What Is a Prompt?
A prompt is the input provided by the user that defines the task a model should perform. For instance, you might say, “I would like to understand all the ins and outs of Kubernetes,” or “I want to excel in my exam performance.” This input specifies the task and guides the model’s actions. It can include context, sample outputs, and specific instructions to enhance clarity.

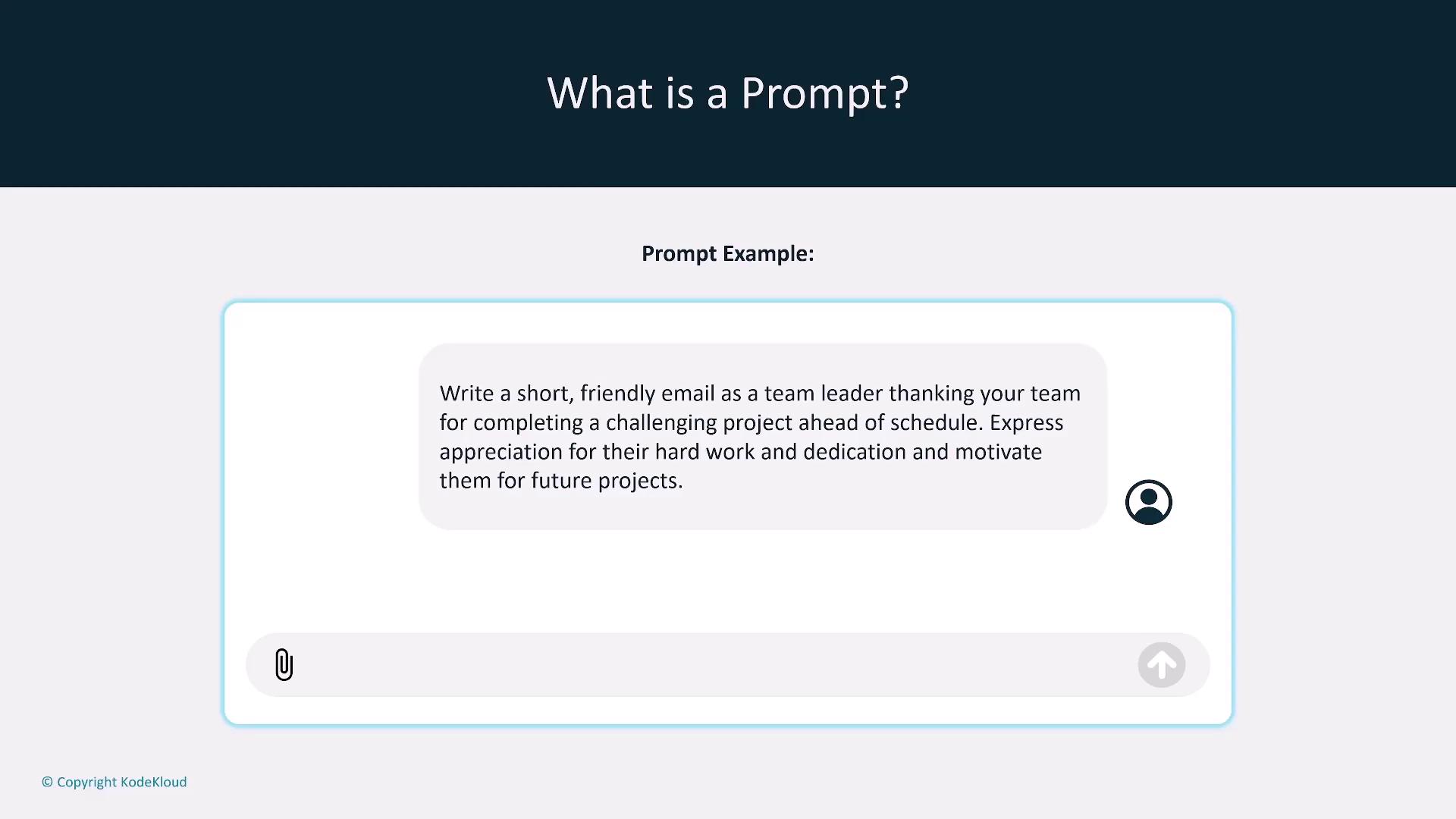
