Exhausting Compute Resources
An attacker may overload worker nodes and kubelets to reduce cluster capacity:- Flood kubelet endpoints (
/healthz,/metrics) or corrupt critical node files, causing nodes to reportNotReady. - Block kubelet health checks, forcing the scheduler to mark nodes as unschedulable.
- Trigger runaway CPU or memory consumption via malicious Pods to deplete node resources.
Resource exhaustion not only disrupts workloads but can also trigger automatic node replacement if cluster autoscaling is enabled.
Disrupting the Control Plane
Targeting core control-plane components can bring the entire cluster down. Common targets include etcd, the API server, the scheduler, and the controller manager.| Component | Ports | Impact of Attack |
|---|---|---|
| etcd | 2379, 2380 | Break quorum, corrupt cluster state, block peer sync |
| API Server | 6443 (TLS), 8080 | Deny API calls from kubectl and internal controllers |
| Scheduler | 10251, 10259 | Prevent new Pods from being assigned to nodes |
| Controller Manager | 10252, 10257 | Halt replica loops, scaling, and other control tasks |
Disrupting the API server or etcd can cause a full outage. Always secure these ports and validate firewall rules to avoid accidental lockouts.
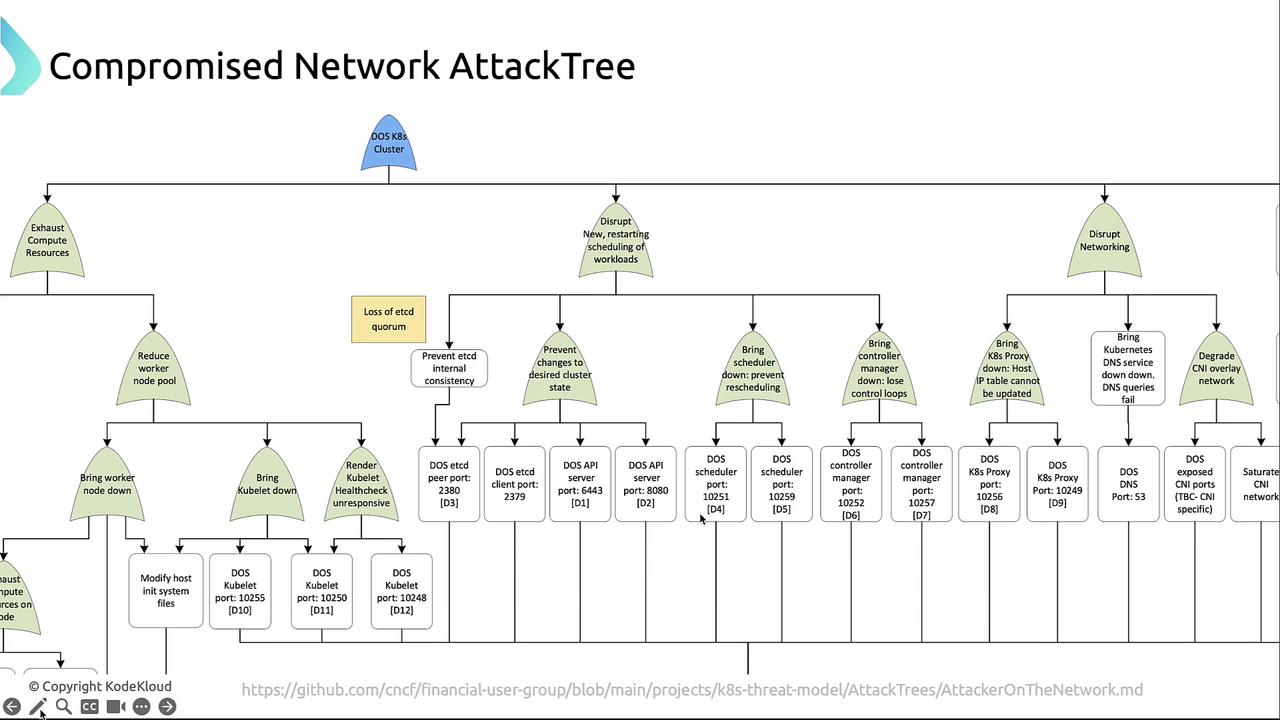
Disrupting Networking
Network-level denial-of-service can interfere with both internal communication and external access:| Networking Component | Ports | Attack Effects |
|---|---|---|
| kube-proxy | 10256, 10249 | Freeze Service-to-Pod traffic |
| DNS | 53 | Block DNS resolution, causing service failures |
| CNI Overlay Network | (varies) | Flood overlays, slow or sever Pod-to-Pod traffic |
| PXE / Network Boot | (varies) | Prevent new nodes from joining the cluster |
Mitigations
Firewall Configuration
Restrict access to critical control-plane endpoints by allowing only trusted IP ranges:- Limit the API server ports (
6443,8080) to your control-plane bastion hosts. - Block all unused Kubernetes ports at the network perimeter.
