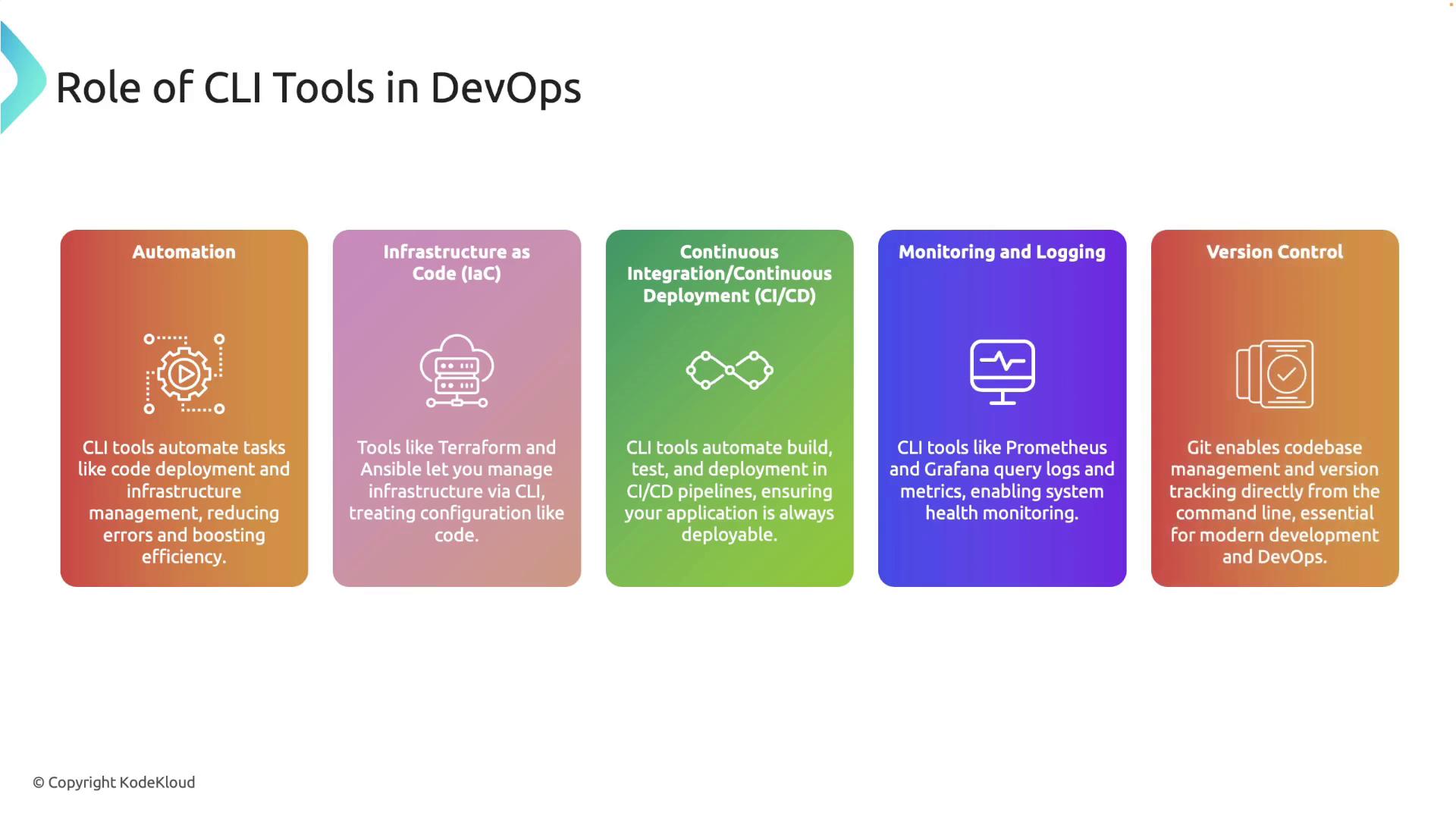
What Are CLI Tools?
A CLI tool allows users to interact with applications or systems through text-based commands rather than a graphical user interface (GUI). Users can input commands in a terminal or command prompt and receive text-based feedback and results. Popular examples of CLI tools include:- Git: A version control system that is vital for tracking changes in source code.
- Docker: A platform that enables developers to build, ship, and run applications inside containers.
- Kubectl: A command line tool essential for interfacing with Kubernetes clusters.
- AWS CLI: A utility for managing AWS services directly from the terminal.
