
Resilience and Recovery in Security Architecture
Resilience is the ability of a system to endure disruptions and quickly bounce back, ensuring continuous operation. Recovery involves returning systems to normal function after an interruption. Together, they minimize downtime, protect vital assets, and maintain trust among customers and stakeholders.
Focusing on resilience and recovery is not just a reactive approach—it is a proactive strategy to ensure long-term business continuity.
Platform Diversity
Platform diversity involves using a mix of hardware and software solutions to avoid dependence on a single vendor or system. By diversifying, you reduce single points of failure and enhance overall security and flexibility. For example, running applications on various operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and macOS and deploying servers from different manufacturers ensures that a vulnerability in one system doesn’t compromise the entire application.
Multi-cloud Systems
Multi-cloud systems distribute workloads and data across multiple cloud service providers, reducing vendor lock-in and enhancing availability. Leveraging the strengths of different providers, such as using Amazon Web Services (AWS) for primary operations and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for backup and disaster recovery, ensures continuous service delivery even if one provider experiences issues.
Always evaluate cloud provider SLAs and security protocols when designing a multi-cloud strategy to avoid unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Continuity of Operations
Continuity of operations means planning and implementing processes that keep critical business functions running during and after disruptions. A solid business continuity plan typically includes strategies for remote work, data backup, and effective communication during crises. Regular testing and updating of these plans are essential to reduce downtime and improve overall crisis preparedness.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning entails determining the necessary resources across three key areas to meet both current and future demands. This process is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and scalability, whether addressing routine operations or unexpected surges.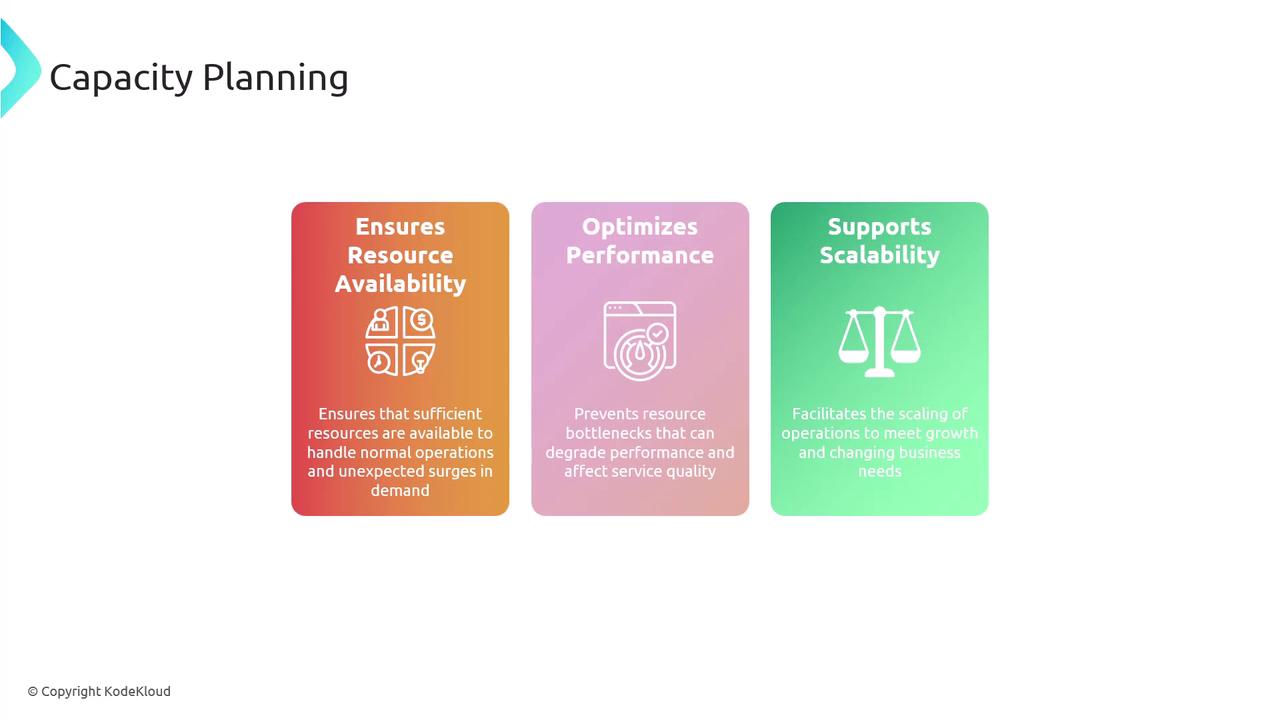
People
Skilled personnel are critical for successful capacity planning. Conduct workforce analyses to assess current staffing levels and identify skill gaps. Implement ongoing training programs to keep team skills up-to-date and aligned with evolving security demands.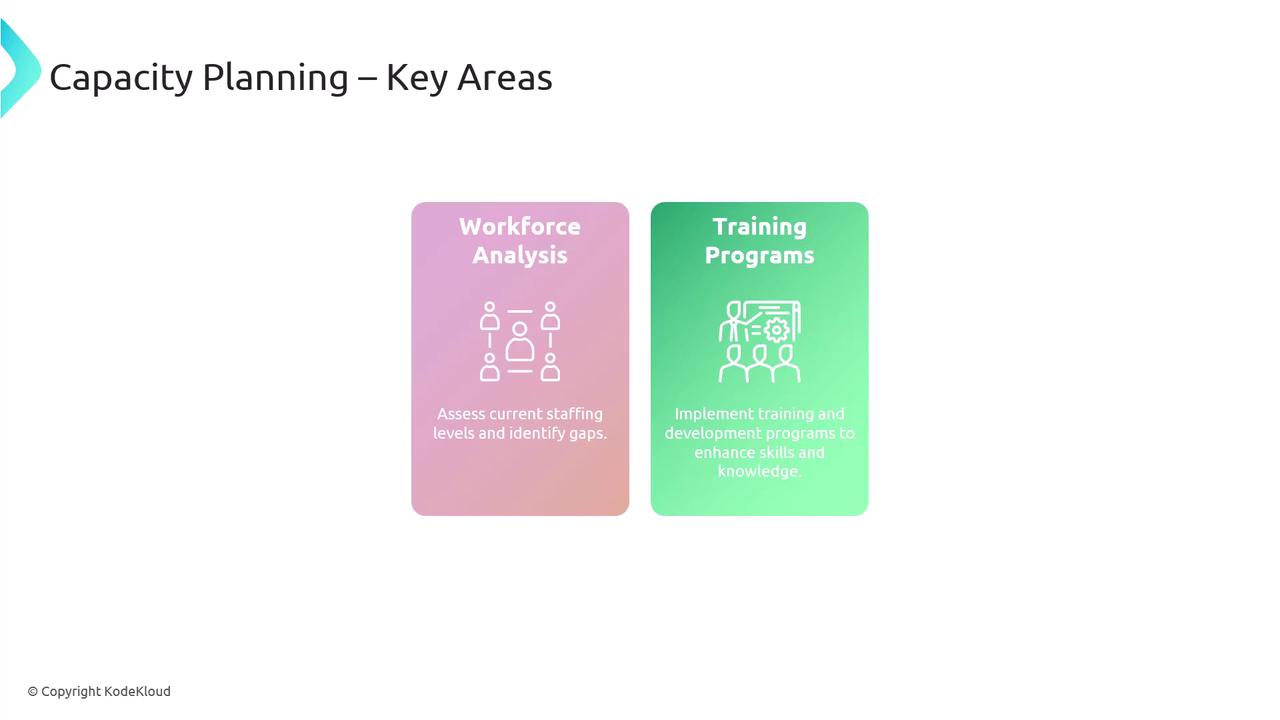
