- Kubernetes Cinder
- A plugin for OpenStack (for environments using OpenShift with OpenStack)
- AWS Elastic Block Storage
- Azure Disk and Azure File
- Google’s Persistent Disk
- vSphere
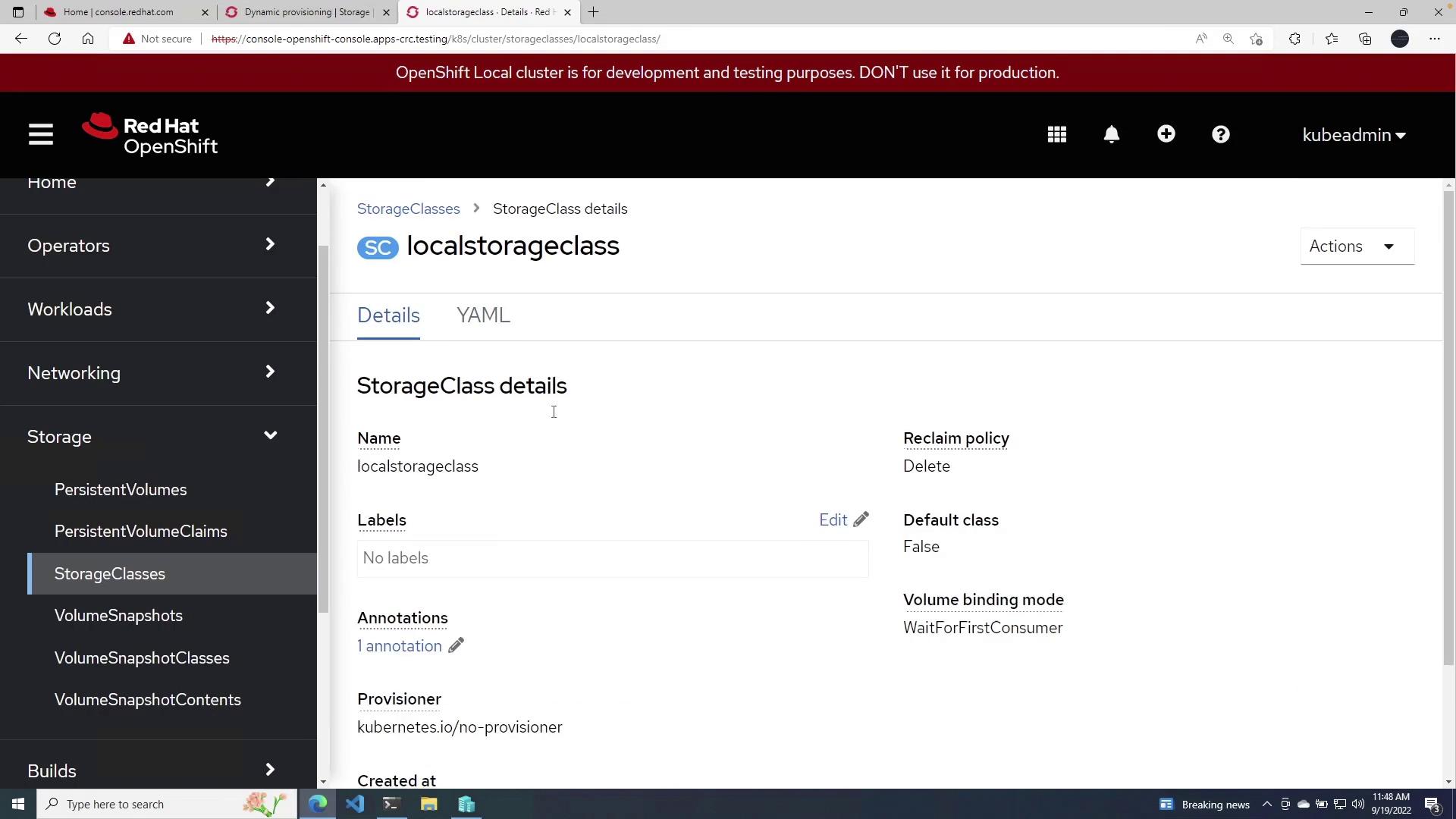
Creating a Storage Class
- In the OpenShift console, navigate to Storage and click on Storage Classes.
- If an existing storage class is present, delete it to start with a clean slate.
