Nodes and Clusters
A node is a machine—physical or virtual—on which Kubernetes is installed. Previously known as minions, nodes serve as the worker machines where containers run. Relying on a single node can lead to application downtime in the event of a failure. To mitigate this risk, nodes are grouped into clusters, ensuring high availability and load distribution. Even if one node fails, the application continues to run on other nodes without interruption.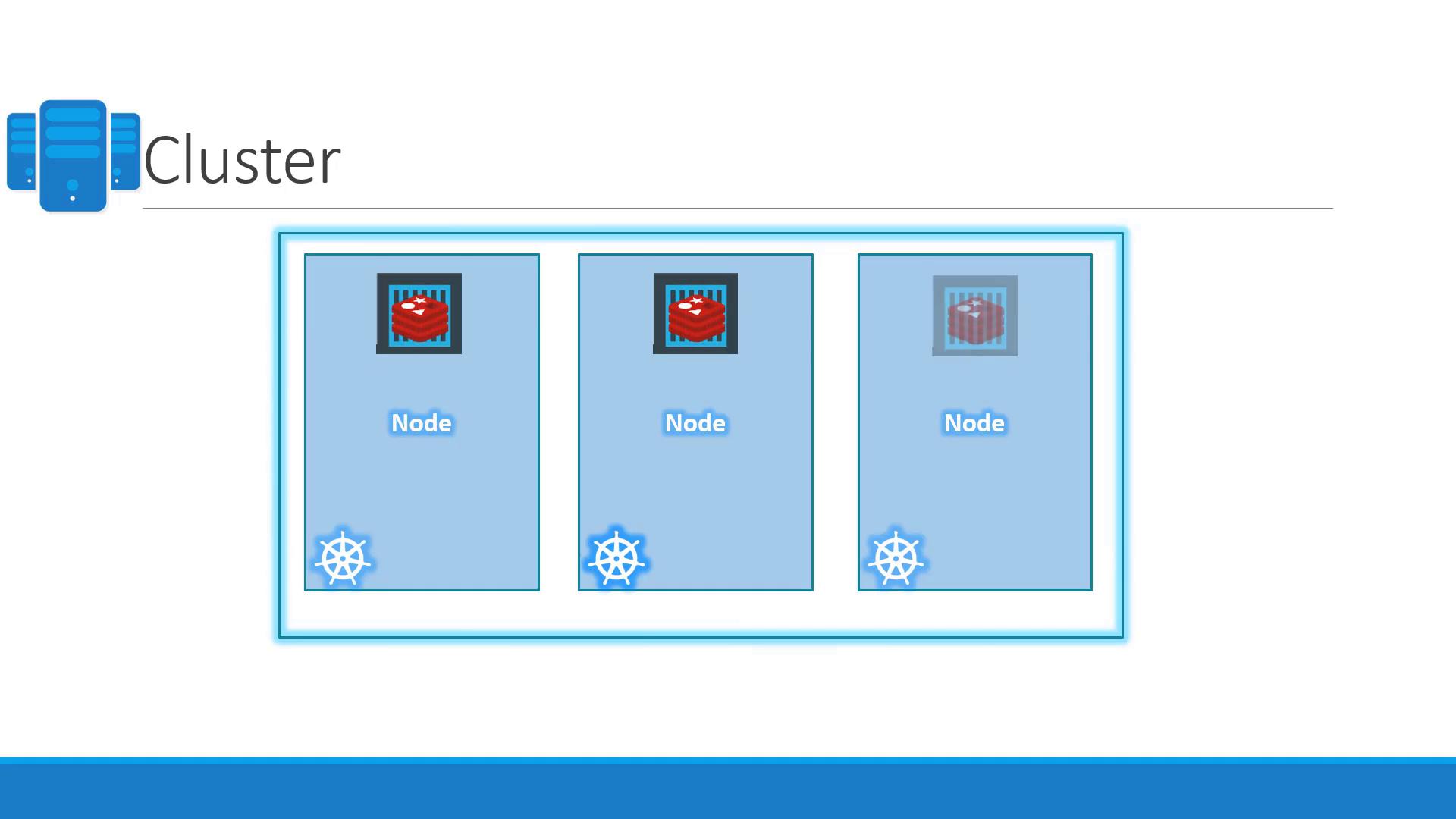
The Master Node and Cluster Management
Managing a Kubernetes cluster requires robust coordination and monitoring. The master node plays a pivotal role by overseeing the entire cluster. Configured with Kubernetes, the master node stores critical cluster information, monitors node health, and redistributes workloads when necessary.