- Use cloud-native firewalls (e.g., AWS Security Groups, GCP Firewall Rules) for dynamic management.
Securing Nodes
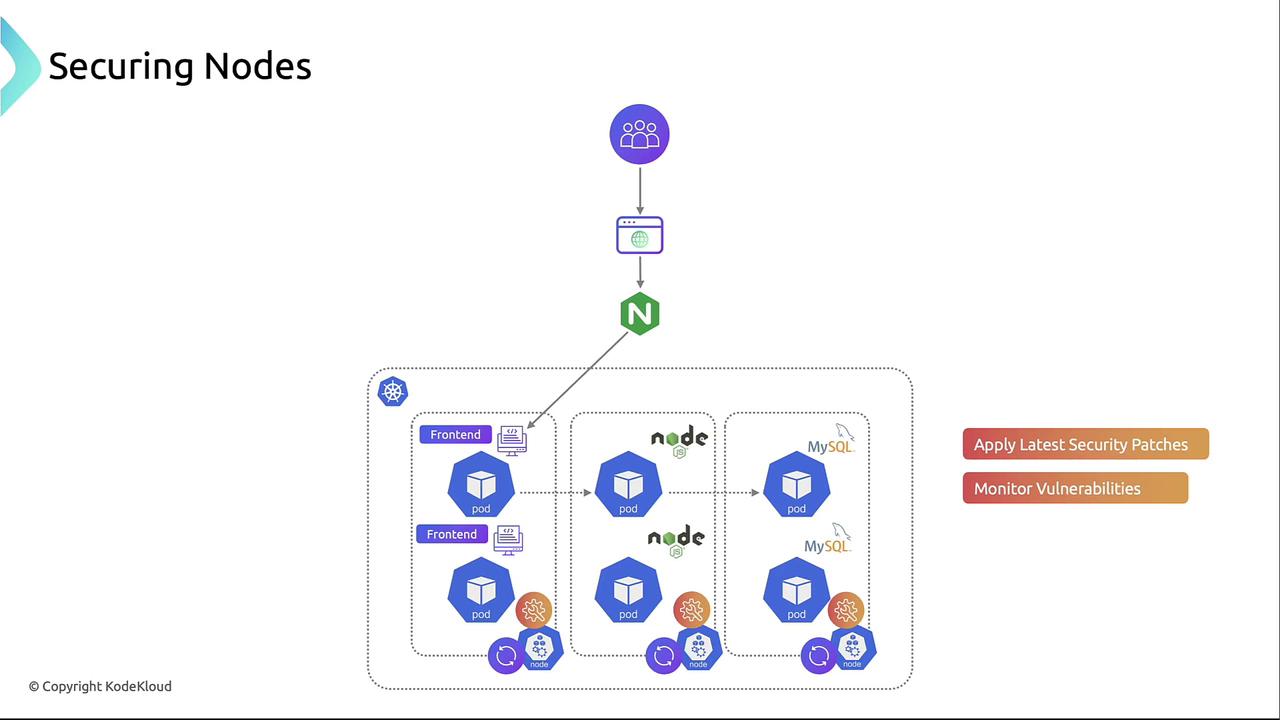
- Keep the host OS and Kubernetes components patched to the latest stable versions.
- Apply CIS Benchmarks or Node Hardening Guides for best practices.
- Monitor runtime vulnerabilities with tools like Falco or Sysdig Secure.
Network Policies
Implement KubernetesNetworkPolicy objects to enforce pod-level traffic controls:
Define both
Ingress and Egress policies to ensure complete traffic segmentation between namespaces and Pods.Strong Authentication and Authorization
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all control-plane access: API server, etcd, and SSH.
- Leverage Kubernetes Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to grant least-privilege permissions.
- Rotate service account tokens and certificates regularly.
Monitoring and Logging
Use Prometheus and Alertmanager to catch abnormal API usage and network spikes:Summary
Network-level attackers can cripple both the compute plane and control plane of your Kubernetes cluster. To defend effectively:- Enforce strict firewall rules around control-plane ports.
- Keep nodes and cluster components up to date.
- Apply
NetworkPolicyfor granular traffic control. - Use MFA and RBAC to secure API access.
- Monitor API calls and network metrics to detect and respond rapidly.