Real-Time Inferencing
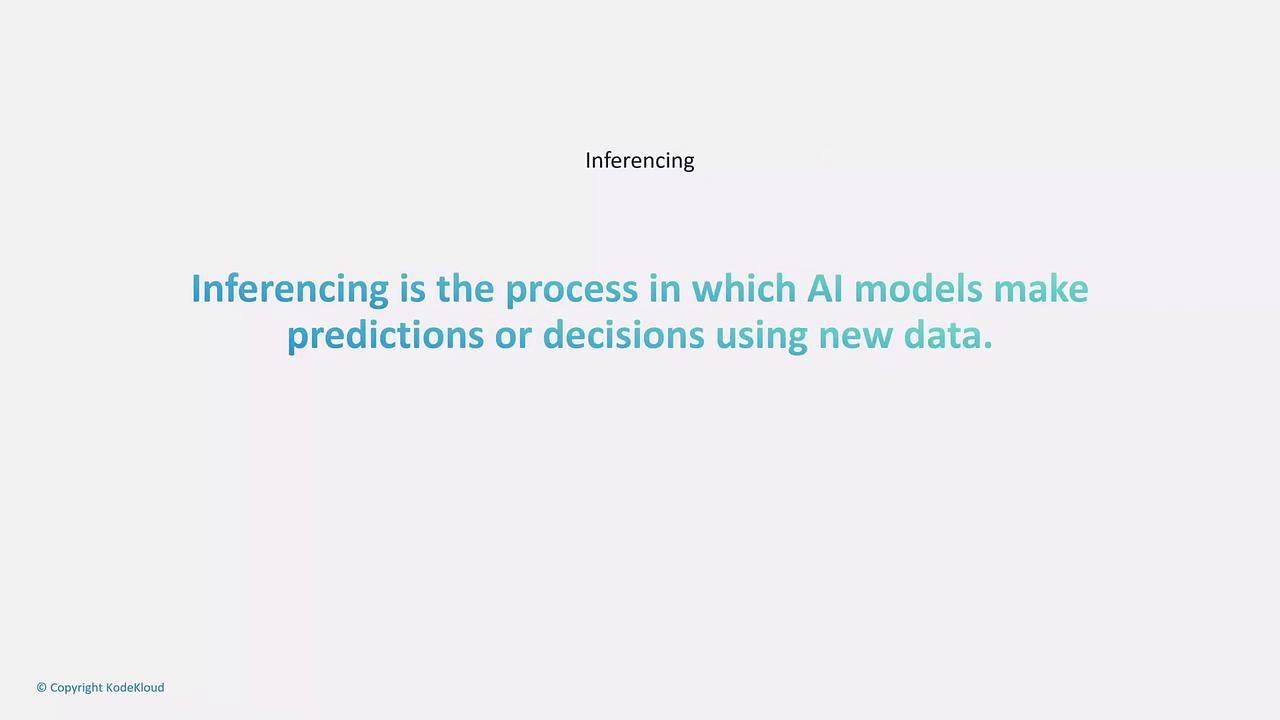
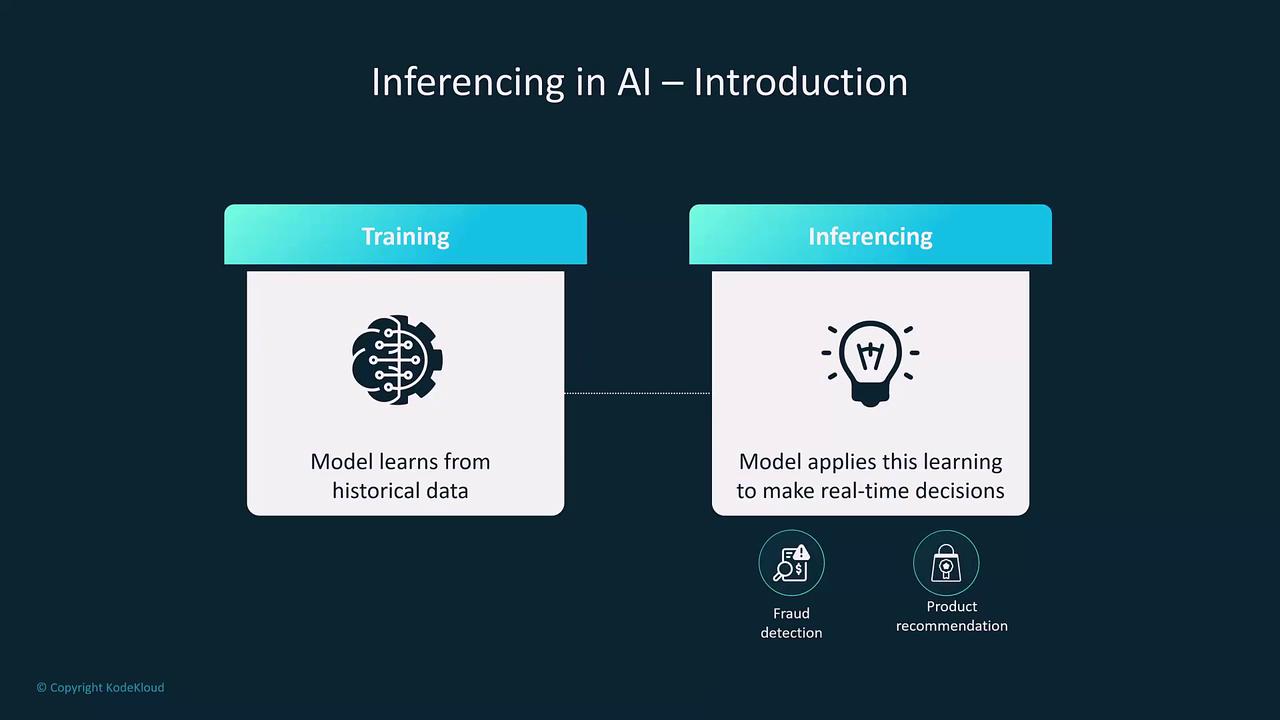
Real-time inferencing generates predictions or classifications instantly as data arrives. This approach is crucial for applications that demand immediate responses—such as chatbots, fraud detection systems, autonomous driving, and voice assistants like Alexa. As soon as an input is received, the model processes it immediately, ensuring prompt decision-making. Amazon SageMaker is one example of a machine learning service that provides endpoints for deploying models capable of real-time inferencing. These endpoints are designed for high scalability and minimal latency.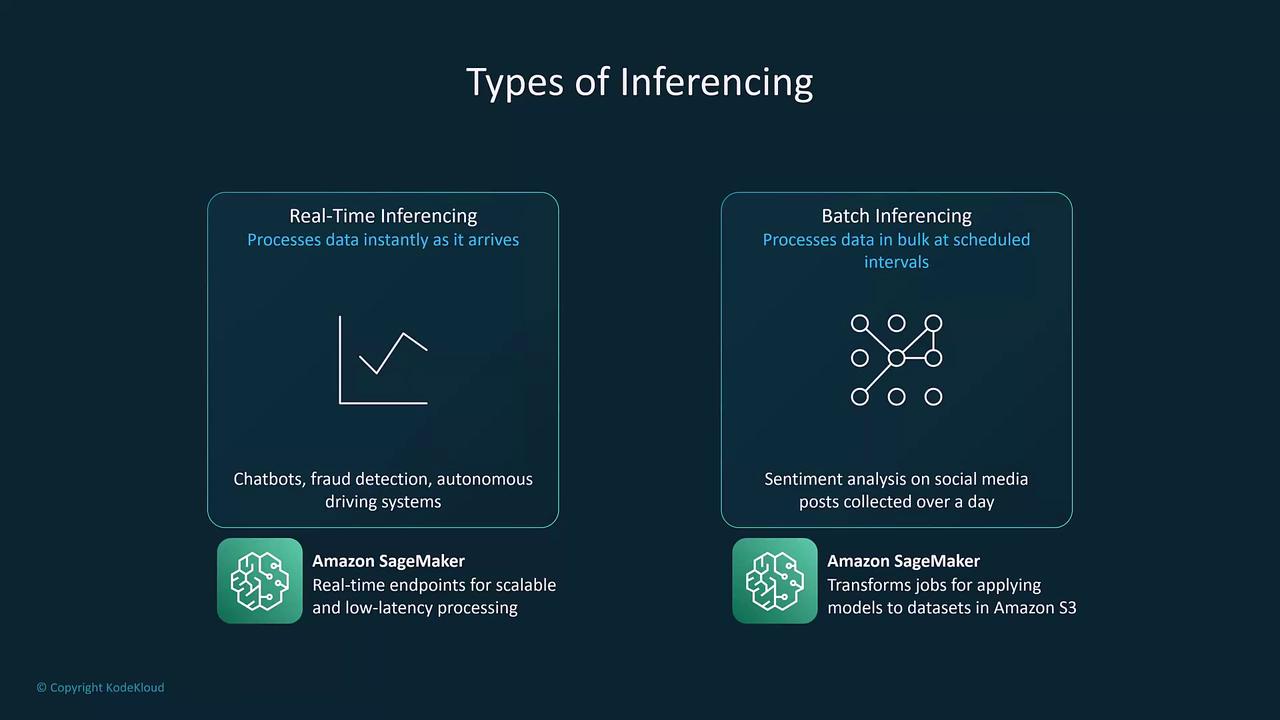

Batch Inferencing
In contrast, batch inferencing handles large volumes of data by processing them collectively at scheduled intervals, rather than one record at a time. This method is best suited for scenarios where immediate responses are not required, but efficiency in processing extensive datasets is essential. Batch inferencing proves ideal for tasks such as sentiment analysis on social media data accumulated over hours or days, stock market predictions, and customer segmentation. Amazon SageMaker also supports batch inferencing through its batch transform jobs, enabling users to process vast datasets collectively.Real-time inferencing is optimal for live applications requiring instant feedback, whereas batch inferencing is better suited for comprehensive analysis where time sensitivity is less critical.
Comparison of Real-Time and Batch Inferencing
| Category | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Inferencing | Processes incoming data immediately, providing instant predictions. | Chatbots, fraud detection, autonomous driving, voice assistants |
| Batch Inferencing | Processes data in bulk at set intervals, ideal for extensive data analysis where immediate response is not necessary. | Sentiment analysis, stock market predictions, customer segmentation |