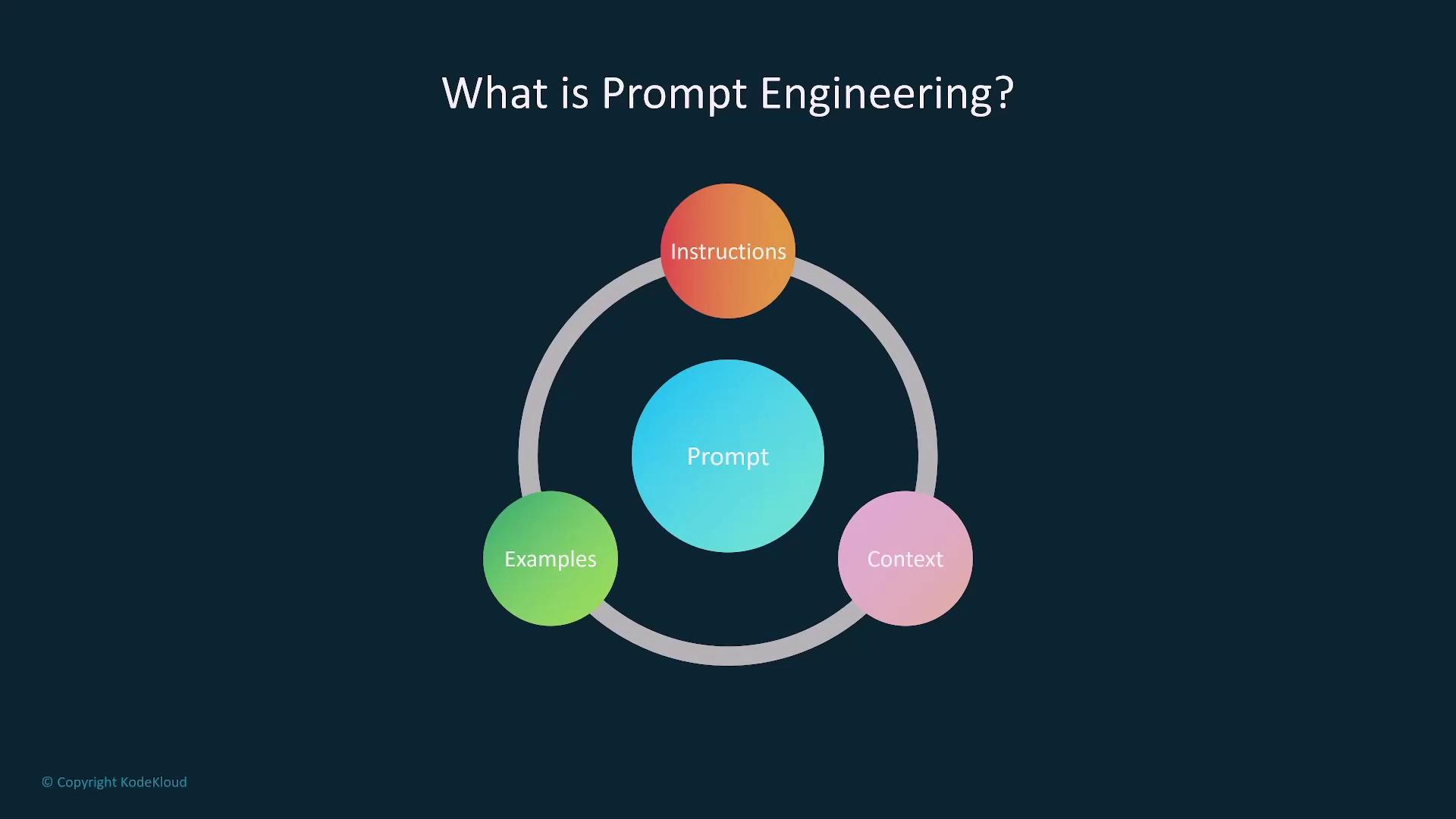
Crafting the Perfect Prompt
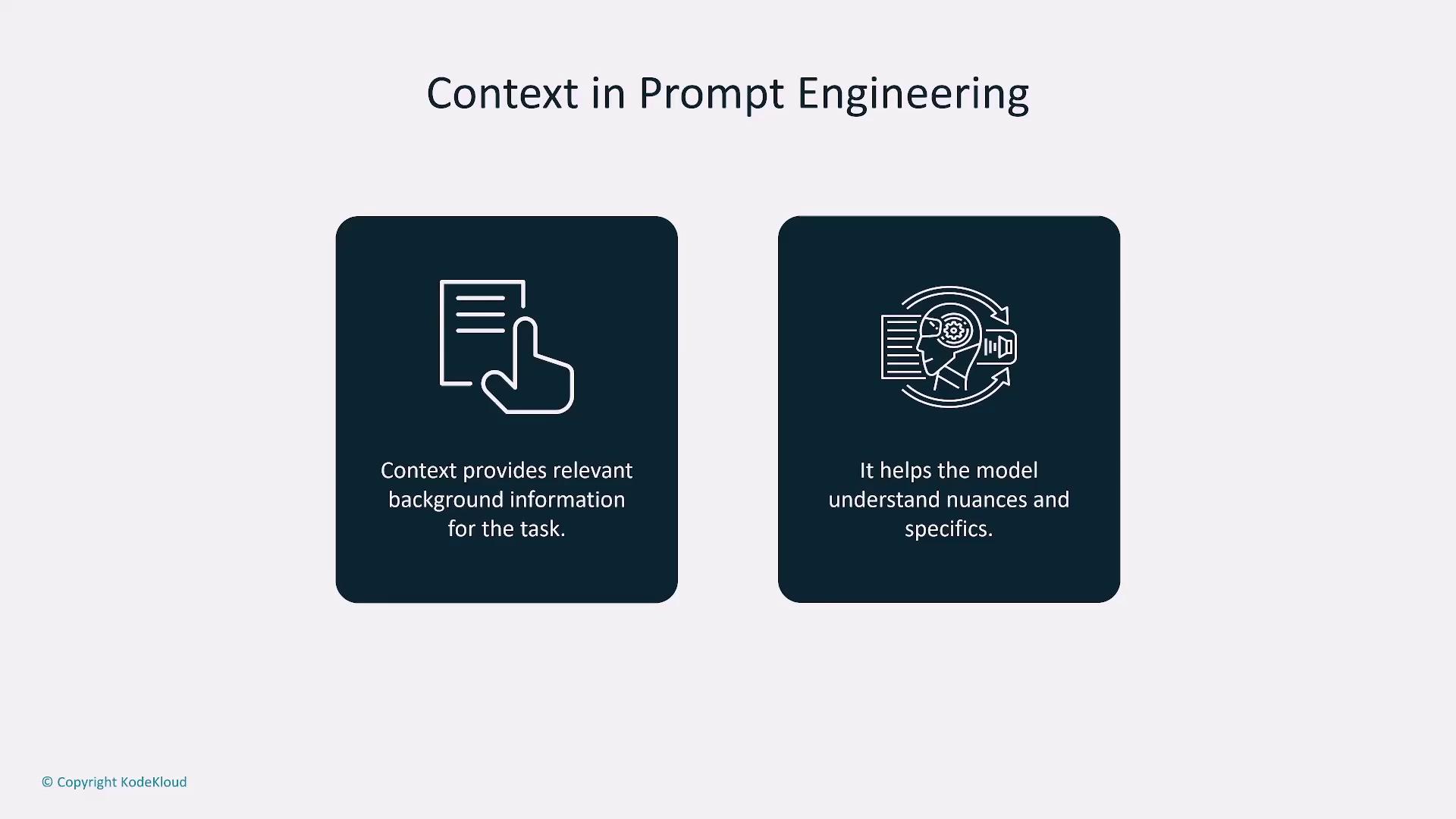
When designing a prompt, consider incorporating the following elements to optimize model performance:- Context:
Provide background and specific instructions to clarify the expected outcome. For example, if crafting a motivational speech prompt for new employees, include details about the audience, experience level, and desired tone.

