System Requirements
The primary requirements for our like system are as follows:- A user should be able to like a post.
- Each user must only be allowed to like a given post once. Allowing multiple likes from the same user would artificially inflate the like count.
- When retrieving a post, the system should also return the total number of likes.
Database Design for the Like System
Similar to how most applications separate concerns by using individual tables for users and posts, the like functionality should be implemented in its own table. The minimal columns essential for our likes table include:| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Post ID | ID of the post being liked |
| User ID | ID of the user who liked the post |
For systems with a more complex voting mechanism, like Reddit’s upvote/downvote model, an additional column can be added to indicate the vote direction. However, in our simple like system, this extra detail is unnecessary.
- A row indicating that post 12 is liked by user 4 is valid.
- Another valid row can indicate that post 28 is liked by user 9.
- However, if user 2 has already liked post 55, the system must reject any additional entries with the combination of (post 55, user 2).
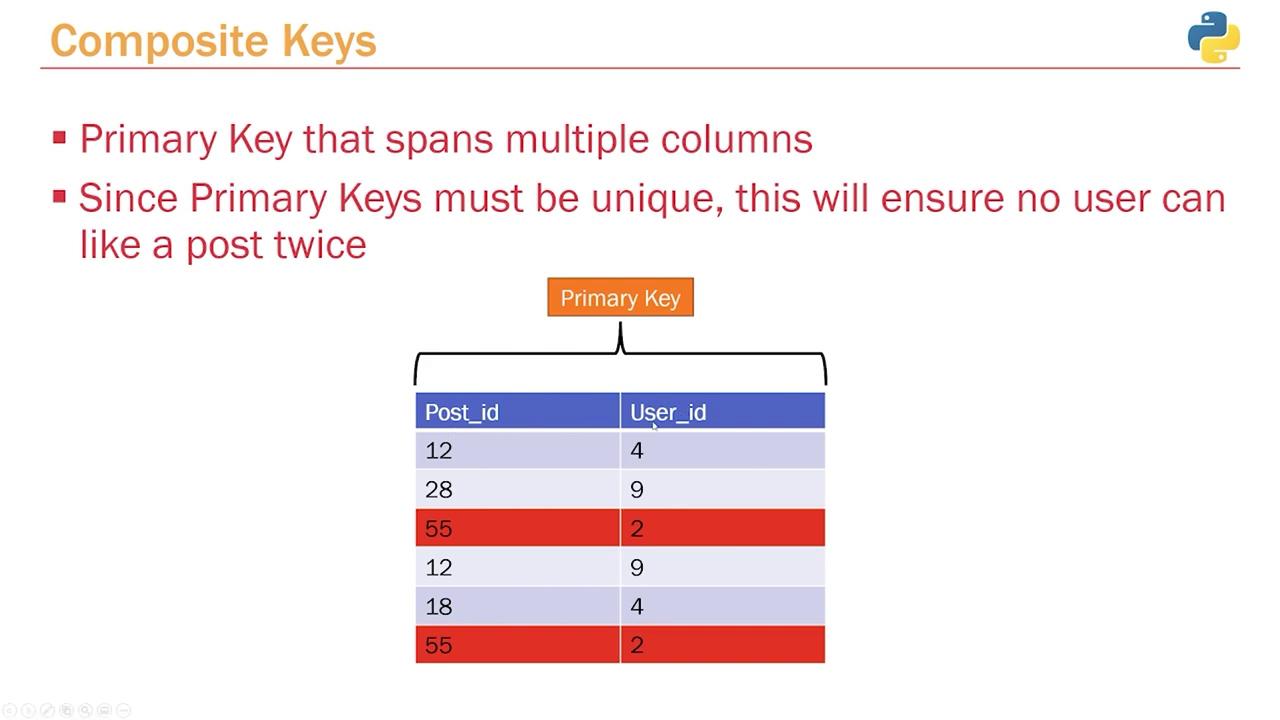
Enforcing Uniqueness with Composite Keys
In relational databases, a composite key is a primary key that is formed by combining two or more columns. Unlike a typical primary key that might consist of a single column (like an ID), the composite primary key in our likes table comprises both the post ID and the user ID. This approach guarantees that a user cannot like the same post more than once. Consider the following scenarios:- For post ID 12, if user 4 and user 9 both like it, there will be two distinct entries: (12, 4) and (12, 9).
- User 9 can like both post 28 and post 12, resulting in two unique pairs: (28, 9) and (12, 9).
- If there is an attempt to record a like with the combination (55, 2) when user 2 has already liked post 55, the database will reject this duplicate.
Ensure that the composite key is properly indexed to enforce the uniqueness constraint. Failure to do so might lead to duplicate records, thereby compromising the integrity of the like count.