Foundation Models Overview
Foundation models are large-scale, pre-trained architectures designed for a wide range of tasks—from language processing and classification to image recognition and generation. Key techniques include pre-training, fine-tuning, and ongoing updates via continuous pre-training.
Pre-training
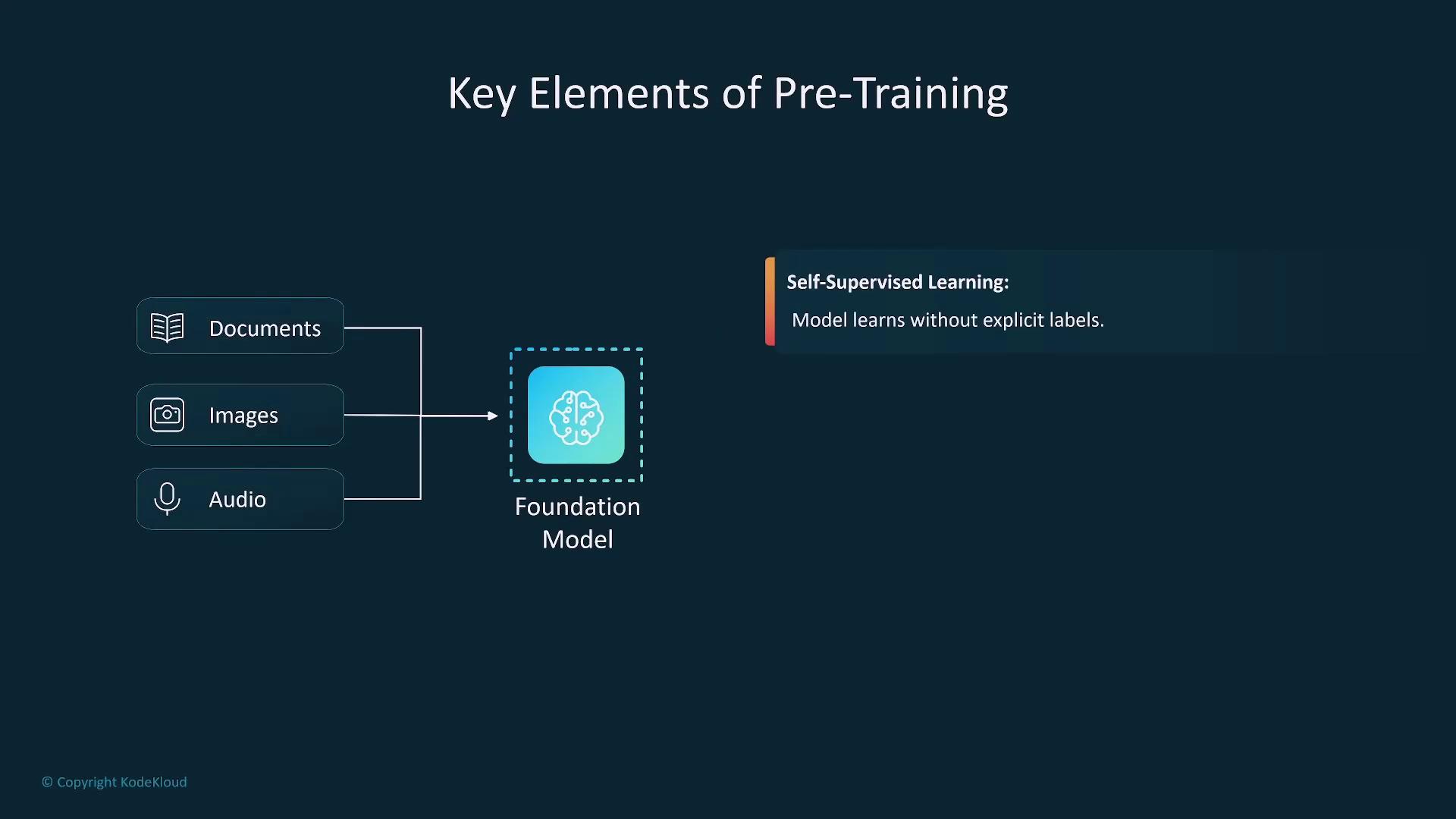
Pre-training is the initial phase where a model is exposed to vast amounts of unsupervised data—such