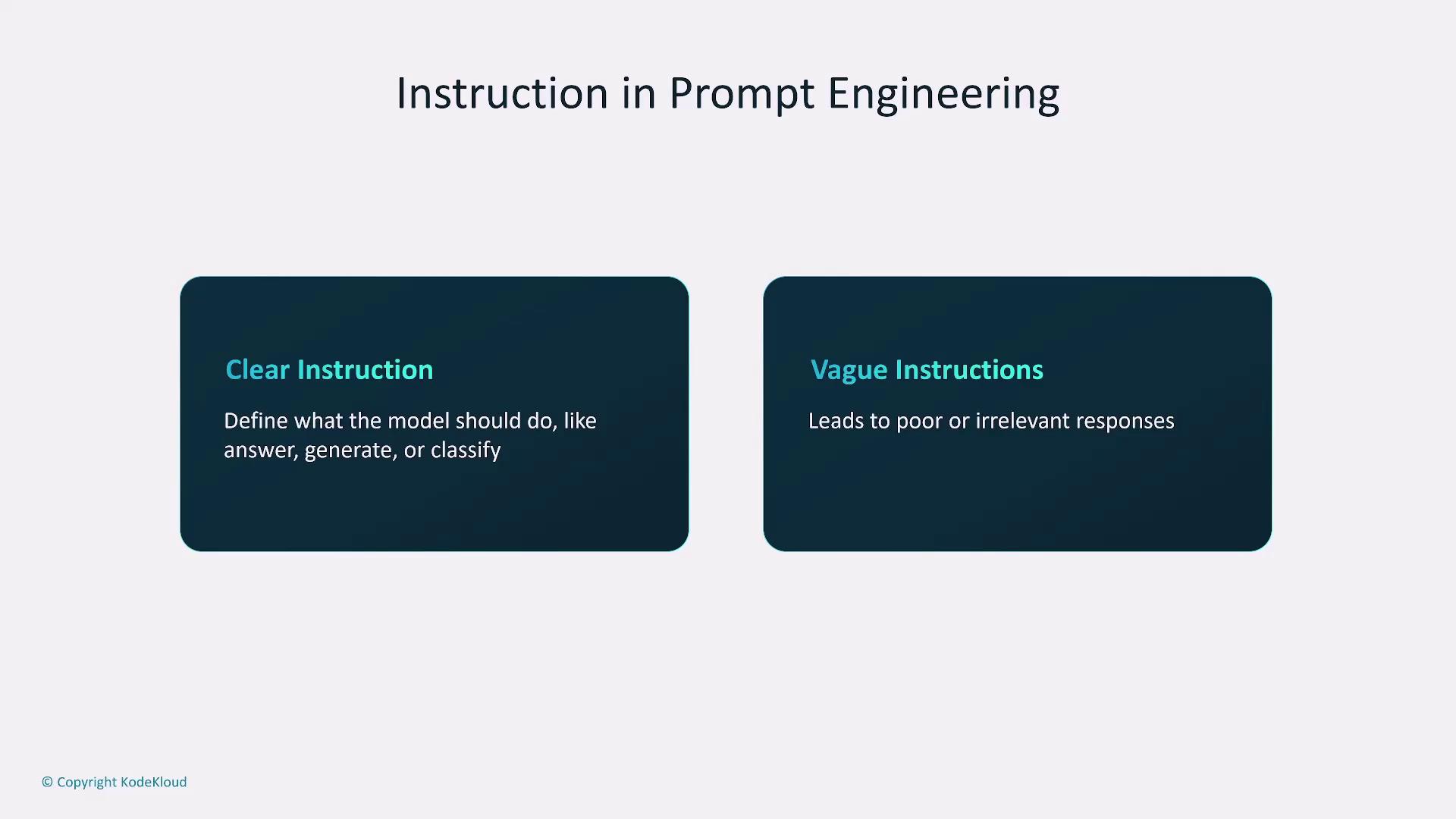
- Instruction:
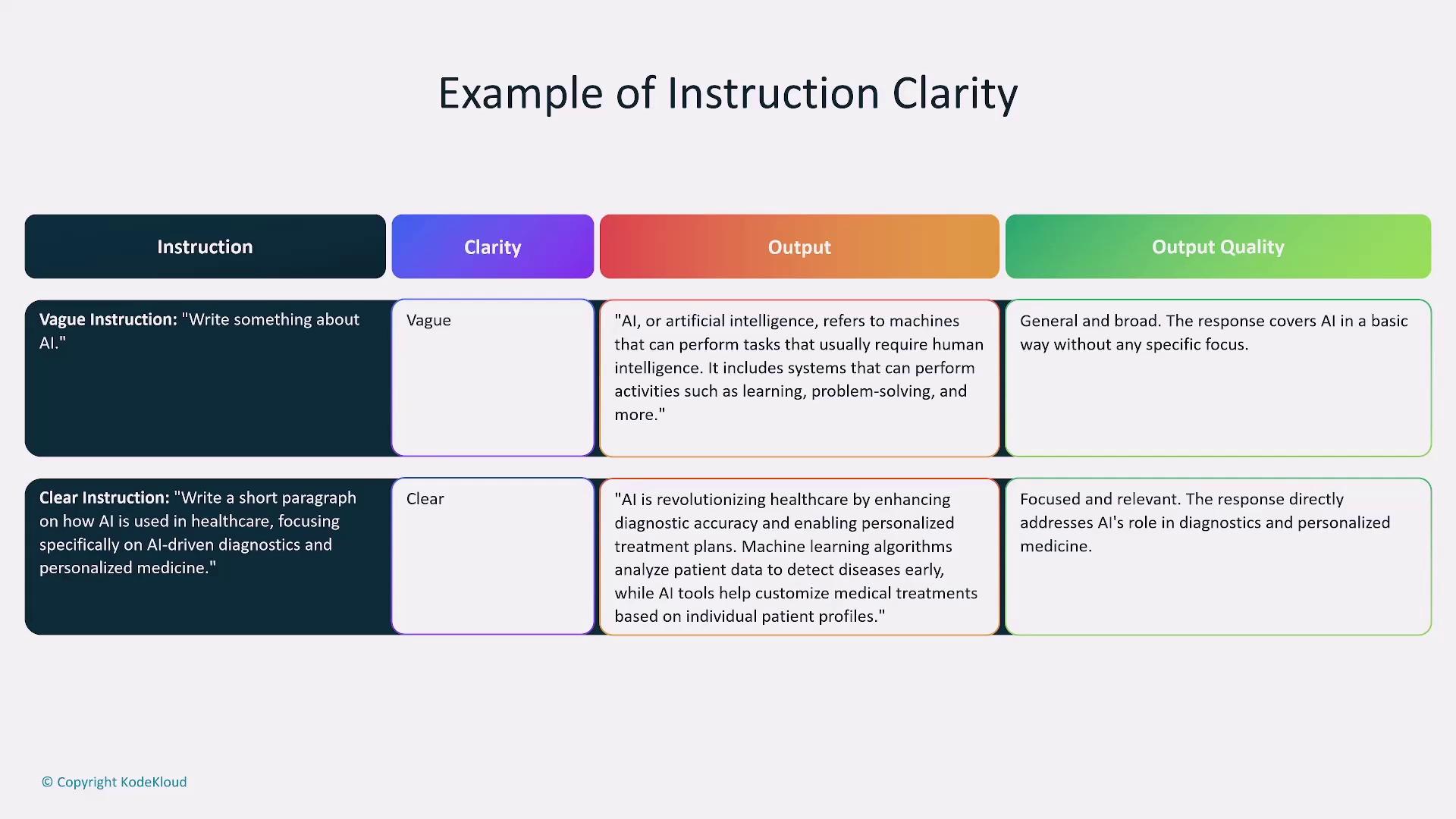
Be precise about what you need. Instead of using a vague prompt like “Write something about AI,” specify “Write a short paragraph about how AI is transforming healthcare with a focus on data analytics.” Clear instructions help reduce ambiguity and guide the model effectively.
- Negative Prompts:
Clearly specify what should be avoided. For example, when writing a product description for a smartwatch, instruct the model to focus on key features