Technology
In the area of technology, capacity planning ensures IT resources such as servers, storage, and network bandwidth are scalable and sufficient. Continuous resource monitoring, forecasting based on historical data, and designing a scalable architecture are pivotal to maintaining high performance.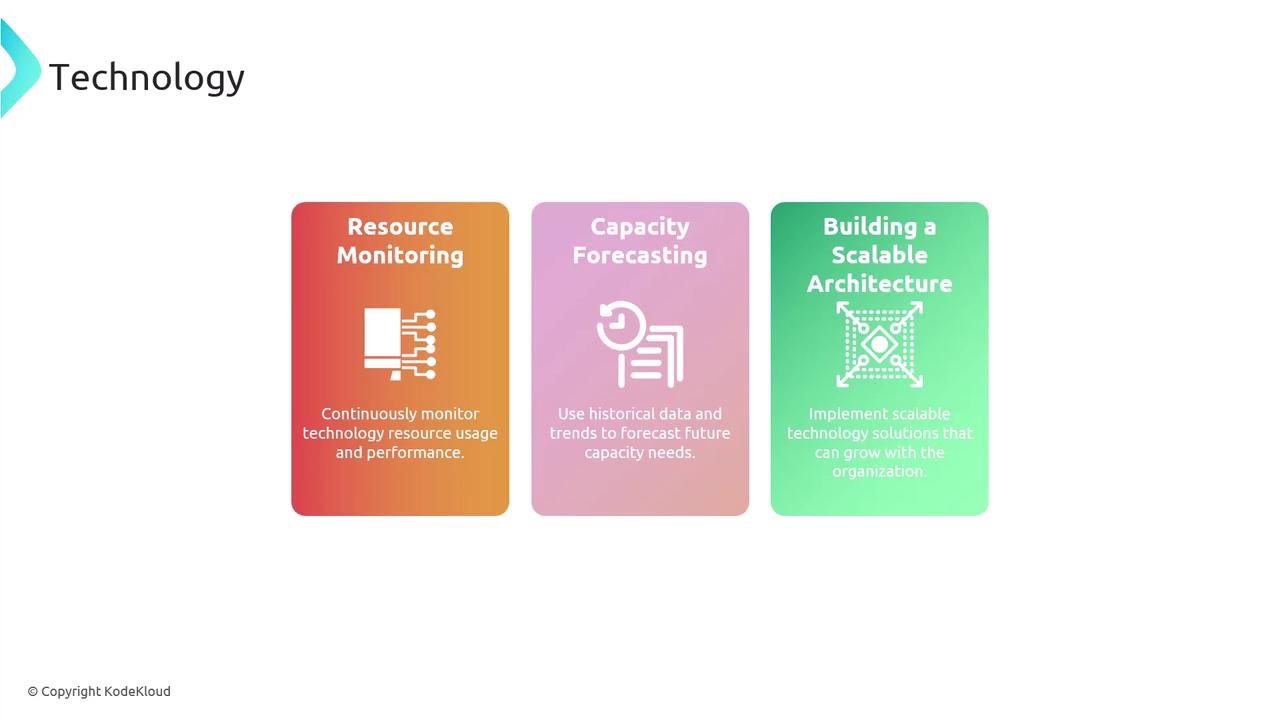
Infrastructure
Infrastructure planning involves ensuring that physical components—like data centers and power supplies—are robust and scalable. Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms to boost resilience and minimize service interruptions. Regular infrastructure assessments help predict future needs and align capacity with operational requirements.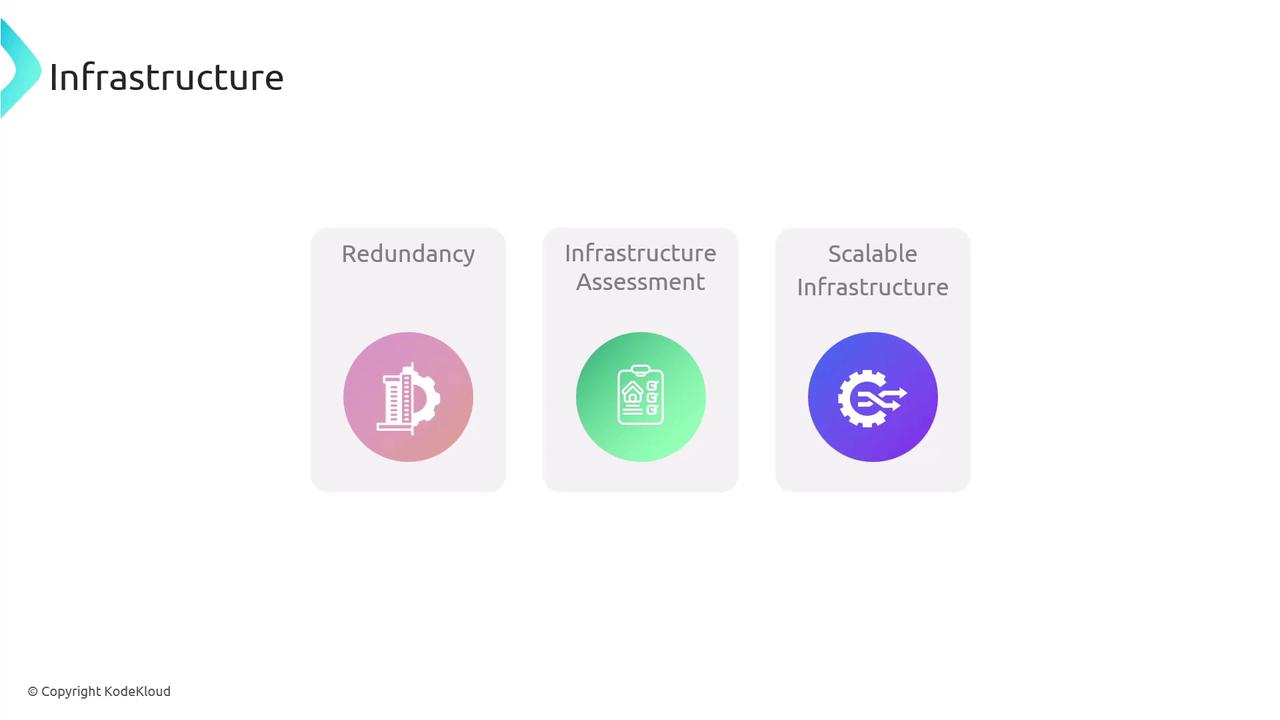
Conclusion
Resilience and recovery are central to a reliable security architecture. By integrating platform diversity, multi-cloud strategies, continuity planning, and comprehensive capacity planning for people, technology, and infrastructure, organizations can effectively withstand disruptions and quickly return to normal operations. This multifaceted approach is key to protecting critical assets, ensuring business continuity, and maintaining trust with customers and stakeholders.