Model Selection and Cost Considerations
When choosing a foundation model, it is crucial to balance cost, accuracy, latency, and precision. Consider these important questions:- Was the model pre-trained on a massive third-party dataset?
- What are the cost implications associated with using this model?
- How do its accuracy and inference speed compare when pitted against simpler alternatives?

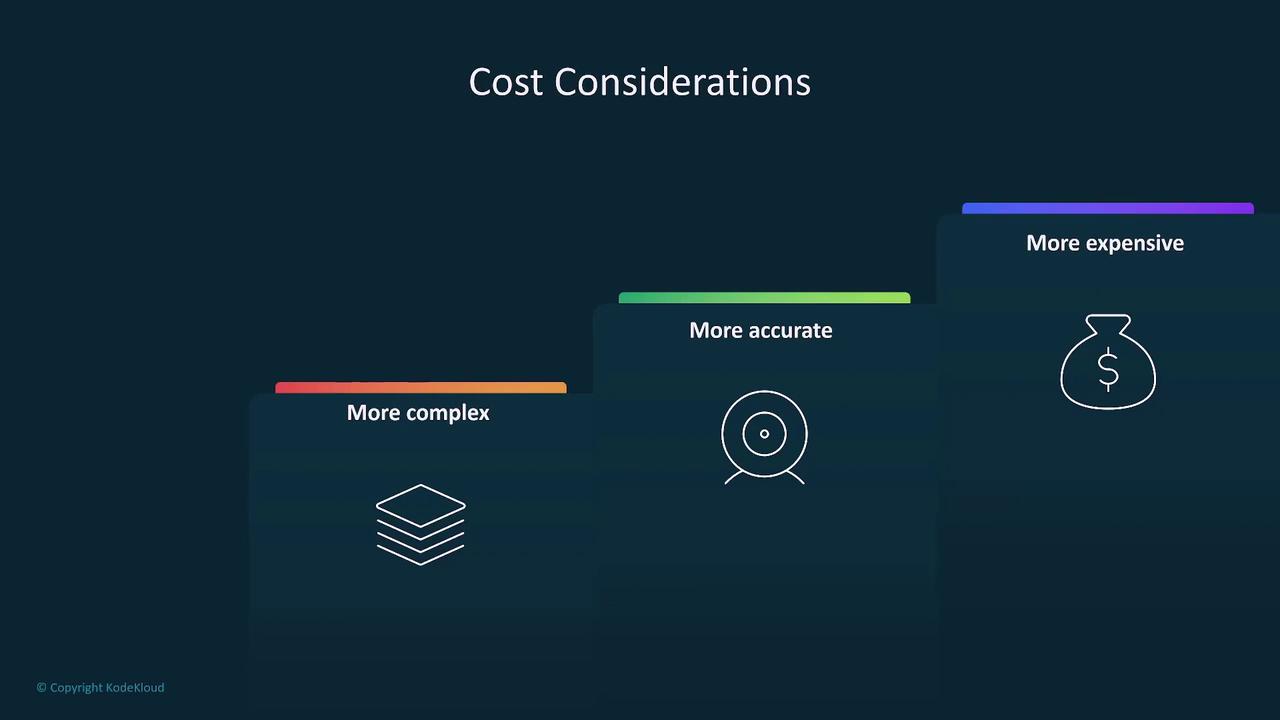
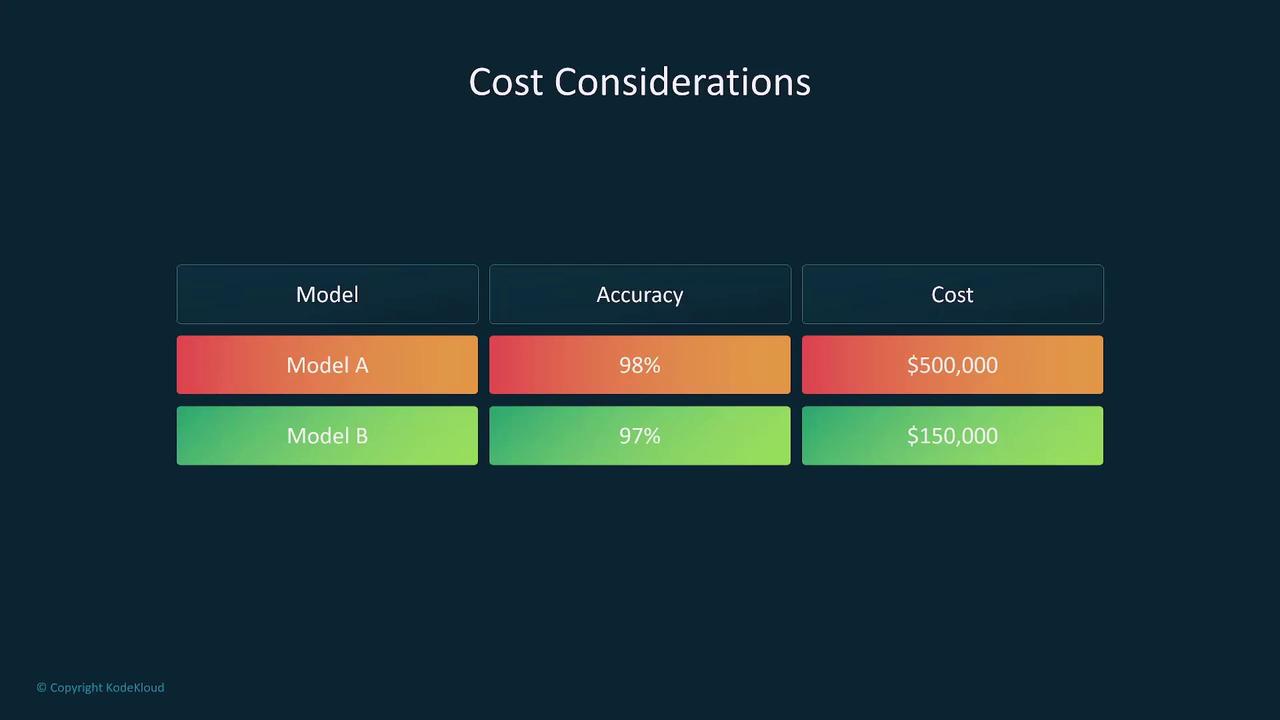
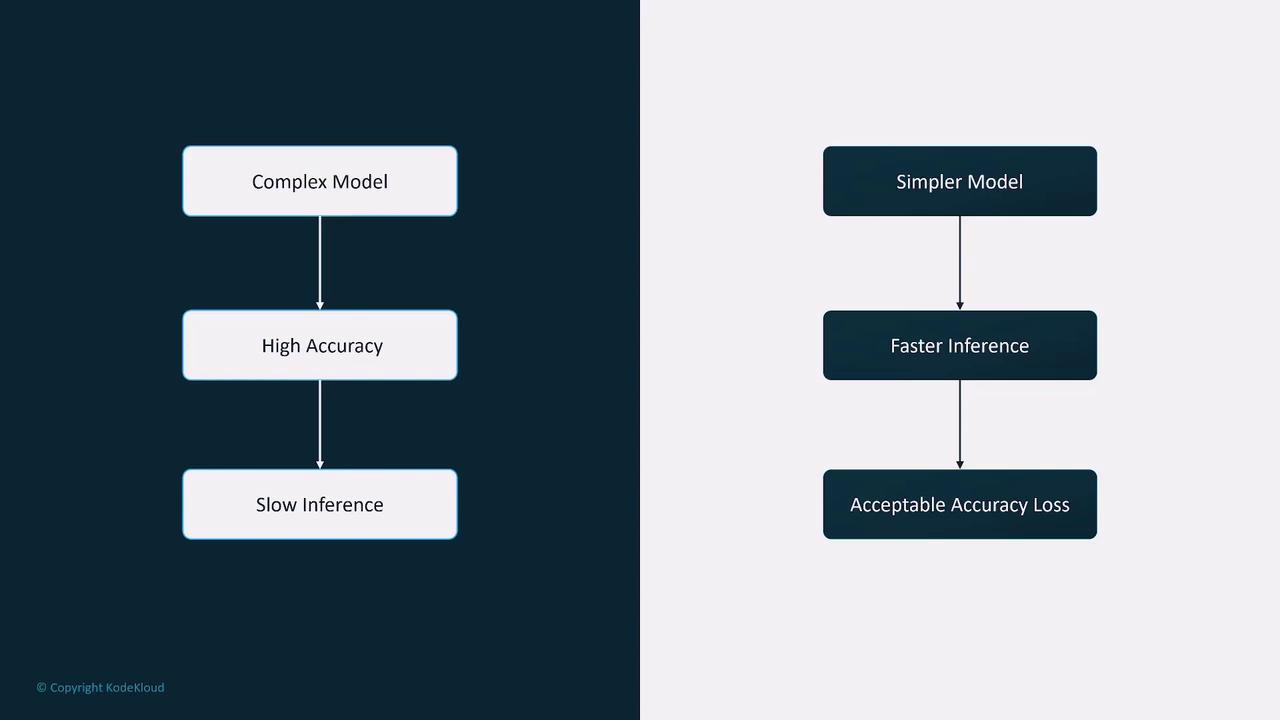
Model Complexity and Inference
A practical example is the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) model used in self-driving vehicle systems. KNN models perform most of their computations during inference, making them computationally intensive. This