like heart rate monitoring, GPS, and battery life—but to avoid details about packaging history or brand backstory.

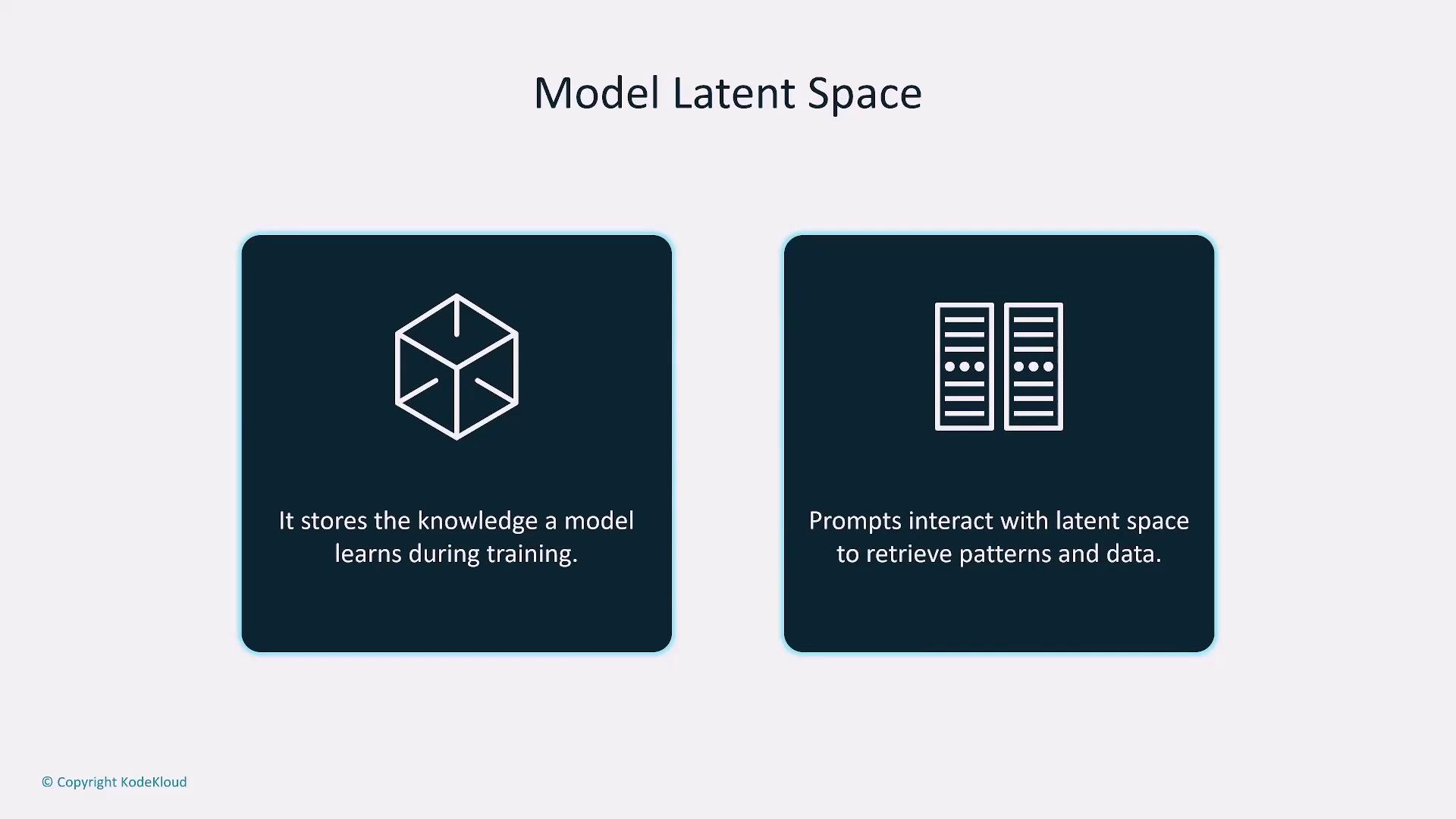
- Latent Space Considerations:
A model’s latent space represents its internal understanding based on training data. Effective prompt design guides the model to retrieve information within this latent space. It is important to note that asking for information beyond a model’s training data (such as recent events post cutoff date) may result in inaccurate or hallucinated responses.