as text, images, or audio. This stage equips the model with broad capabilities, although it demands significant computational resources.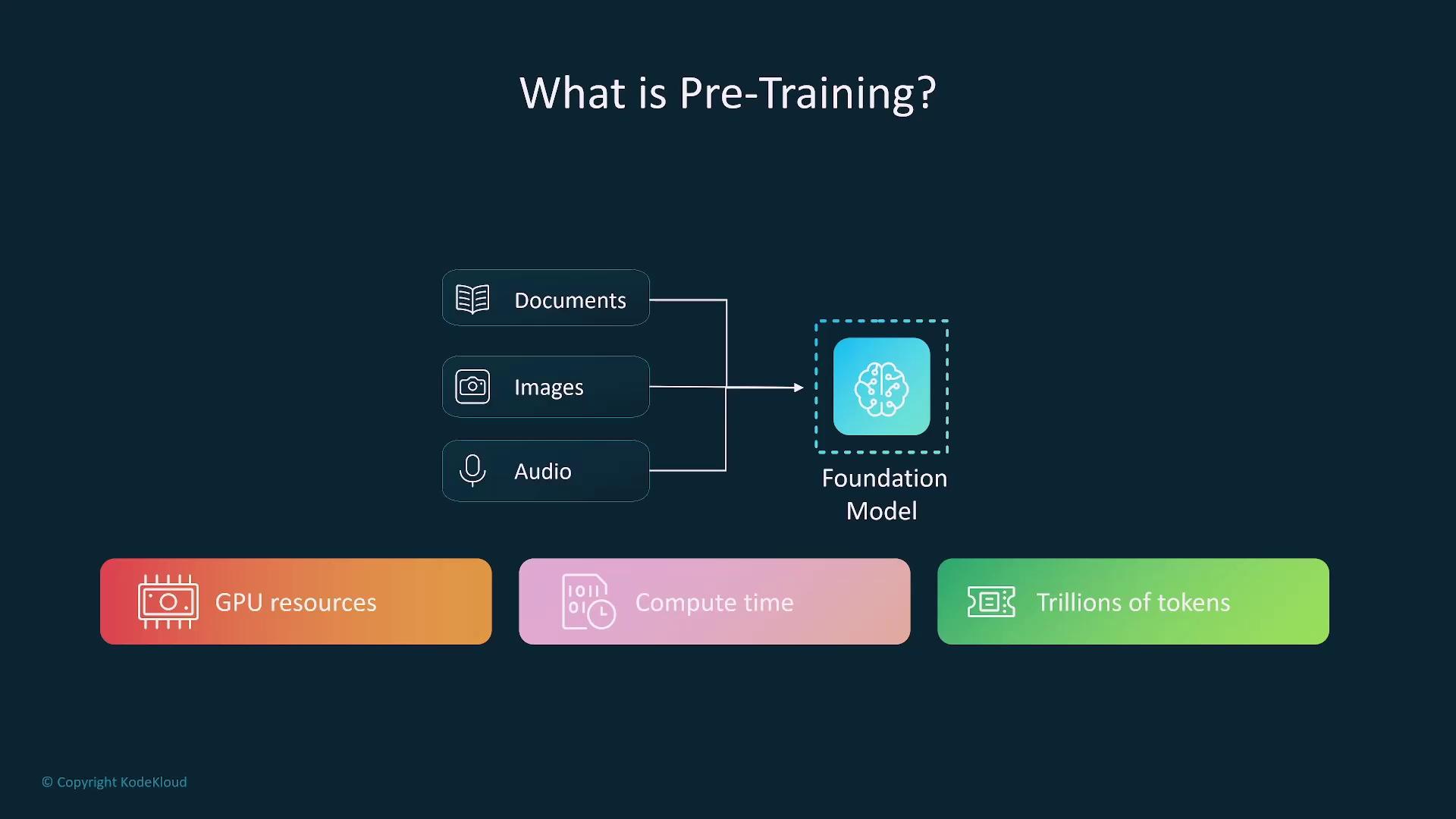
Fine-tuning
Fine-tuning adapts the general pre-trained model to specific tasks using domain-specific or task-specific labeled data. For instance, a language model may be fine-tuned for medical transcription to enhance its accuracy in that field.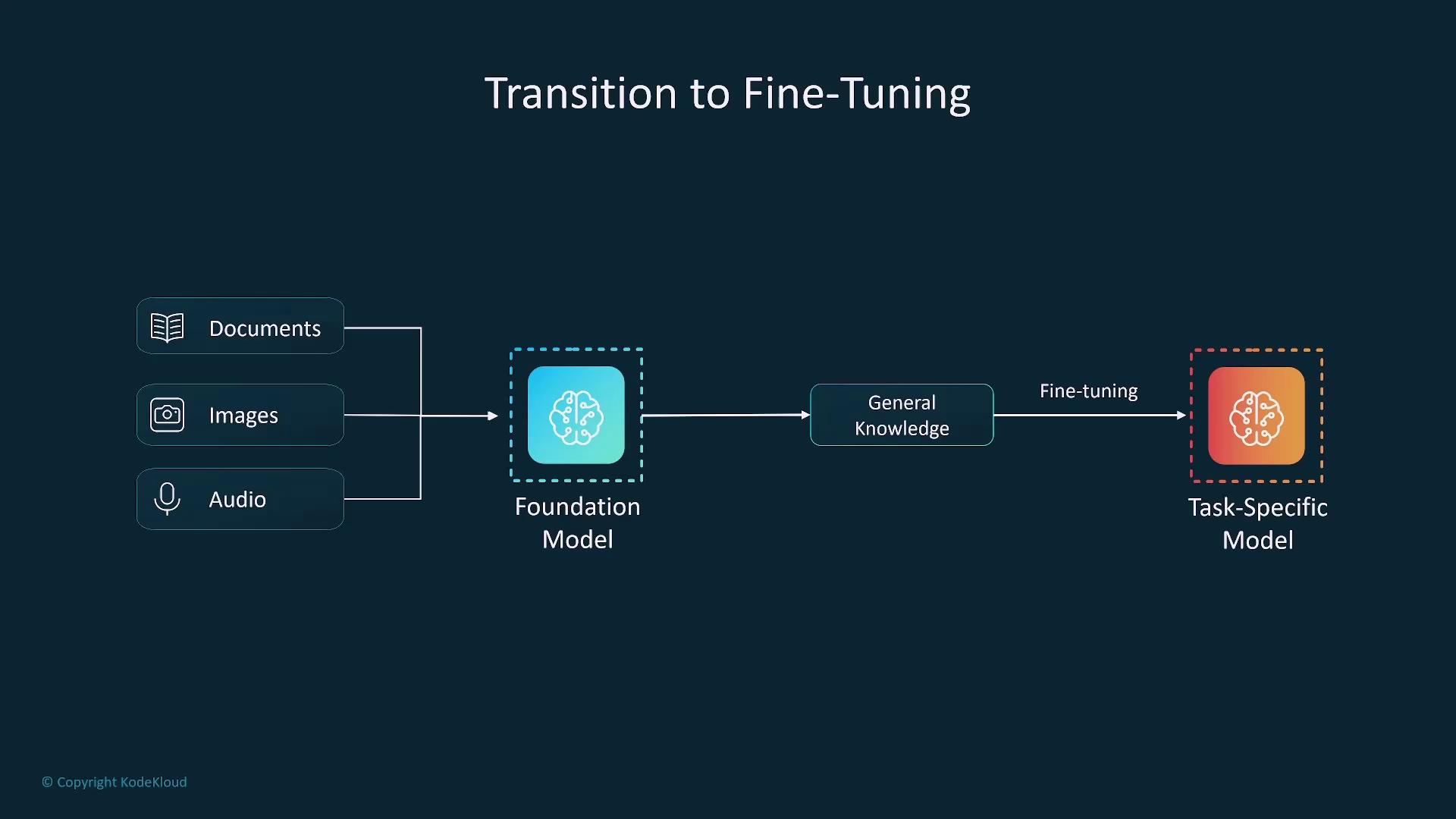