characteristic renders them less ideal for real-time decision-making in high-dimensional scenarios. In these cases, opting for a more complex model may be necessary to balance inference speed with overall complexity.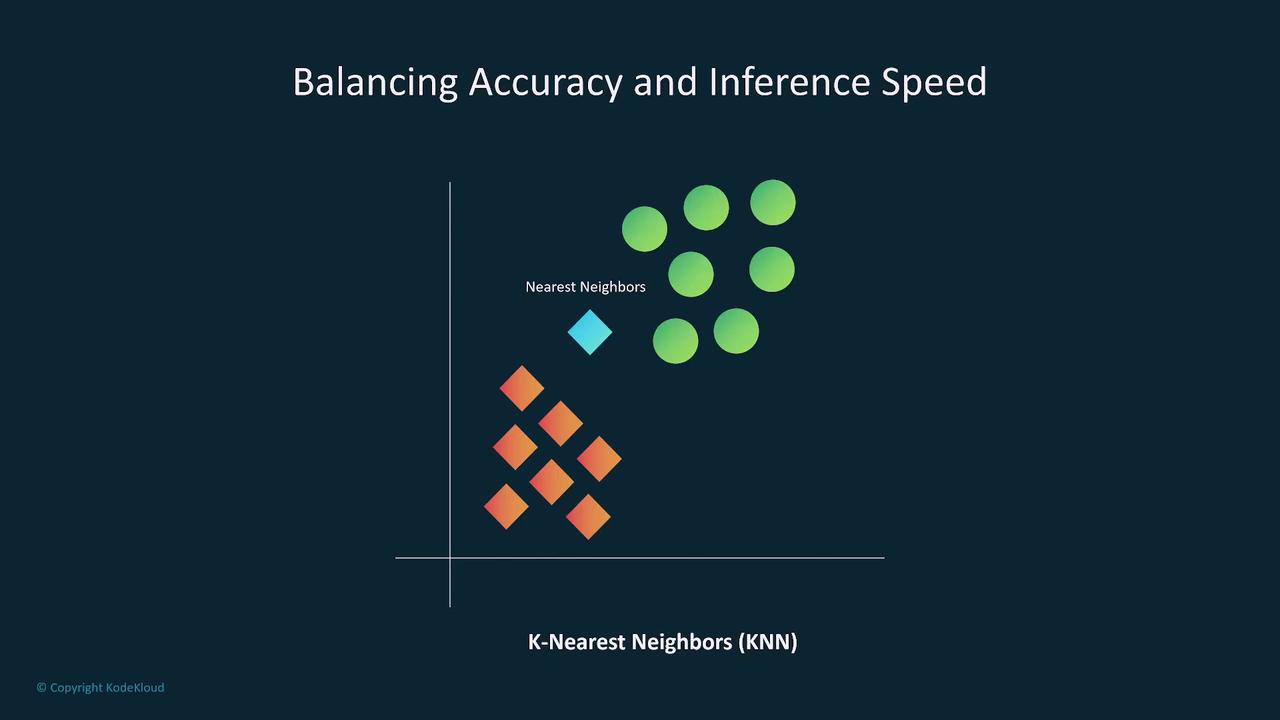
Modality and Data Input Considerations
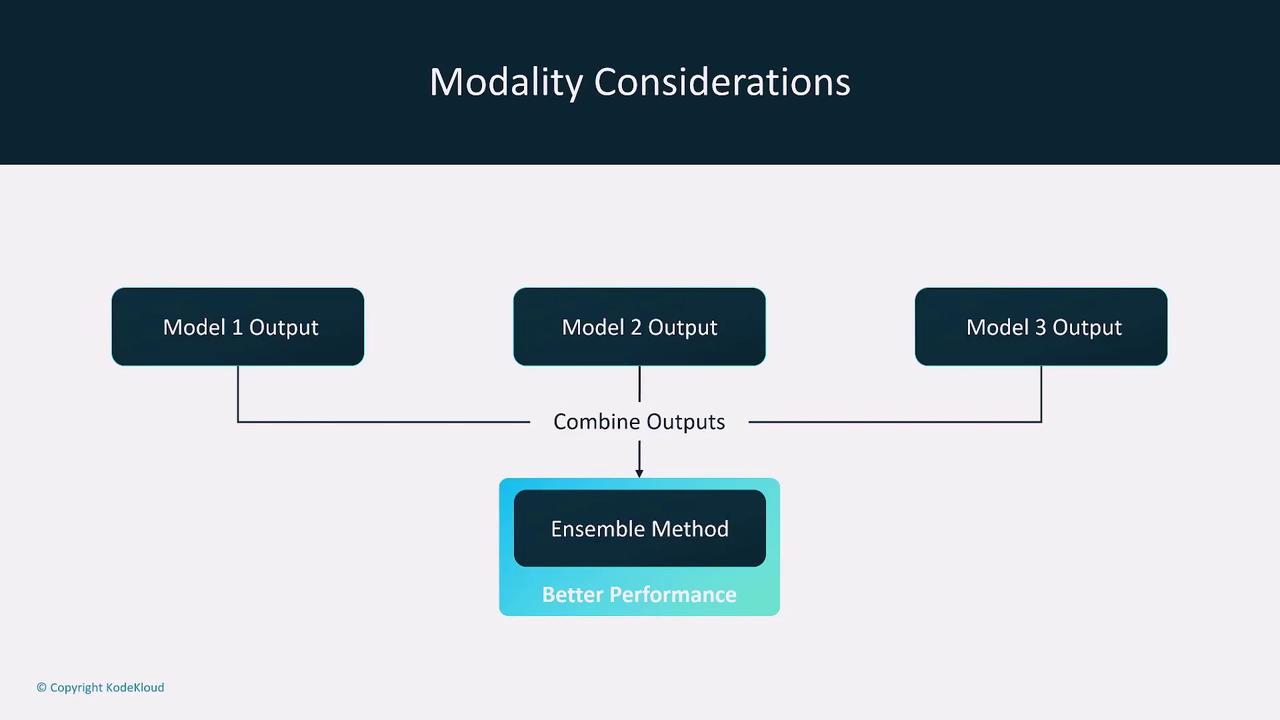