Prompting Techniques
Several prompting techniques can optimize your interaction with AI models:Zero-Shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting involves providing only the instruction without examples. For instance, a prompt like “Write a short poem about the ocean” relies solely on the model’s pre-existing knowledge.One-Shot and Few-Shot Prompting
One-shot prompting includes a single example alongside the instruction, while few-shot prompting incorporates multiple examples. These approaches act as in-context training, enabling the model to better understand the desired output by examining a set of examples.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Chain-of-thought prompting encourages the model to break down its reasoning into clear, logical steps before providing the final answer. This method is particularly effective for solving complex math problems or decision-making tasks, as it enhances both transparency and coherence.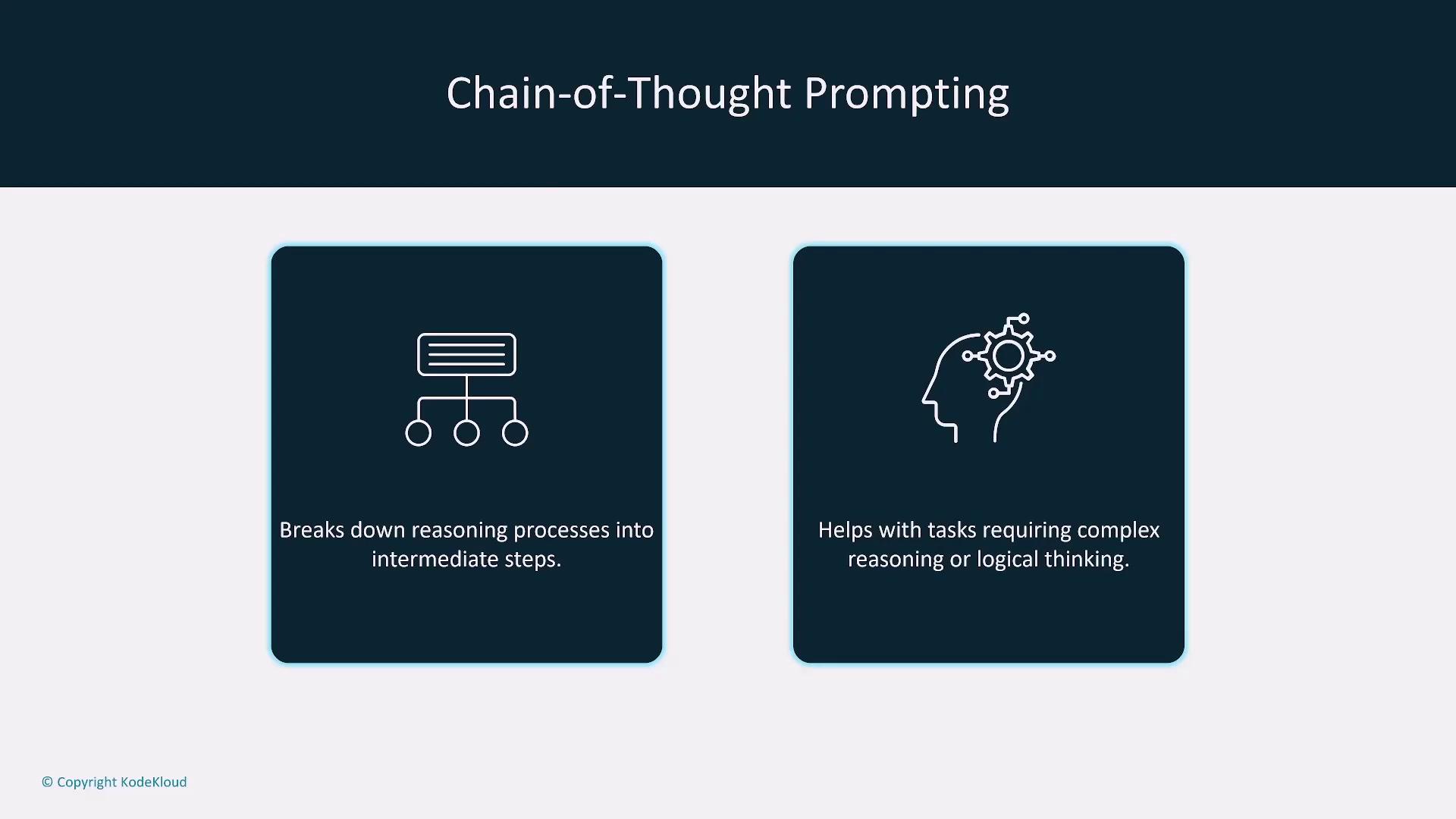