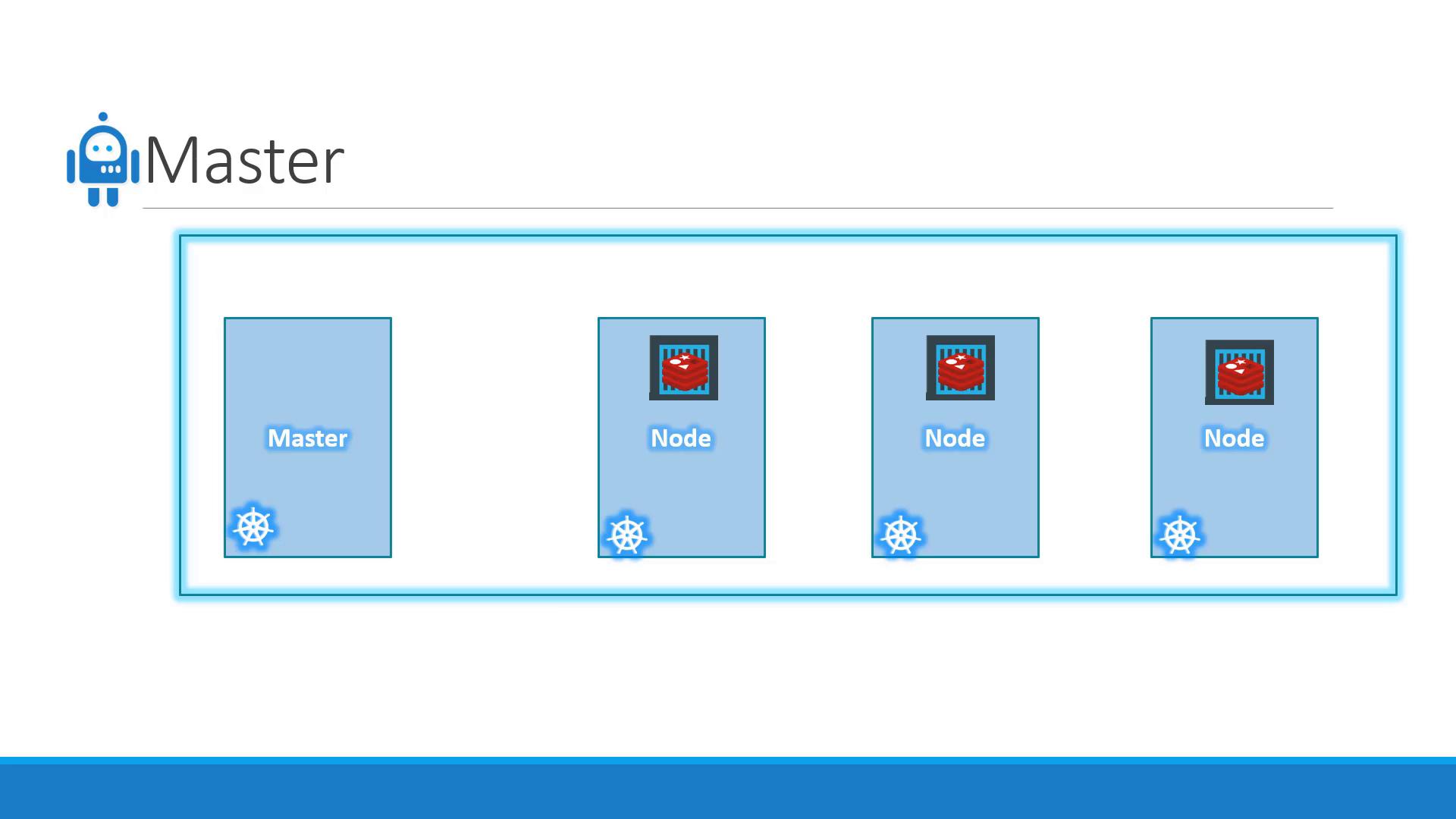
When installing Kubernetes, several core components are automatically deployed:
- API Server: Serves as the front end, processing commands from users and interfaces.
- etcd: A distributed key-value store that holds all cluster data and ensures consistency.
- Kubelet: An agent on every node that ensures containers are running as expected.
- Container Runtime: Software (such as Docker) that runs the containers.
- Controllers: Monitor cluster state and take corrective actions, like replacing containers when nodes fail.
- Scheduler: Distributes container workloads across nodes by assigning new containers to the most suitable node.