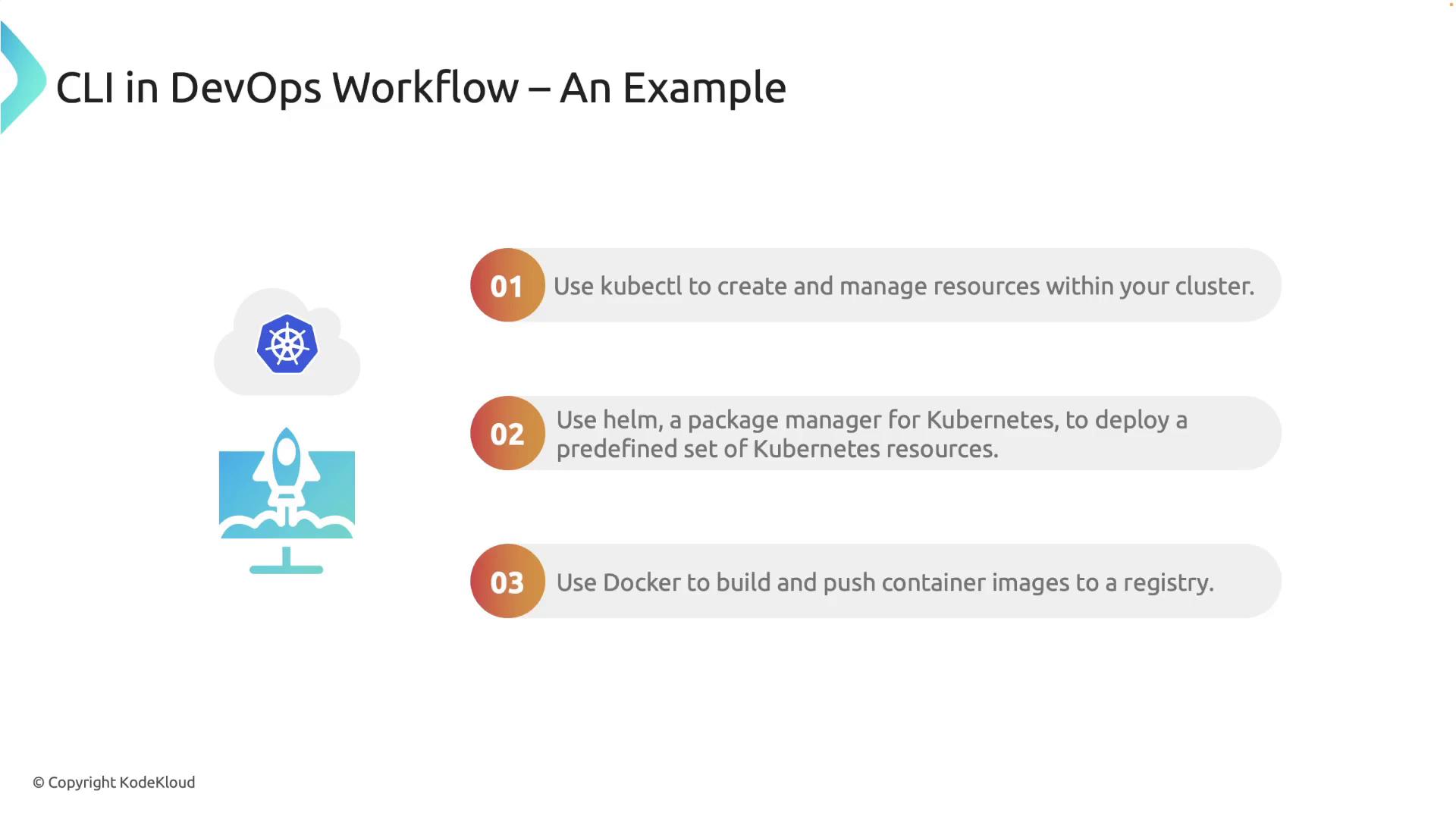
CLI Tools in a DevOps Workflow
Imagine deploying an application to a Kubernetes cluster. In such a scenario, CLI tools streamline the deployment process:- Kubectl: Manage and create resources directly within your Kubernetes cluster.
- Helm: Act as a package manager to deploy a predefined set of Kubernetes resources.
- Docker: Build and push container images to a container registry, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Why Use Rust for Building CLI Tools?
Rust offers several significant benefits for developing CLI tools:- Performance: Rust is designed as a systems programming language that delivers speed and efficiency, ideal for handling complex and large-scale operations.
- Memory Safety: Rust’s unique ownership model ensures high memory safety without requiring a garbage collector.
- Concurrency: Rust enables robust concurrency, allowing your applications to perform multiple tasks simultaneously without data races.

Rust’s ecosystem includes libraries such as CLAP (Command Line Argument Parser), which simplifies parsing and managing command line arguments for your applications. Additionally, Rust’s package manager, Cargo, streamlines the process of compiling your CLI tools for Linux, macOS, and Windows.

Ensure that you follow best practices in Rust development and regularly update your toolchain to keep your CLI tools secure and efficient.