Prompt Templates
Reusable prompt templates help maintain consistency and efficiency across similar tasks. Whether you are generating exam questions, structuring documents, or providing code examples, a standardized template expedites the process and supports collaborative improvements.Prompt Tuning
Prompt tuning is the process of optimizing the prompt itself during training without modifying the main model parameters. This technique allows you to fine-tune instructions for specific tasks—similar to using a specialized system prompt—ensuring the model’s outputs are more closely aligned with your requirements.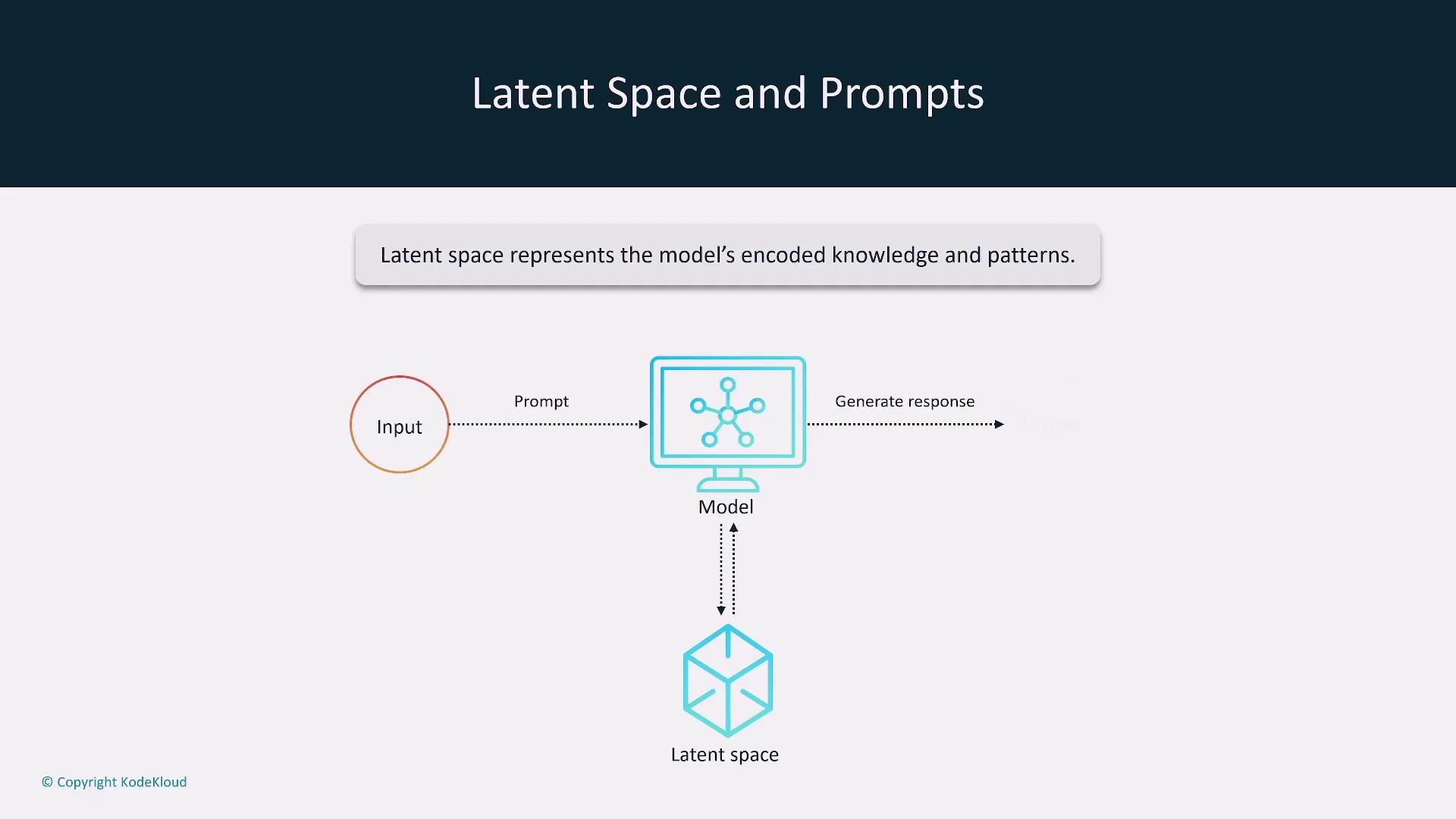
Integrating with AWS Bedrock
AWS Bedrock supports a wide range of prompt engineering techniques by offering a comprehensive model hosting service. When using LLMs on Bedrock, crafting effective prompts is