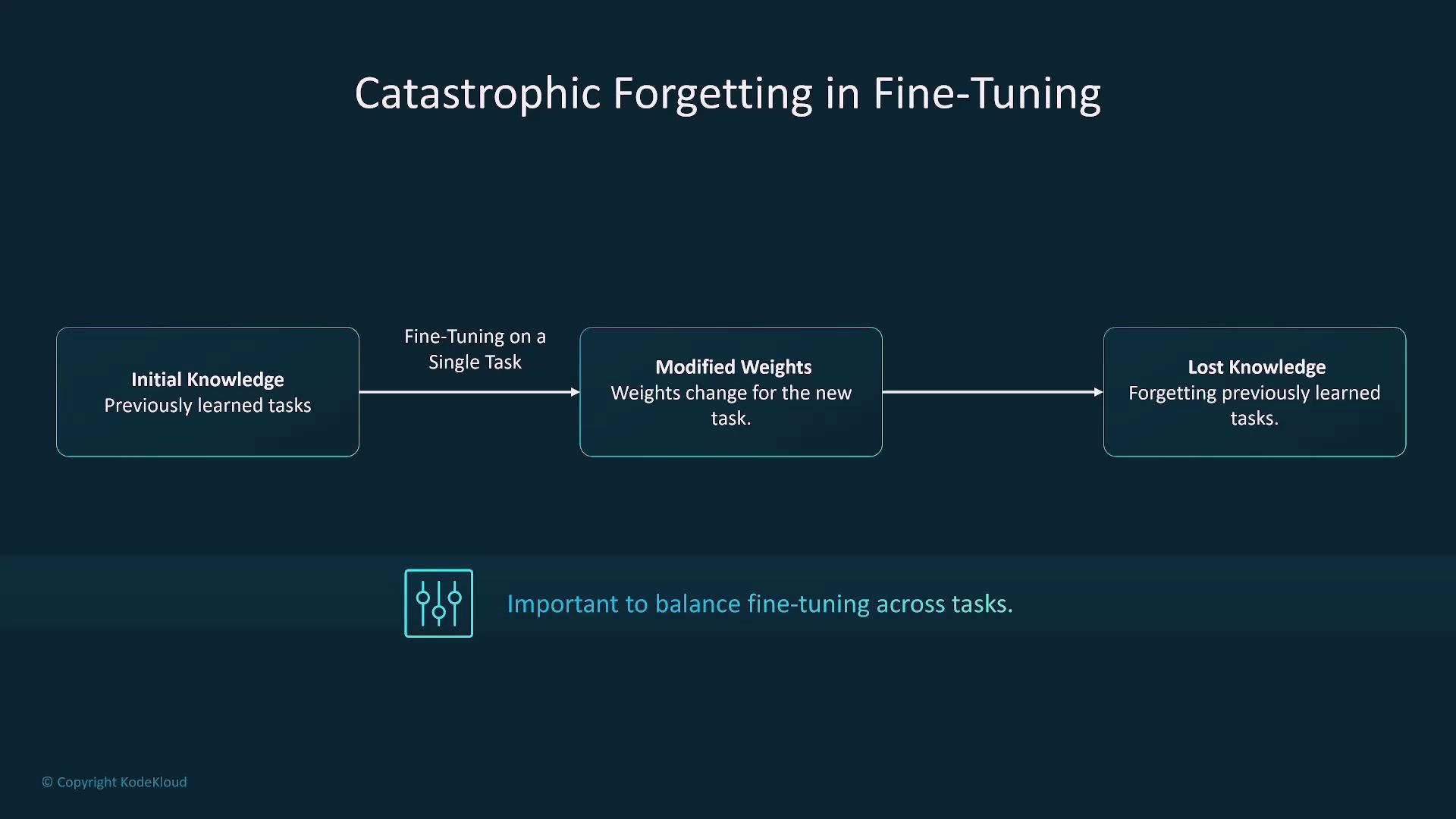
Ensure a balanced fine-tuning process to prevent over-specialization. Over-tuning for a single task can lead to catastrophic forgetting, where the model loses its general capabilities.
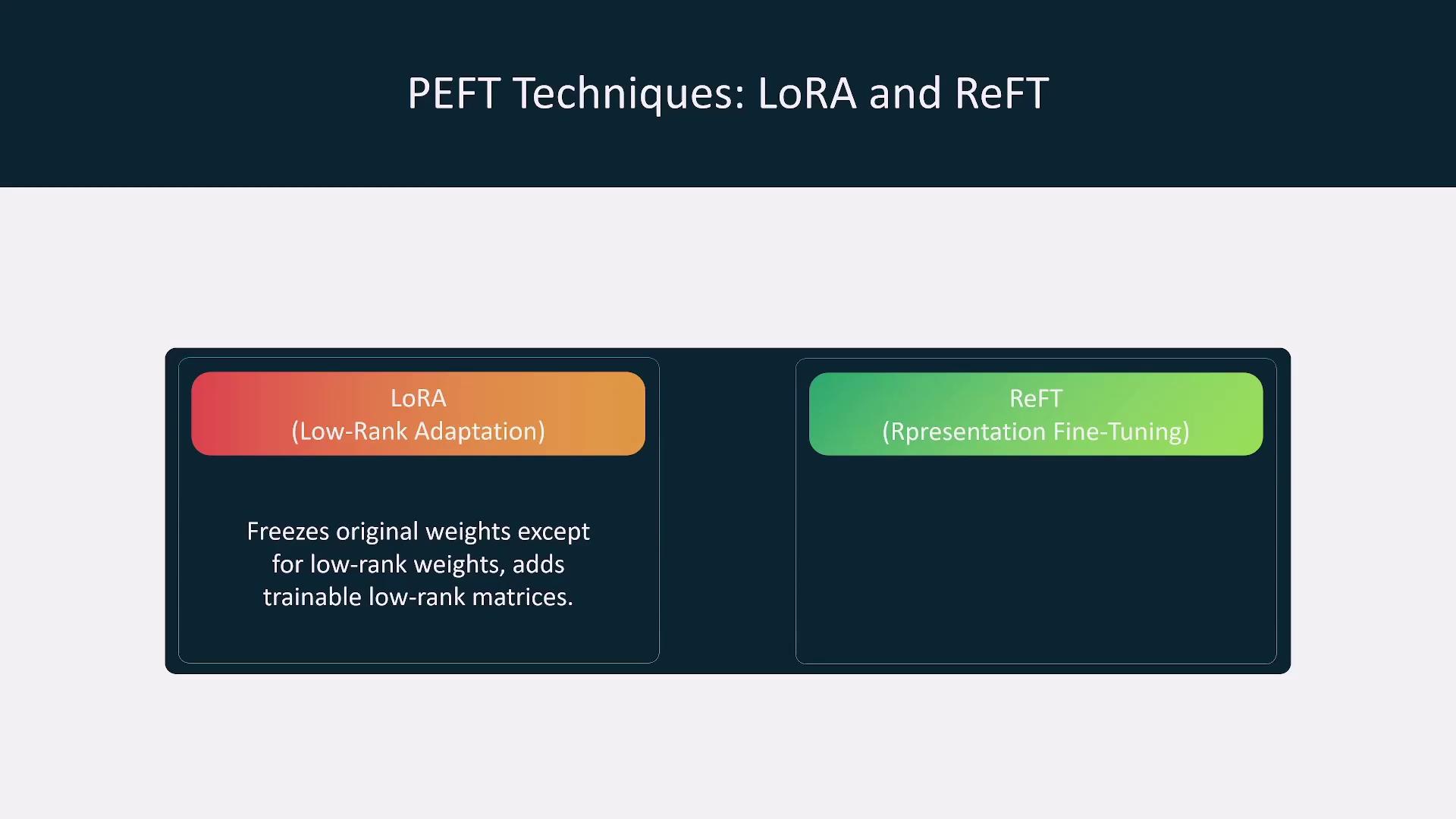
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT)
To minimize resource consumption during fine-tuning, parameter-efficient techniques have been developed. These methods involve freezing