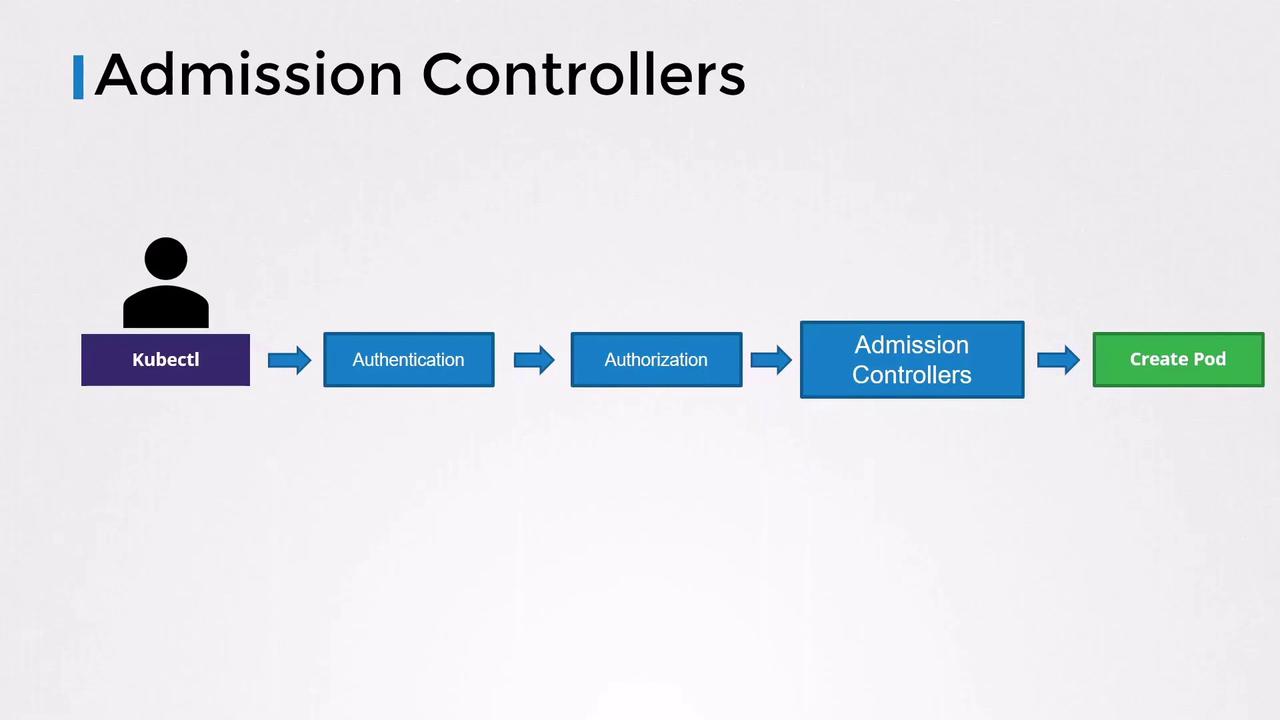
Kubernetes API Request Flow
When you run akubectl command (e.g., creating a Pod), the request follows these steps:
- Authentication (AuthN): Verify user identity (usually via certificates in your kubeconfig).
- Authorization (AuthZ): Check if the requester has permission (via RBAC, ABAC, Node, Webhook).
- Admission Control (Admission Controllers): Validate or mutate objects.
- Persistence: Store the final object in etcd.
Authentication & Authorization Examples
kubeconfig Snippet
RBAC Role for Pod Operations
Why Admission Controllers?
RBAC governs who can perform what at the API surface. It cannot inspect or change the contents of an object. For example, you may want to enforce:- Only use images from an internal registry
- Disallow
:latesttags - Prevent containers from running as root
- Inject security capabilities or sidecars
- Require specific labels or annotations
Admission Controllers can validate (reject bad requests) or mutate (inject defaults, sidecars) before persistence.
Built-in Admission Controllers
Kubernetes includes many Admission Controllers out of the box. Below is a summary of some common ones:| Admission Controller | Behavior |
|---|---|
| AlwaysPullImages | Forces image pull for every Pod creation |
| DefaultStorageClass | Labels PVCs with a default StorageClass |
| EventRateLimit | Throttles API events to prevent overload |
| NamespaceExists | Rejects requests for non-existent namespaces |
Namespace Admission Controllers
NamespaceExists
By default, creating resources in a namespace that doesn’t exist yields:NamespaceAutoProvision
NamespaceAutoProvision (disabled by default) automatically creates a namespace if it doesn’t exist when you submit a request.
Viewing Enabled Admission Controllers
Enabling an Admission Controller
Update the API server’s startup arguments:Editing the
kube-apiserver flags requires careful coordination. After changes, restart the API server or apply the updated control-plane manifest.NamespaceLifecycle Admission Controller
The NamespaceLifecycle plugin supersedes bothNamespaceExists and NamespaceAutoProvision. It:
- Rejects requests to unknown namespaces
- Prevents deletion of critical system namespaces (
default,kube-system,kube-public)