essential. For example, creating a travel planning chatbot on AWS Bedrock could involve integrating with Amazon Lex, connecting to databases like Amazon Redshift, and utilizing services such as Amazon Cognito. Refined prompt engineering guides chatbot interactions and ensures optimal performance.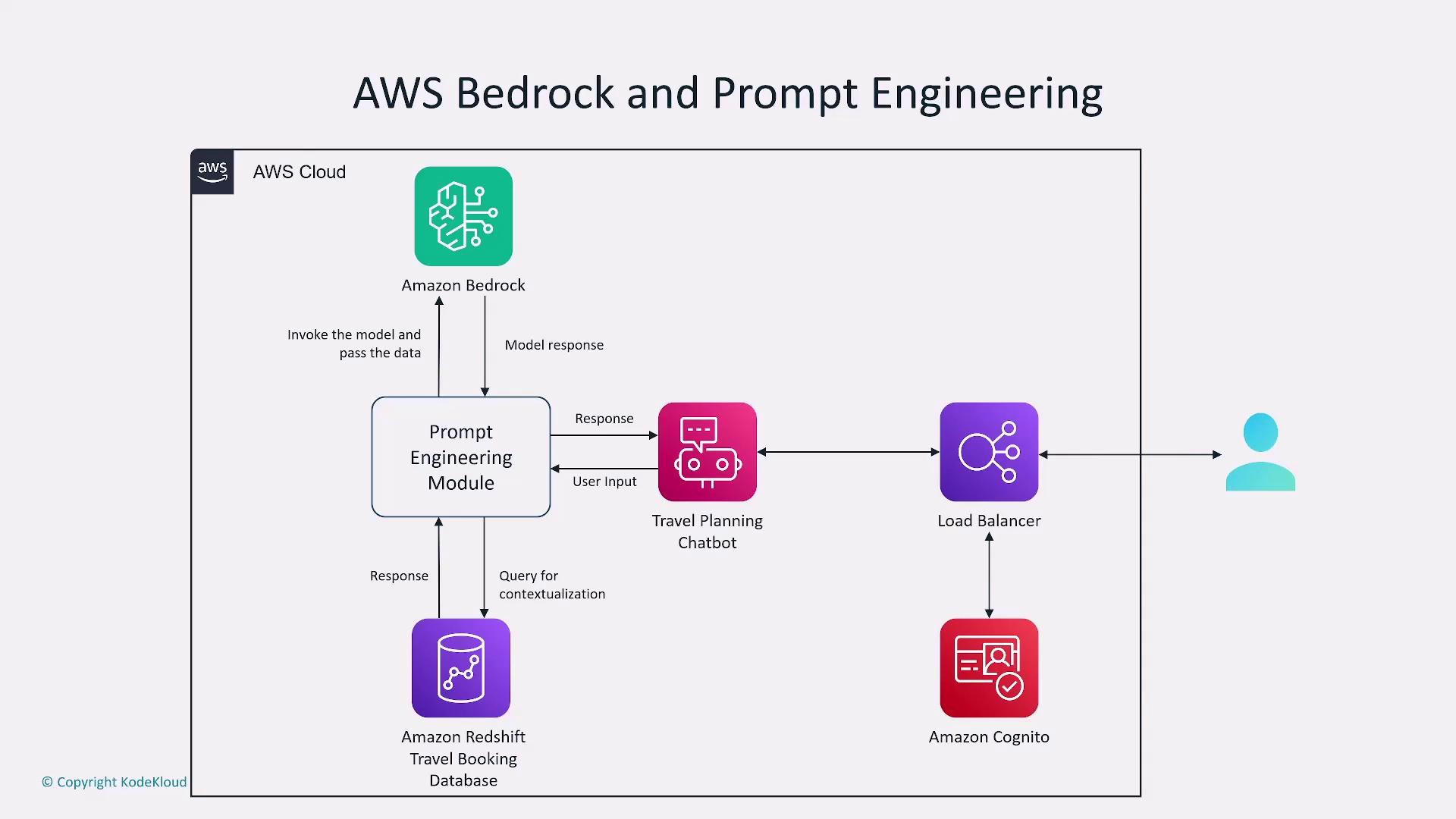
The quality and comprehensiveness of a model’s latent space depend heavily on its training data. Smaller or less comprehensive models might not capture all details, potentially leading to hallucinated outputs if prompts request data beyond the model’s scope.

Security and Safety in Prompt Engineering
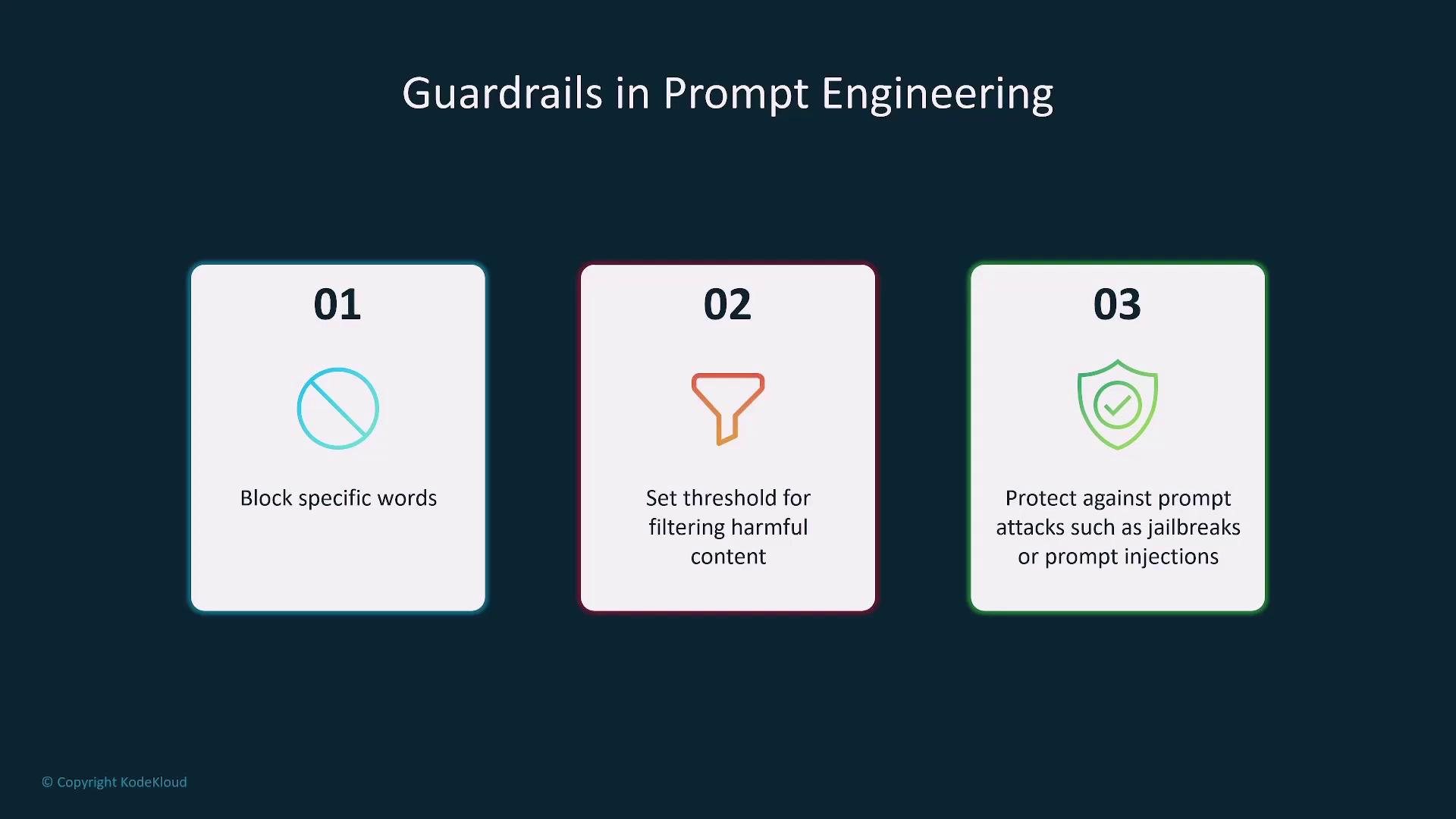
Security measures are essential to prevent the generation of harmful content or the exposure of sensitive data. AWS Bedrock includes Guardrails—a product designed to filter harmful content, block specific keywords, and safeguard against prompt injections.