Modality refers to the type of input data a model can handle, such as text, images, and audio. While many simpler models are limited to one or two types of data, multimodal models can process multiple inputs concurrently. If you are dealing with single-input models, consider using ensemble methods to combine the outputs of several specialized models.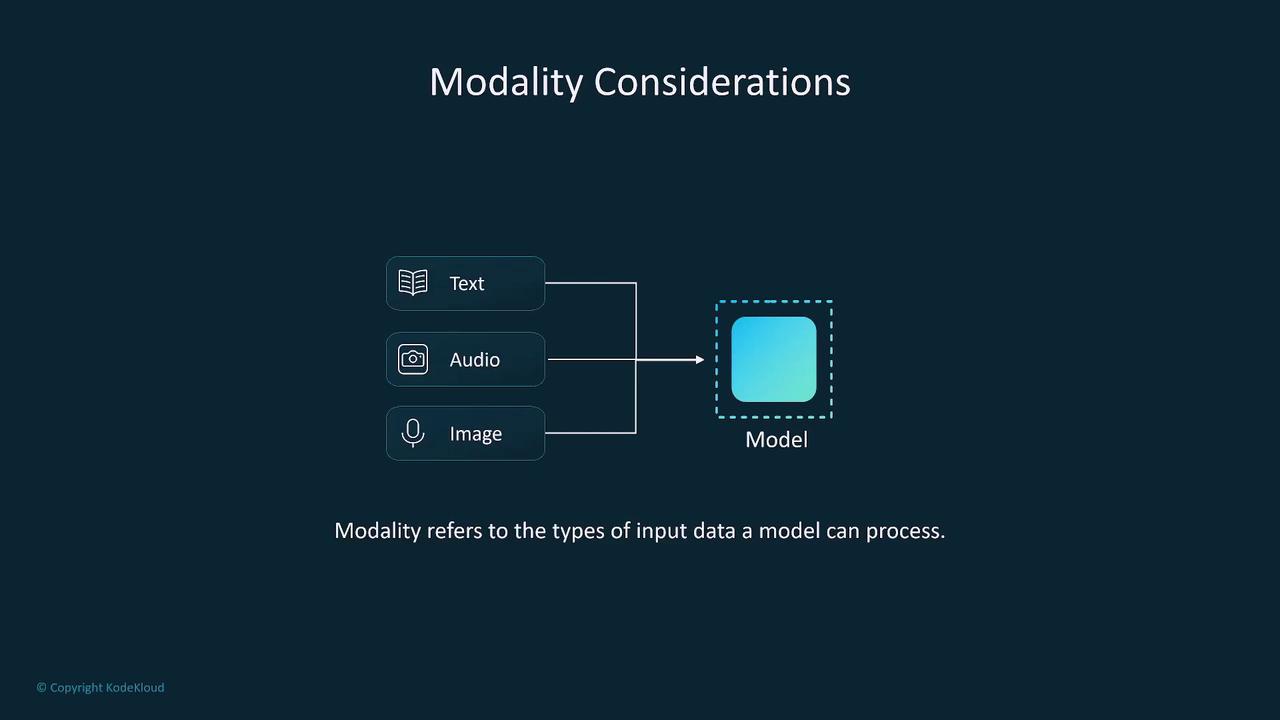

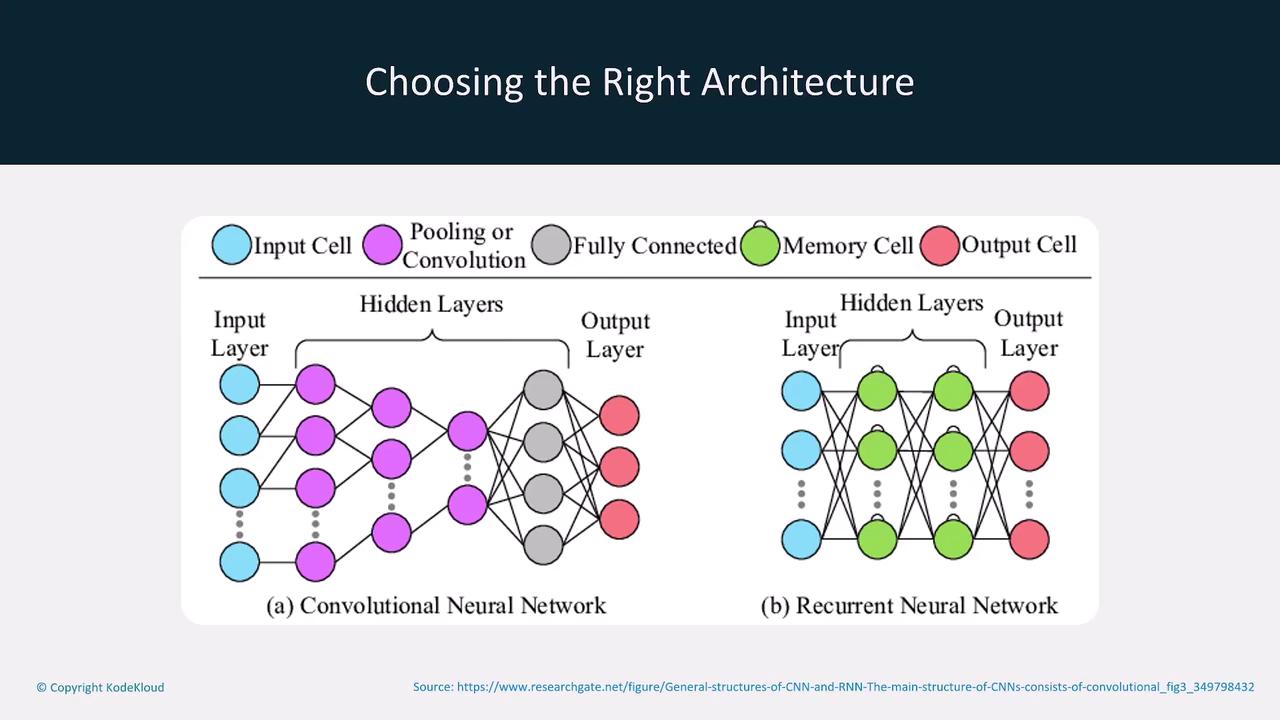