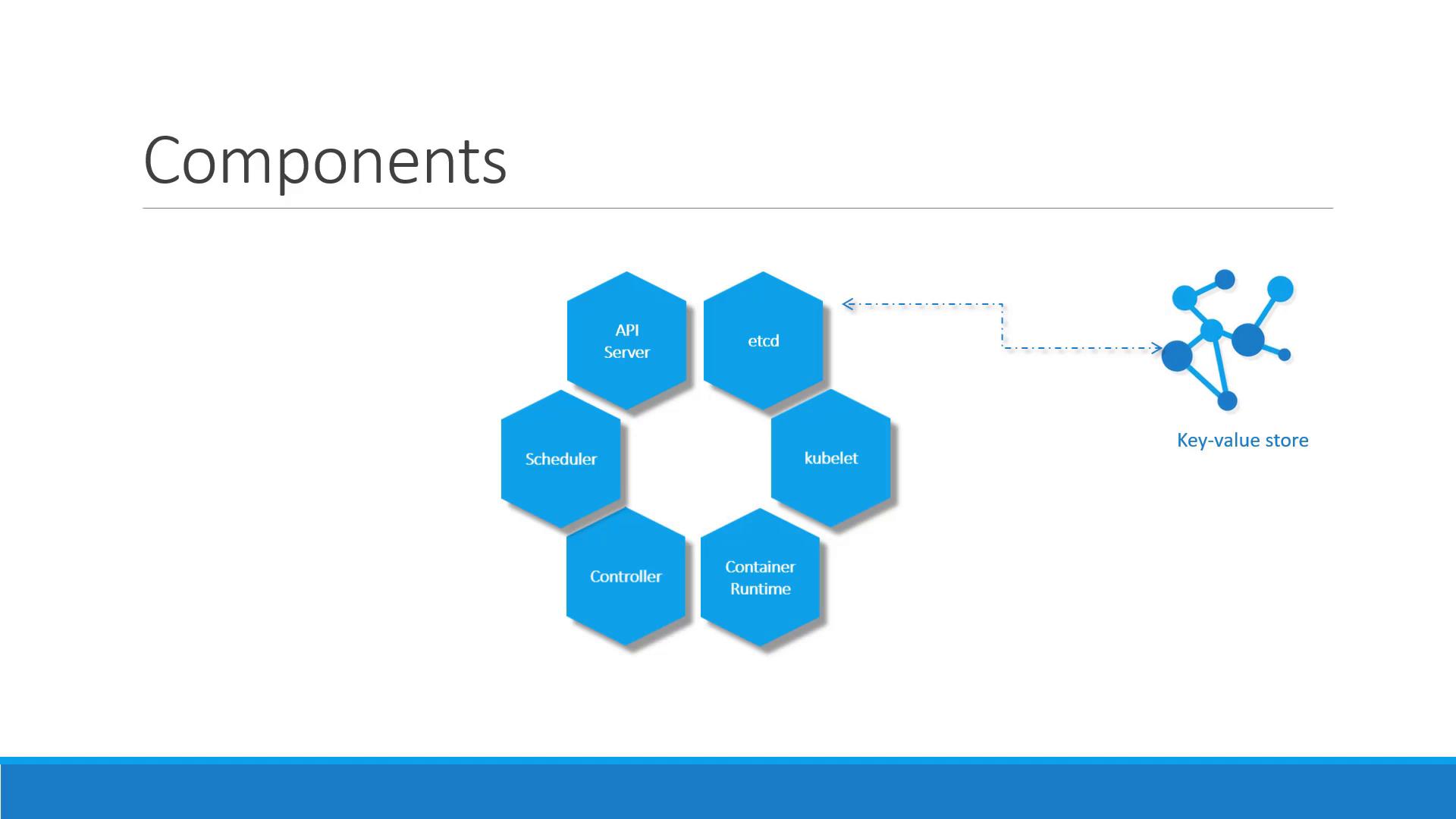
Distribution of Components
In a Kubernetes cluster:- The master node hosts the API server, controller manager, scheduler, and the etcd key-value store.
- The worker nodes run the kubelet agent and the container runtime (like Docker) to host and run containers.
Managing the Cluster with kubectl
The Kubernetes command-line tool, kubectl, is essential for deploying and managing applications within the cluster. It allows you to retrieve cluster information, control nodes, and perform various administrative tasks. Here are some fundamental commands:- The first command launches an application.
- The second displays cluster information.
- The third lists all nodes in the cluster.
As you advance in your Kubernetes journey, you will explore additional kubectl commands and more complex cluster management tasks.