much of the pre-trained model’s parameters and fine-tuning only a small subset of task-specific layers.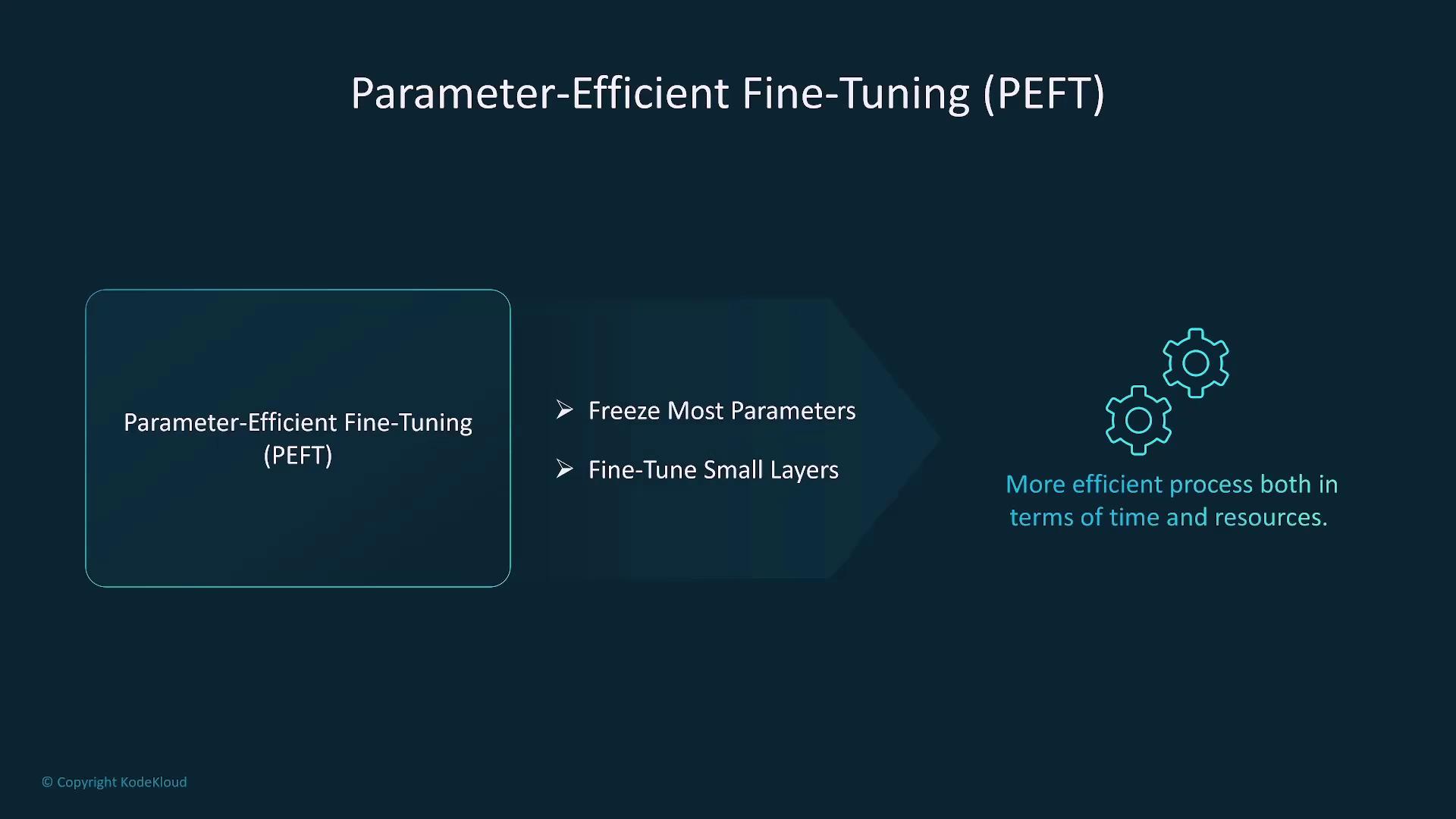
- Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA): Freezes the majority of the model weights, allowing only low-rank matrices to update during training.
- Representation Fine-Tuning (REFT): Adjusts internal representations rather than direct weights, ideal for tasks involving coding or logical reasoning.