Choosing the Right Model Architecture
Different tasks require specific model architectures. For example:- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Ideal for image recognition tasks.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Better suited for natural language processing (NLP).
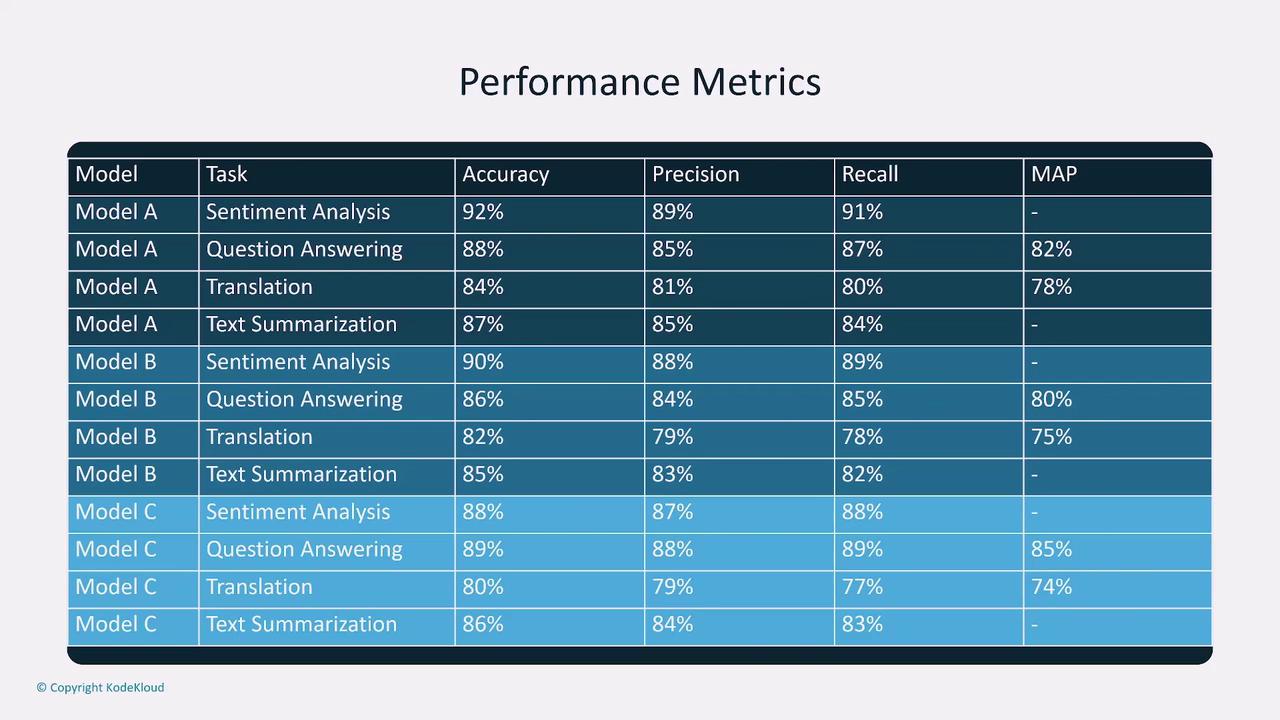
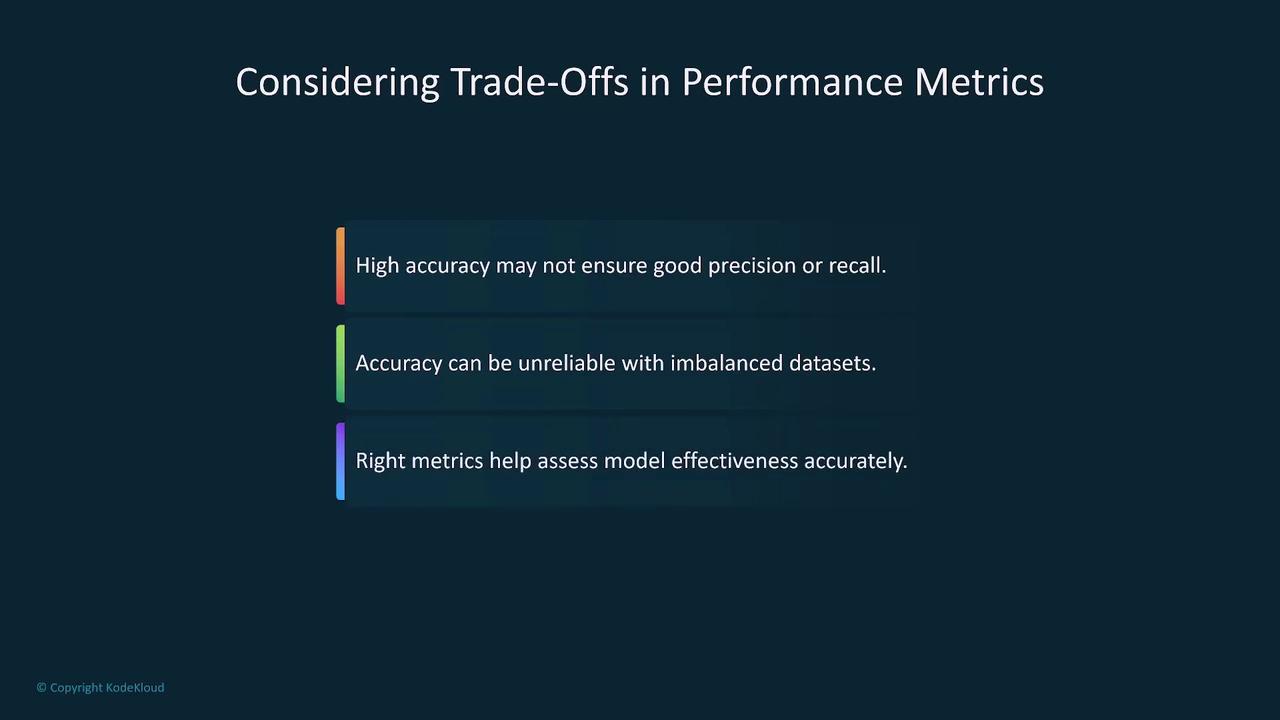
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics are critical for evaluating model effectiveness. Some key metrics include:- Accuracy: How often the model makes correct predictions.
- Precision: The quality of positive predictions, measured as the proportion of true positives among all positive predictions.
- Recall: The model’s ability to capture all relevant instances.
- F1 Score: The harmonic mean of precision and recall, especially useful for imbalanced datasets.
Customizing Models
Customization can be achieved through different approaches:- Fine-Tuning: Minor adjustments such as adding system prompts or exposing the model to new data without retraining entirely.
- Full Retraining: Offers complete control and specialization, but with higher costs and longer training durations.