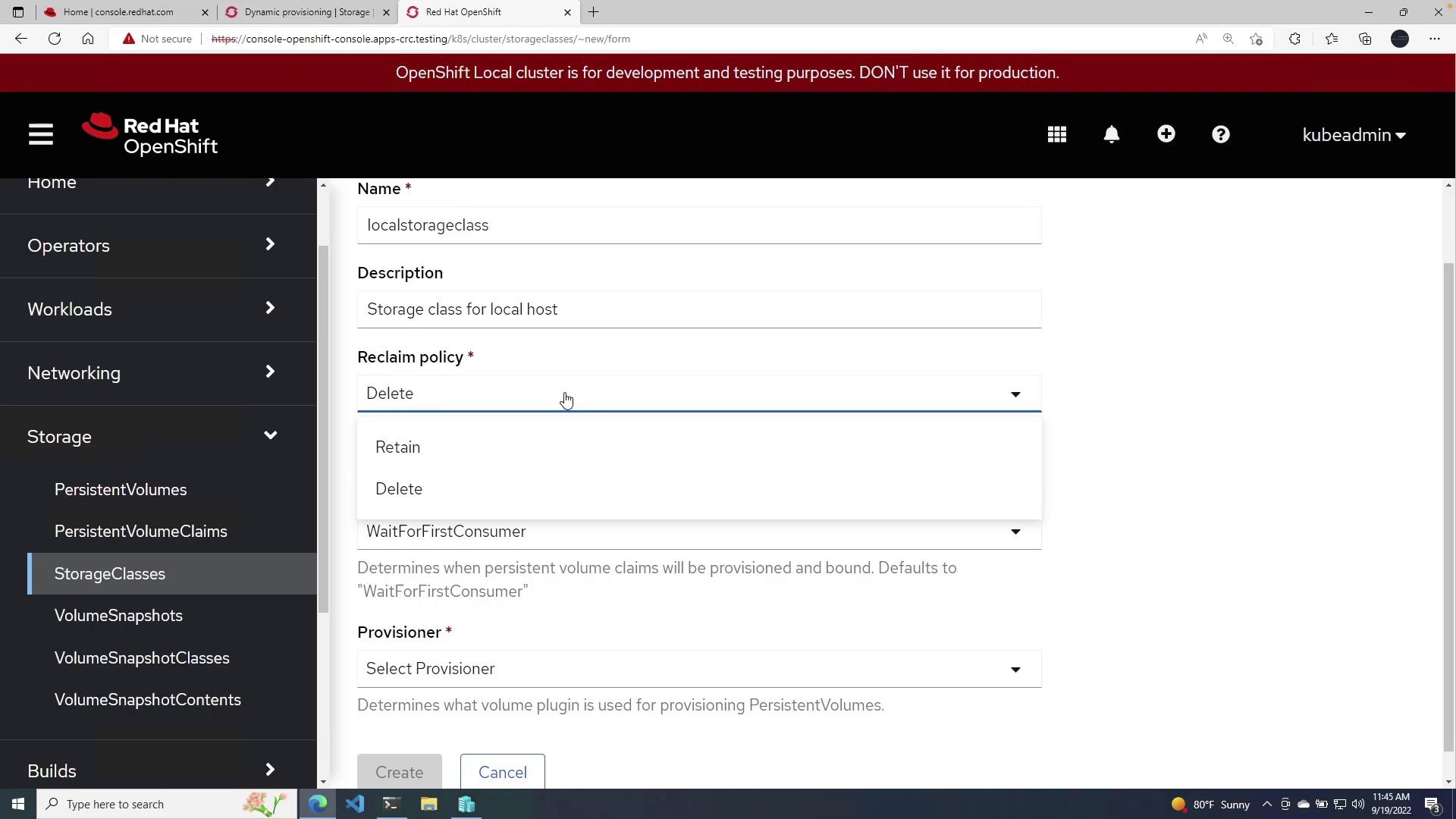
- Click the blue Create Storage Class button.
- Name: local Storage Class
- Description: Storage class for local host
- Reclaim Policy: Select an option to either retain or delete the data when the Persistent Volume (PV) is removed. For this demo, choose delete.
- Volume Binding Mode: Choose one of the following options:
- Immediate: Binds the volume as soon as the claim is created.