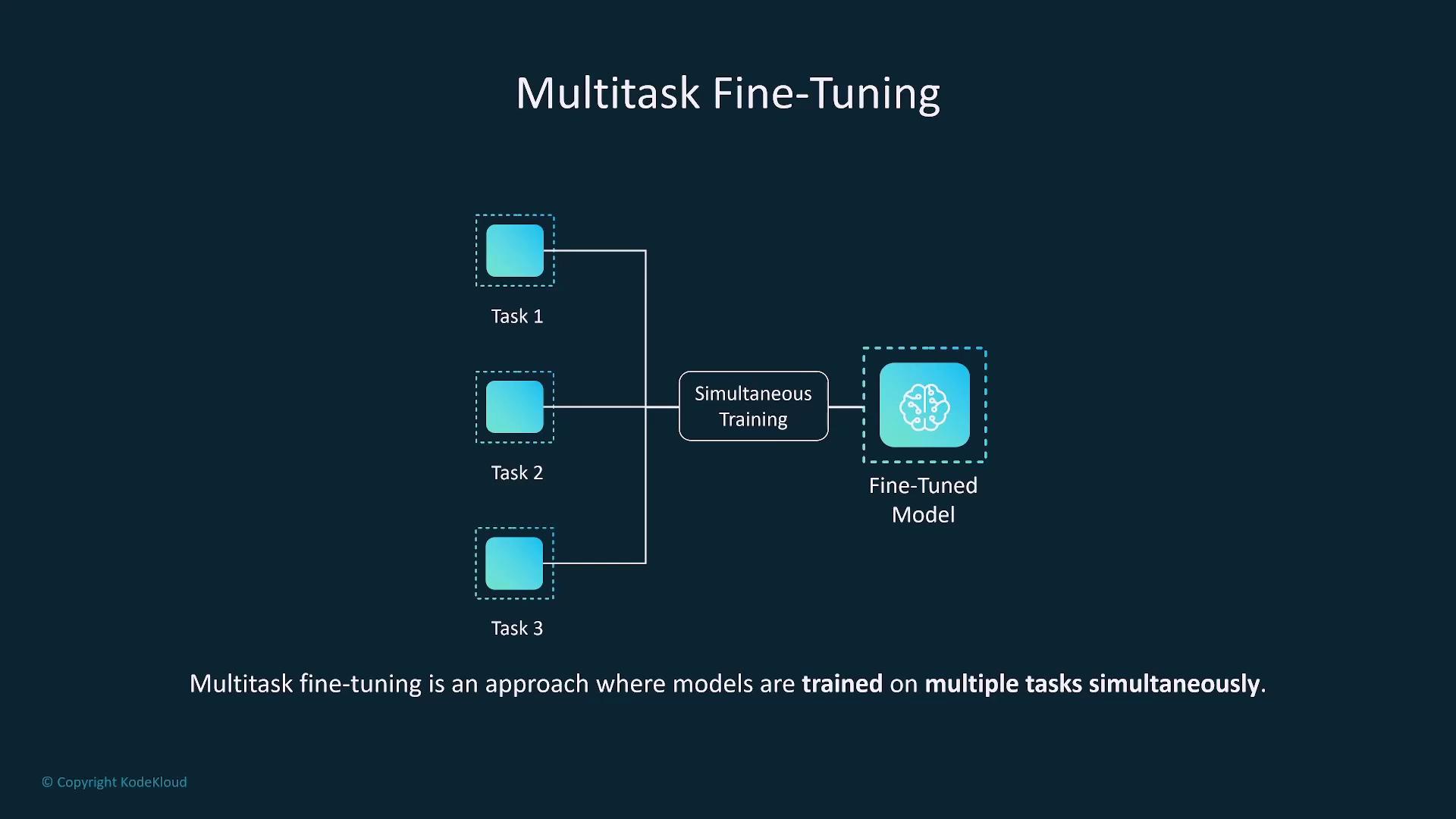
Multi-Task and Domain-Specific Fine-Tuning
Beyond single-task fine-tuning, consider these advanced approaches:- Multi-Task Fine-Tuning: Trains the model on several tasks simultaneously, enhancing versatility and reducing the risk of catastrophic forgetting.
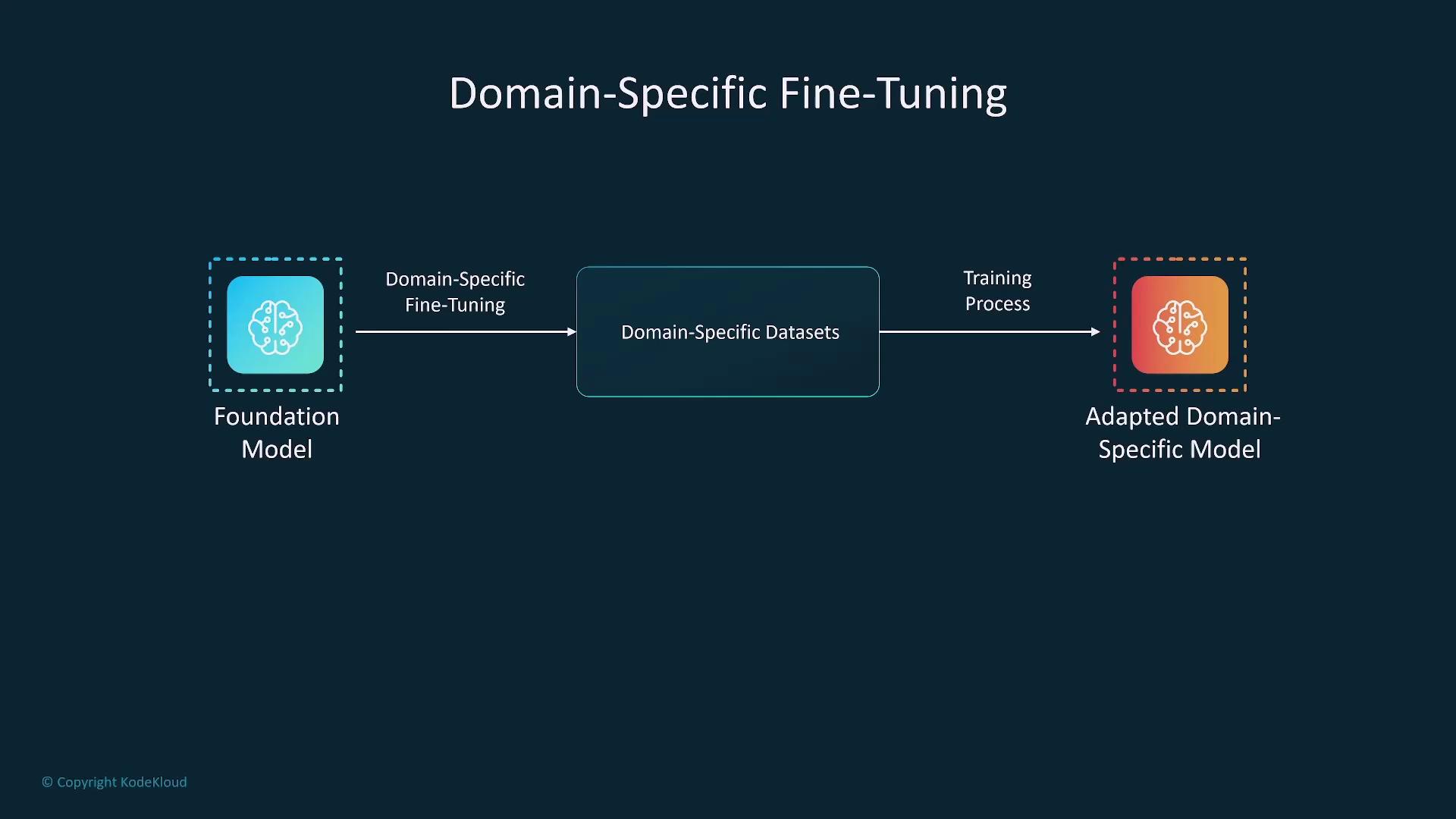
- Domain-Specific Fine-Tuning: Uses data from specific industries (e.g., healthcare, finance, legal) to optimize model performance for industry-centric challenges.