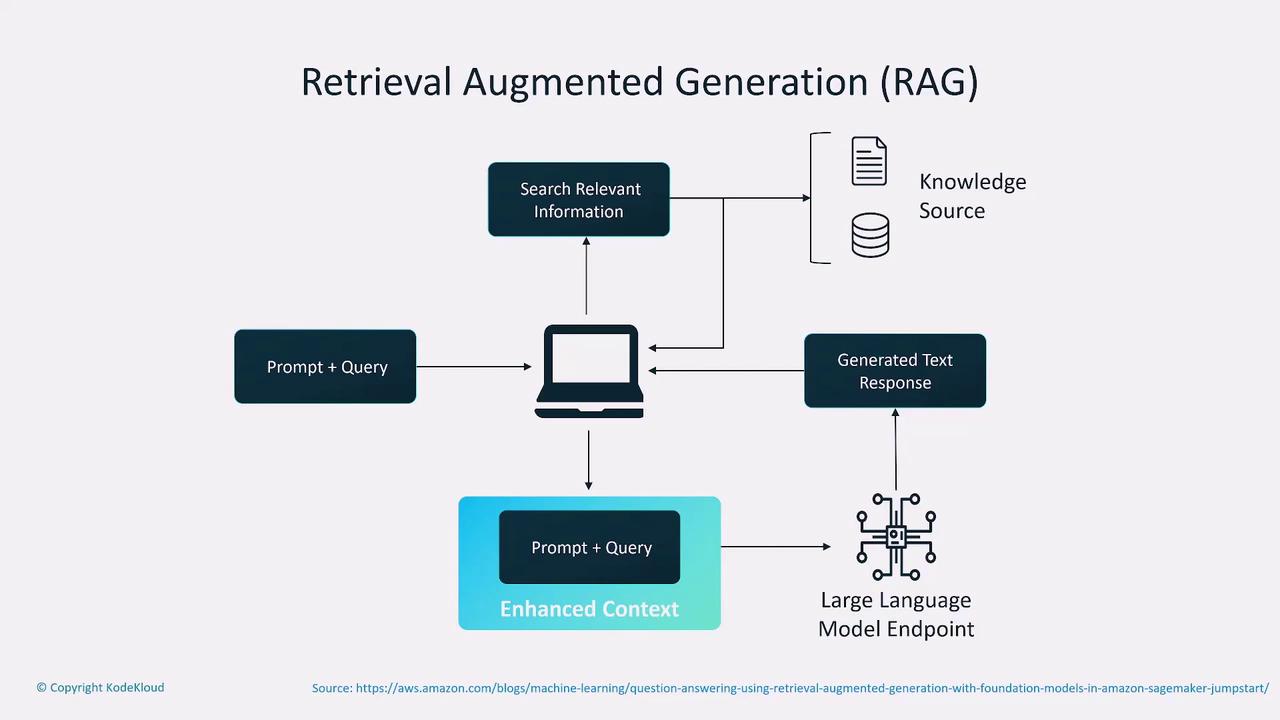
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances model responses by retrieving additional, relevant documents during the query process. This technique merges retrieval-based methods with generative models, thereby improving the quality of answers in customer-facing applications. The process involves:- Receiving a prompt.
- Retrieving pertinent data from a knowledge base.
- Combining this information with the initial query.
- Sending the enriched prompt to a large language model to generate the final response.
Storing Embeddings in Vector Databases
Embeddings are numerical representations of tokens derived from input queries. Storing these embeddings in vector databases enables efficient semantic retrieval—especially useful when managing large, predefined knowledge bases. Options for vector databases include:| Database Technology | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|
| DocumentDB | Document-oriented storage and querying | Use for structured documents |
| Neptune | Graph database to capture relationships | Ideal for connected data |
| RDS with Postgres | Traditional relational database | General-purpose applications |
| Aurora with Postgres | Scalable, managed relational database | High performance, scalable |
| OpenSearch | Search engine with vector support | Semantic search and retrieval |

Conclusion
Balancing cost, latency, and model complexity is paramount when designing AI solutions with foundation models. By carefully evaluating performance metrics, customizing models appropriately, and employing techniques like RAG and vector databases, you can tailor your solution to meet specific business objectives with efficiency and precision.For more insights and detailed documentation on model evaluation and deployment best practices, explore our MLOps Guidelines.