Tunneling
Tunneling involves encapsulating data within another protocol to establish a secure pathway over an unsecured network, such as the internet. Once established, the tunnel ensures that traffic flows securely from one point to another by maintaining:- Confidentiality: Data remains private during transmission.
- Integrity: Data is protected from tampering and unauthorized modifications.
- Authentication: The identities of communicating parties are verified.
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol that secures network communications by ensuring data encryption, authentication, and integrity verification. TLS protects data transmitted between clients and servers using several key mechanisms:- Handshake: The client and server exchange greetings and negotiate encryption parameters.
- Certificate Exchange: The server presents its digital certificate to authenticate its identity.
- Session Keys: Both parties generate temporary session keys used for encrypting data.
- Secure Communication: Encrypted data is transmitted over the secure channel.
TLS plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive online transactions and communications by preventing eavesdropping and data breaches.
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
IPsec is a suite of protocols designed to secure internet communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet in a session. It provides several essential security features:- Encryption: Maintains the confidentiality of IP packets.
- Authentication: Verifies that the source of each packet is legitimate.
- Integrity: Ensures the data has not been altered during transmission.
- Key Exchange: Uses the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol to establish secure channels.
Transport Mode
In Transport Mode, only the payload of the IP packet is encrypted, leaving the IP header intact.
Tunnel Mode
In Tunnel Mode, the entire IP packet — both header and payload — is encrypted, providing a higher level of security, particularly for communications between networks.IPsec is widely used in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to secure data exchanges over the internet.
Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN)
SD-WAN is an advanced network architecture that leverages software-defined networking to manage and optimize wide-area networks efficiently. Its main features include:- Centralized Management: Offers a unified control plane to monitor and manage WAN traffic.
- Dynamic Path Selection: Optimizes traffic routing by choosing the best available paths based on performance metrics and policies.
- Enhanced Security: Integrates encryption, firewalls, and intrusion prevention to safeguard data transmissions.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is a transformative network architecture that combines wide area networking with comprehensive network security services delivered as a cloud service. The main pillars of SASE include:- Converged Networking and Security: Merges SD-WAN with security solutions such as secure web gateways, Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB), and Zero Trust network access.
- Cloud-Native Architecture: Offers scalability and flexibility by leveraging cloud delivery models.
- Unified Policy Management: Centralizes the management of security policies across all endpoints and locations.

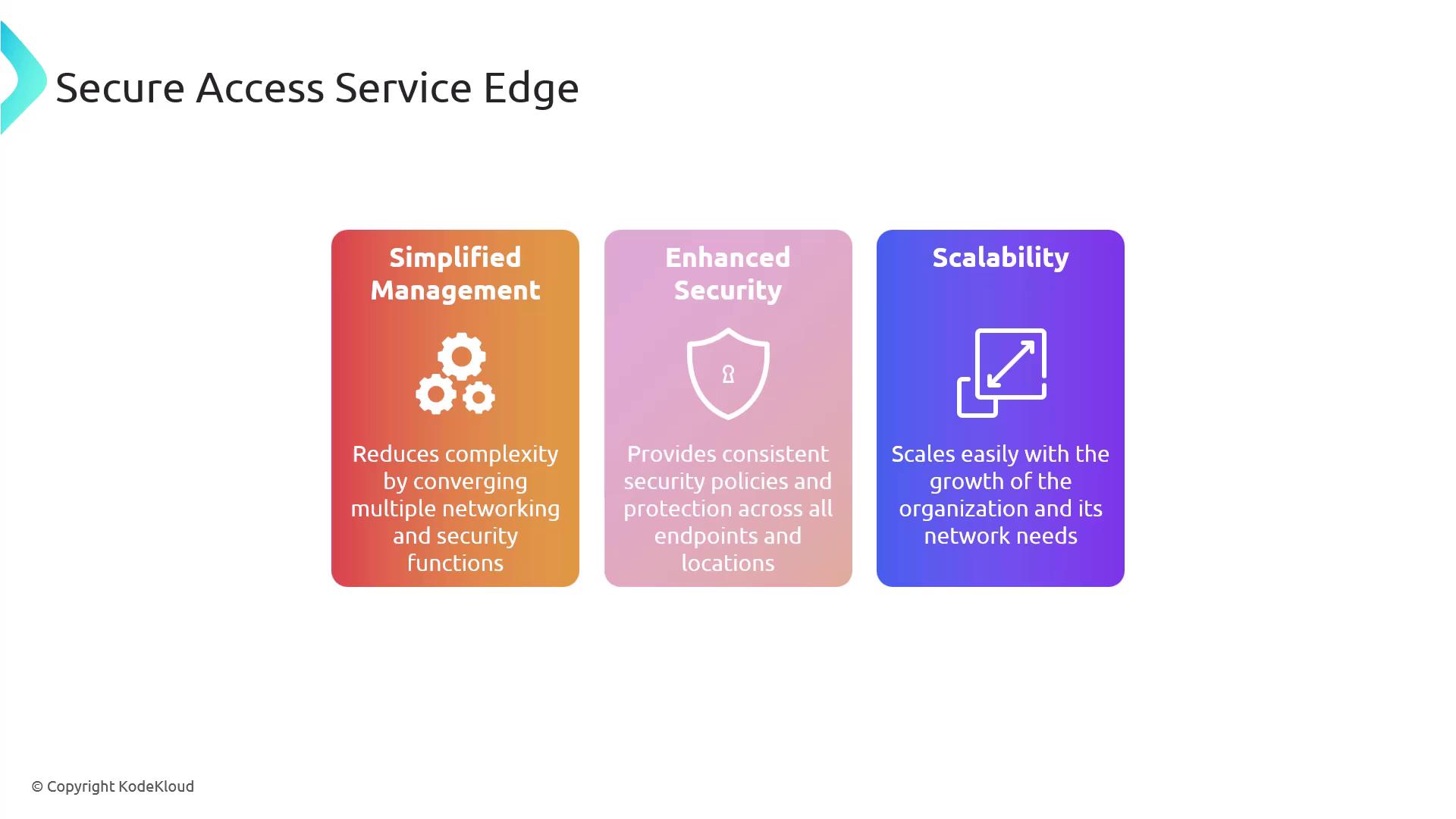
SASE represents the future of network security by reducing complexity and providing consistent protection across dynamic and dispersed environments.
Conclusion
In summary, secure communication and access form the backbone of an effective cybersecurity strategy. By implementing robust tunneling protocols like TLS and IPsec, leveraging SD-WAN for efficient and secure network management, and embracing SASE for a converged and scalable security approach, organizations can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data. These technologies equip enterprises with the tools needed to combat modern cyber threats and facilitate secure, reliable communication.