Continuous Pre-training
Continuous pre-training involves regularly updating models with new data to maintain relevance and performance. For instance, OpenAI discloses the training data cutoff to signal the recency of its training corpus.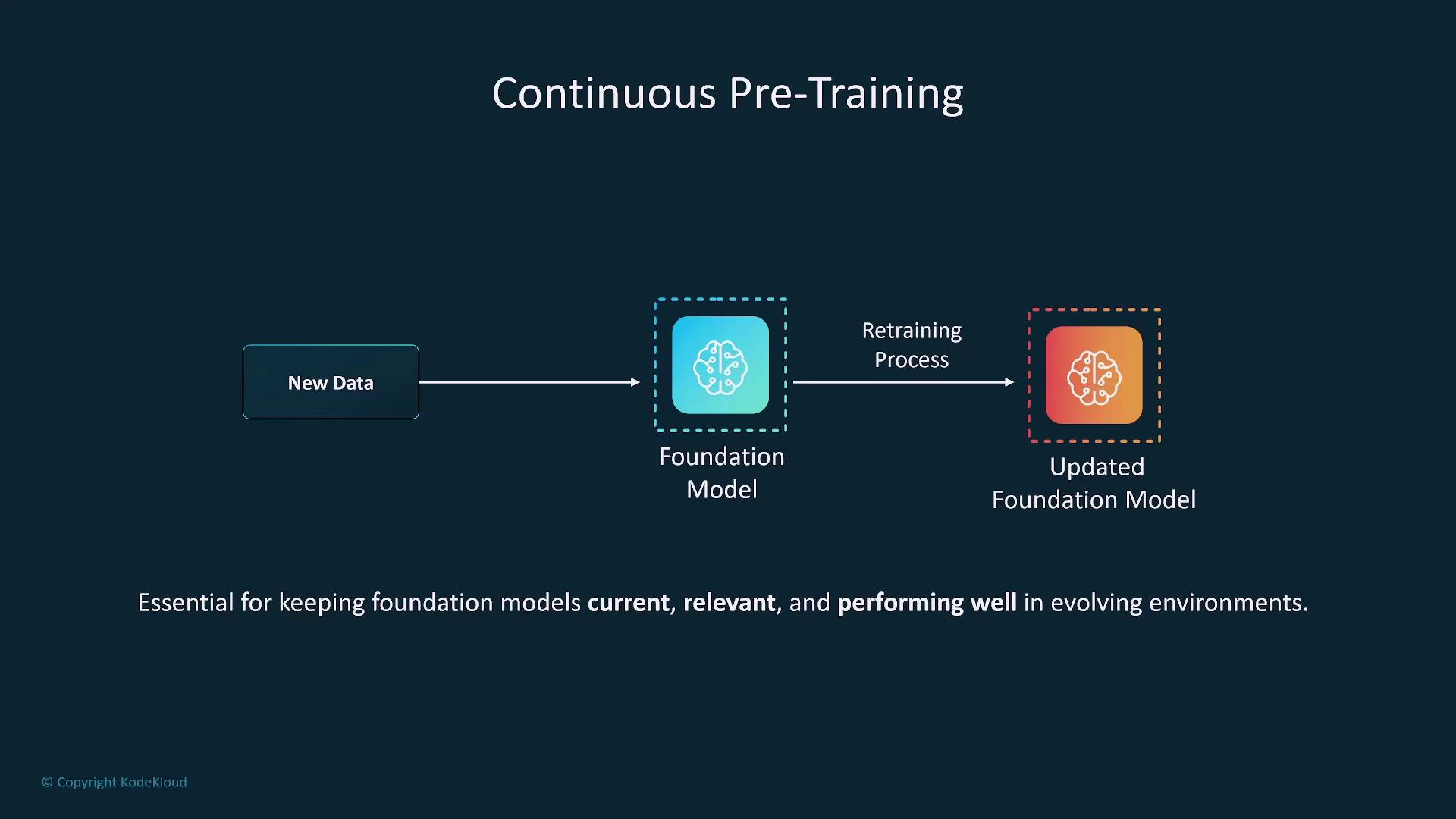
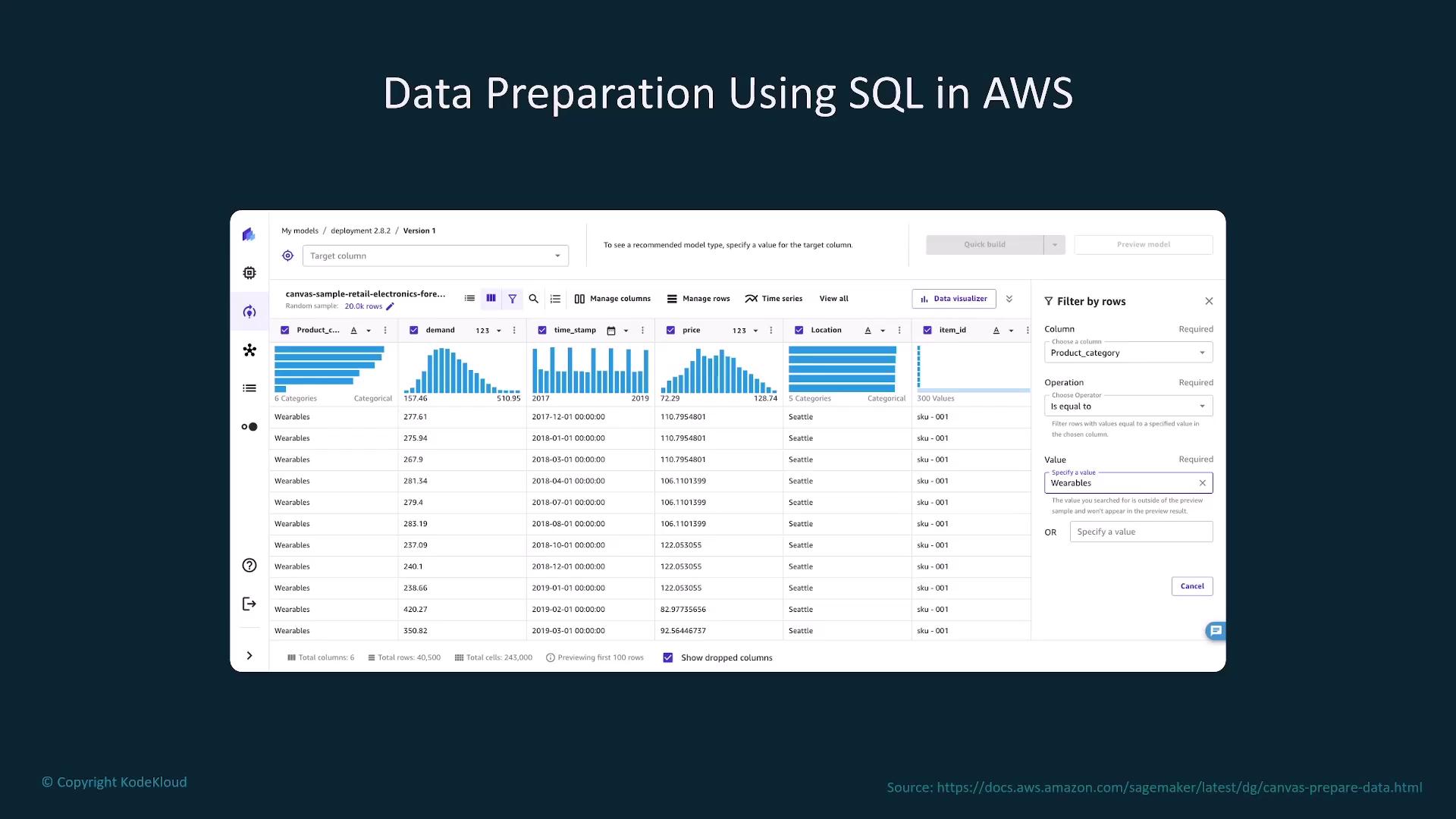
Data Preparation for Training