- Wait for first consumer: Delays binding until a pod is scheduled to a node with available storage. This is recommended for ensuring the volume is provisioned on a node that meets resource requirements.
Creating a Persistent Volume Claim
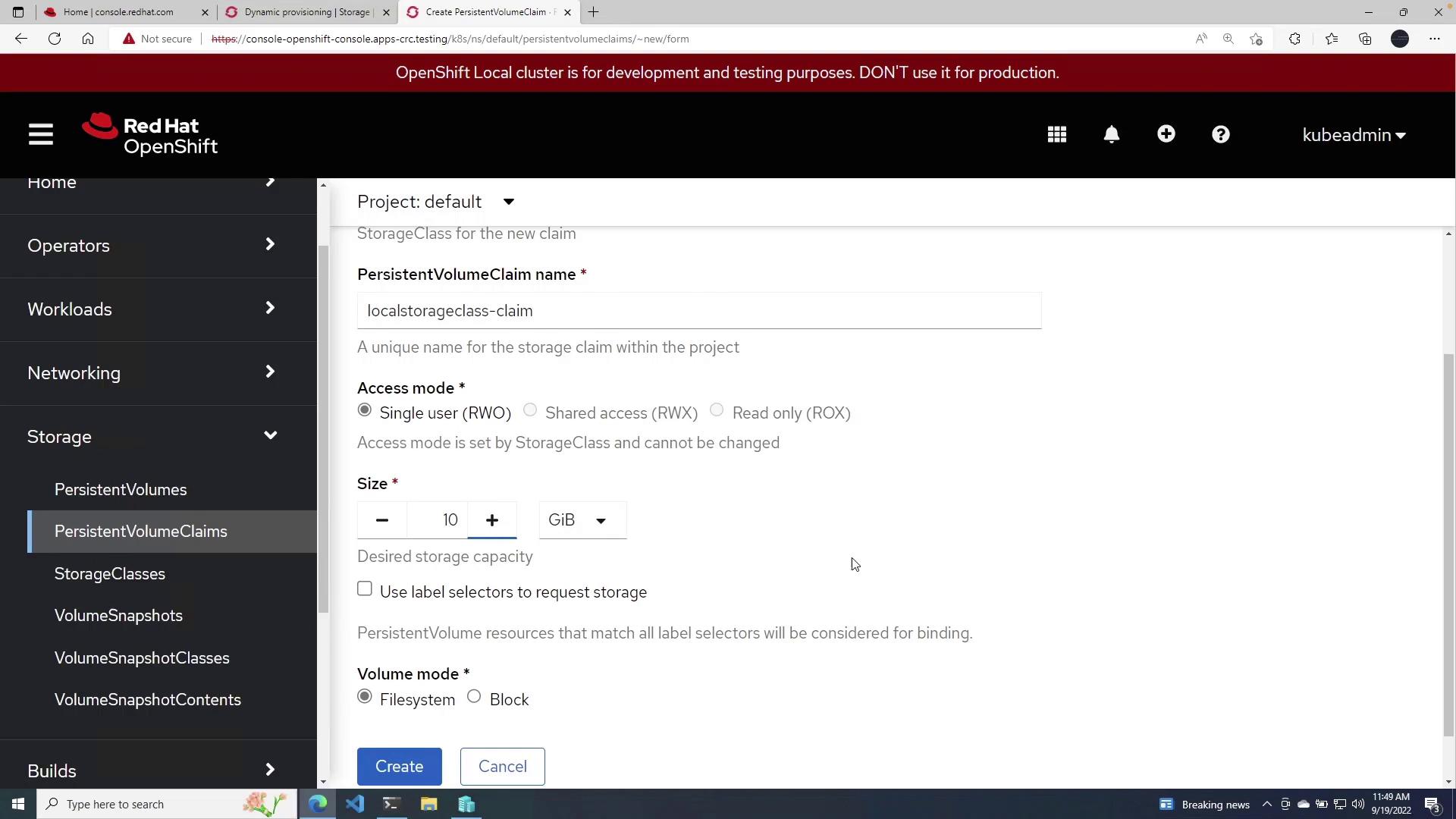
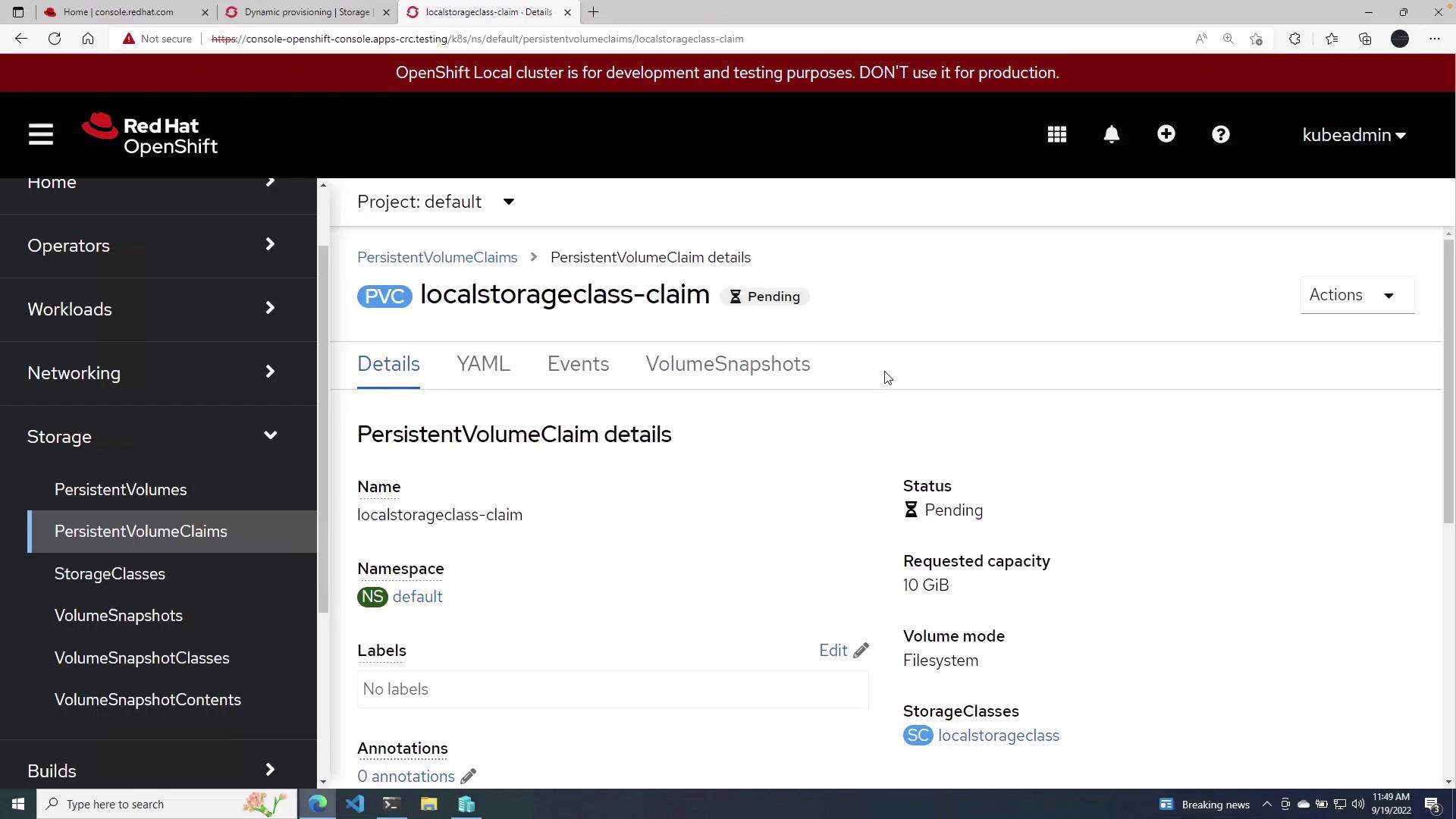
To utilize your newly created Storage Class, create a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) by following these steps:- Navigate to Persistent Volume Claims in the OpenShift console.
- Click the blue Create Persistent Volume Claim button.
- From the Storage Class dropdown list, select
local Storage Class. - Provide a name for your claim (e.g., local Storage Class Claim).
- Set the access mode to ReadWriteOnce for single user access.
- Specify the claim size; for this demo, enter 10 GiB.
- Keep the volume mode as File System unless block storage is required.
- Click Create to complete the process.
Remember to adjust configurations based on your specific environment and storage requirements.