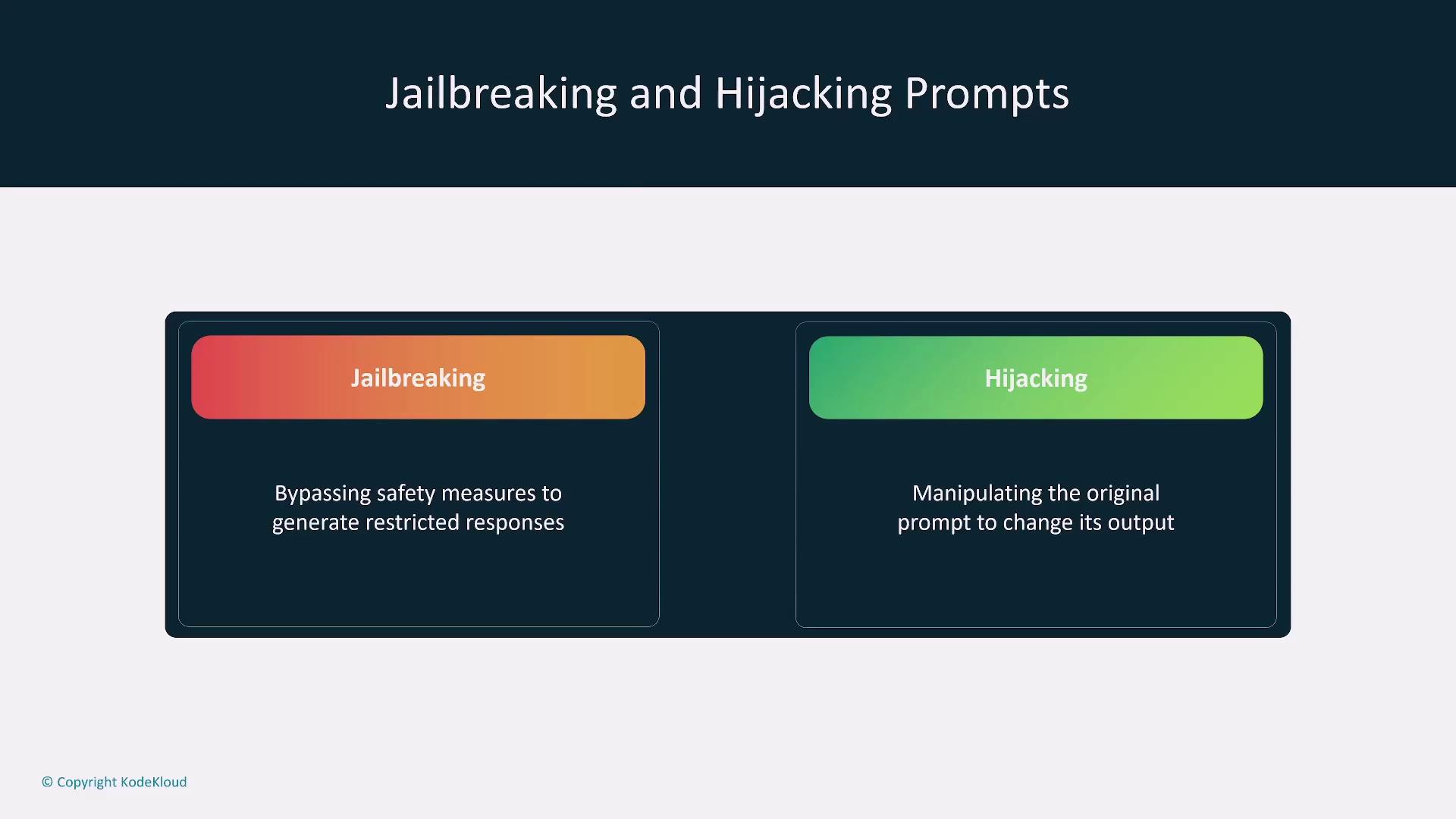
Summary
Effective prompt engineering combines clarity, specific context, well-defined examples, and a strong understanding of the model’s latent space. Key takeaways include:- Use zero-shot prompting for general tasks.
- Apply one-shot or few-shot prompting when additional guidance is necessary.
- Leverage chain-of-thought prompting for complex reasoning.
- Utilize prompt templates to maintain consistency across similar tasks.
- Employ prompt tuning to optimize instructions without altering model parameters.