High-quality, structured, and clean data is essential regardless of the training method. Effective data preparation includes structuring, cleaning, and segmenting data to maximize training efficiency.

Model Evaluation
Model evaluation is a crucial step after completing fine-tuning or continuous pre-training. Use a validation set to optimize parameters and subsequently test the model with unseen data to ensure that performance meets expectations.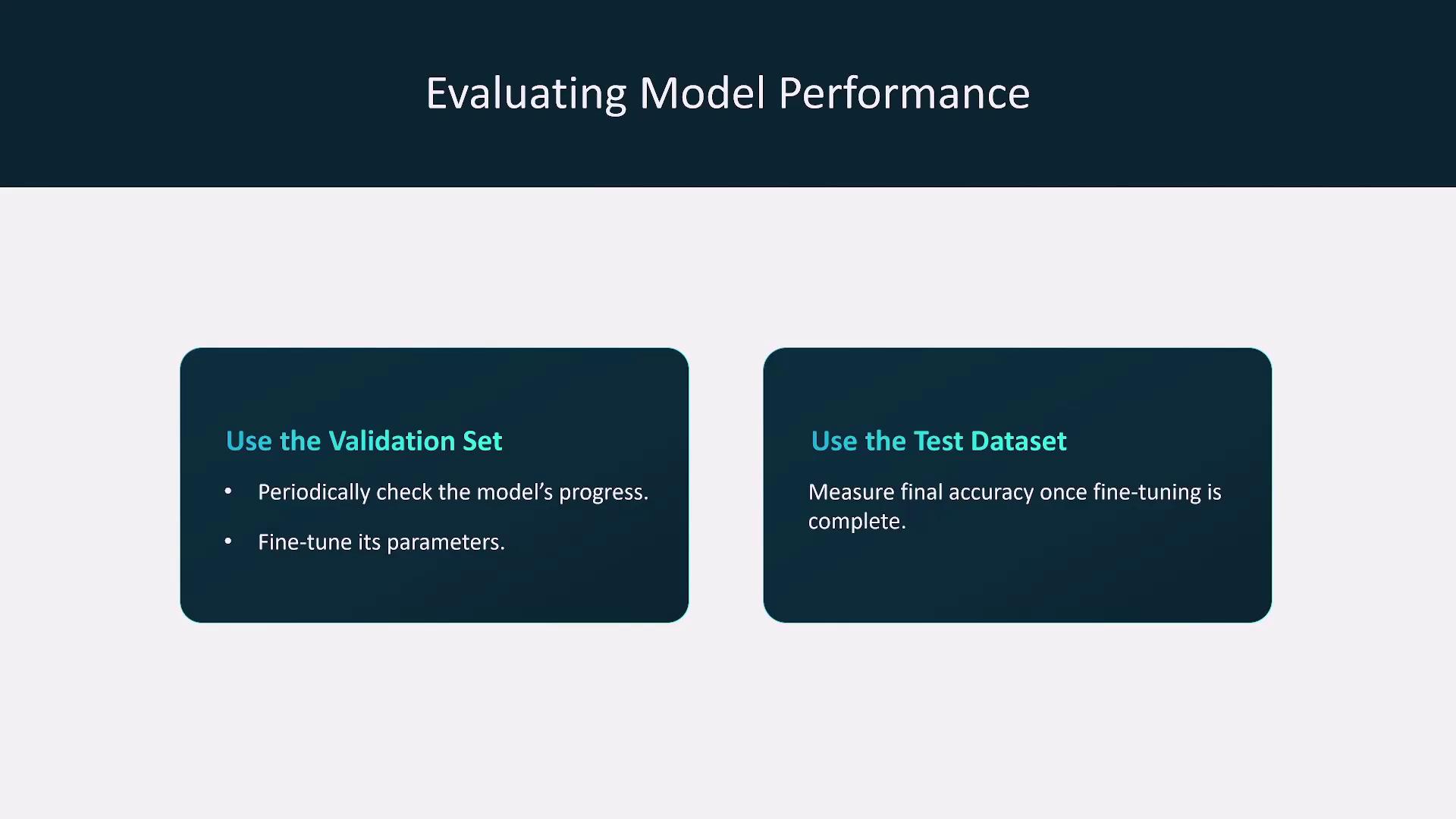
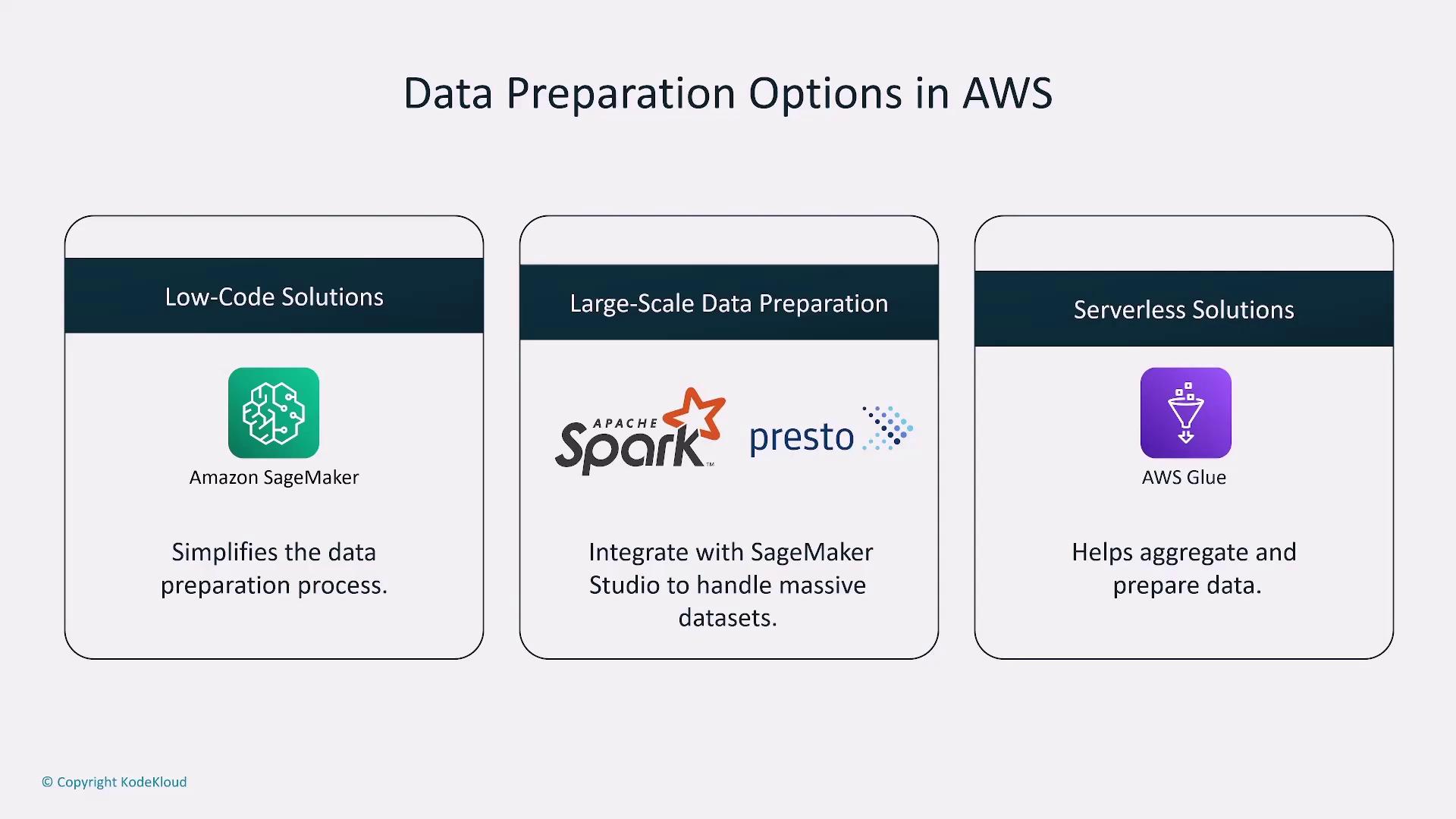
AWS Tools for Data Preparation and Training
AWS provides a suite of tools that simplify data preparation and model training:- Data Wrangler: A low-code solution for efficient data preparation.
- Athena or Apache EMR: Ideal for large-scale data processing.
- AWS Glue: A robust ETL service for data integration.
- SageMaker Studio: Facilitates comprehensive data modeling and training workflows.