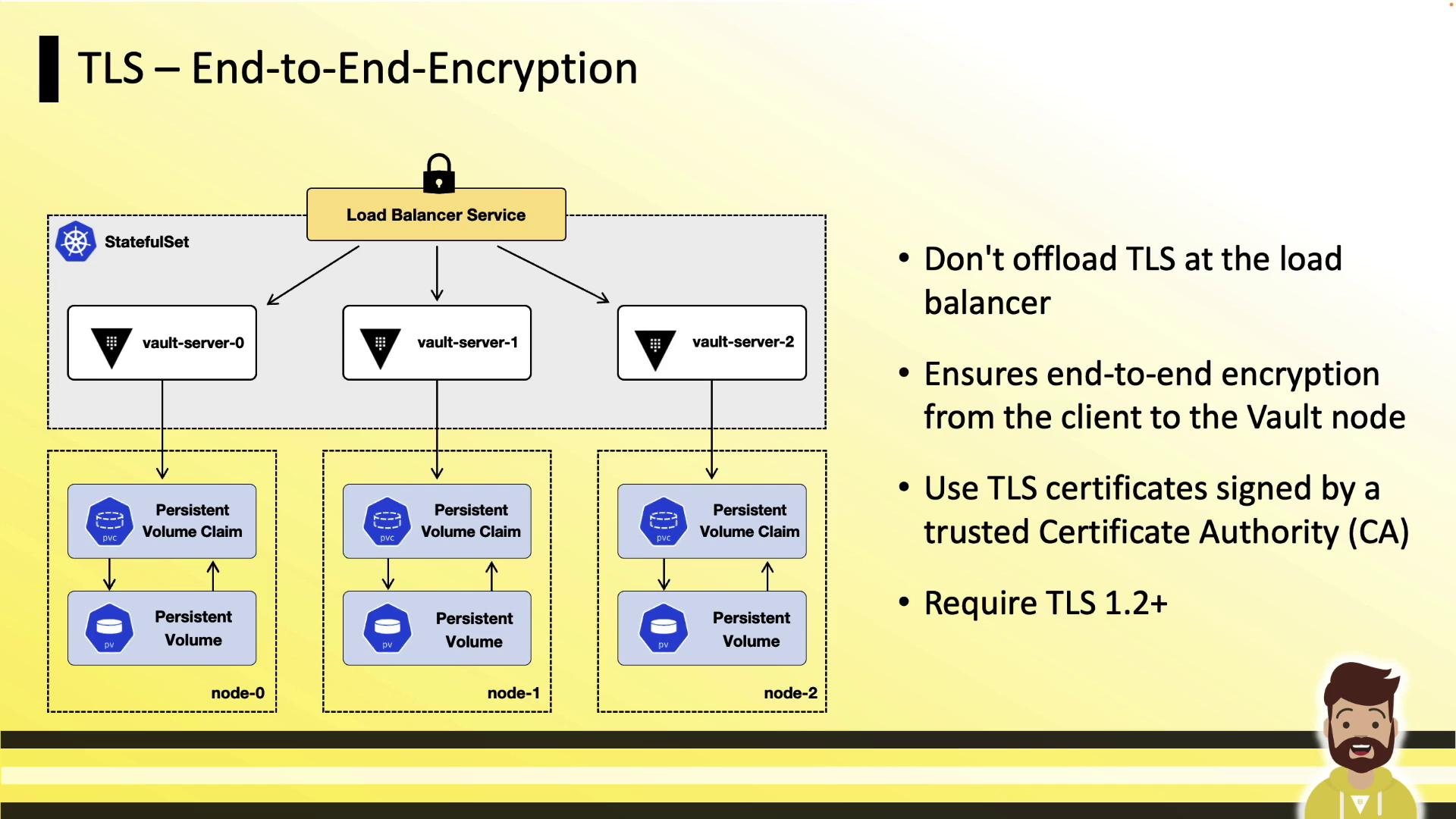
Disable Core Dumps
Core dumps can inadvertently capture Vault’s in-memory encryption keys. Disable them at the kernel and container levels:A core dump could expose sensitive encryption keys. Always set
RLIMIT_CORE to 0 in your containers.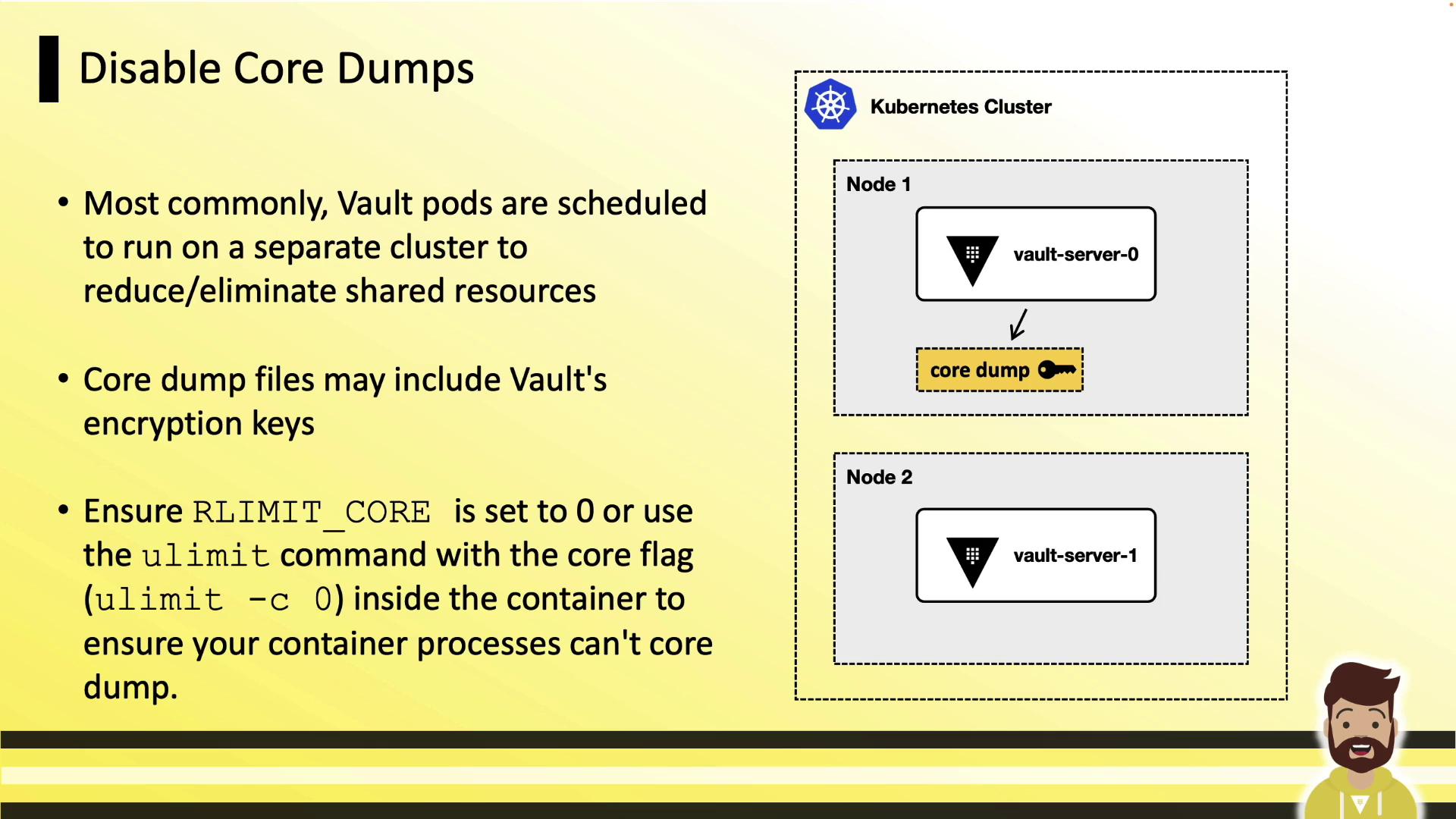
Enable mlock
Prevent Vault’s memory from being swapped to disk by granting theIPC_LOCK capability. This ensures in-memory encryption keys never hit swap:
Run as Non-Root & Read-Only Filesystem
Running Vault as root increases risk if a container escape occurs. Enforce non-root execution and mount the filesystem read-only:
Security Context Cheat Sheet
| Feature | Configuration Snippet | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Disable Core Dumps | limits.core: 0 | Prevents writing memory dumps to disk |
| Enable mlock | capabilities.add: [“IPC_LOCK”] | Locks memory to avoid swapping |
| Non-Root Execution | runAsNonRoot: true runAsUser: 1000 | Reduces attack surface in container |
| Read-Only Root Filesystem | readOnlyRootFilesystem: true | Prevents unwanted file modifications |
Additional Best Practices
- Deploy Vault on a dedicated Kubernetes cluster.
- Minimize enabled auth methods and secrets engines.
- Keep token TTLs short and prune unused policies regularly.
- Ensure Vault is the main process (PID 1) in each container, so it receives signals properly.
HashiCorp Learn tutorial on running Vault in Kubernetes.
Other useful references: