MLOps Lifecycle Overview
MLOps mirrors the traditional software development lifecycle while adapting to the unique needs of machine learning. The process begins with gathering data, problem analysis, and model development. It then progresses to model verification, packaging, release, configuration, hyperparameter tuning, inferencing, and live system monitoring. If performance deviations are detected during monitoring, the model is retrained with new data.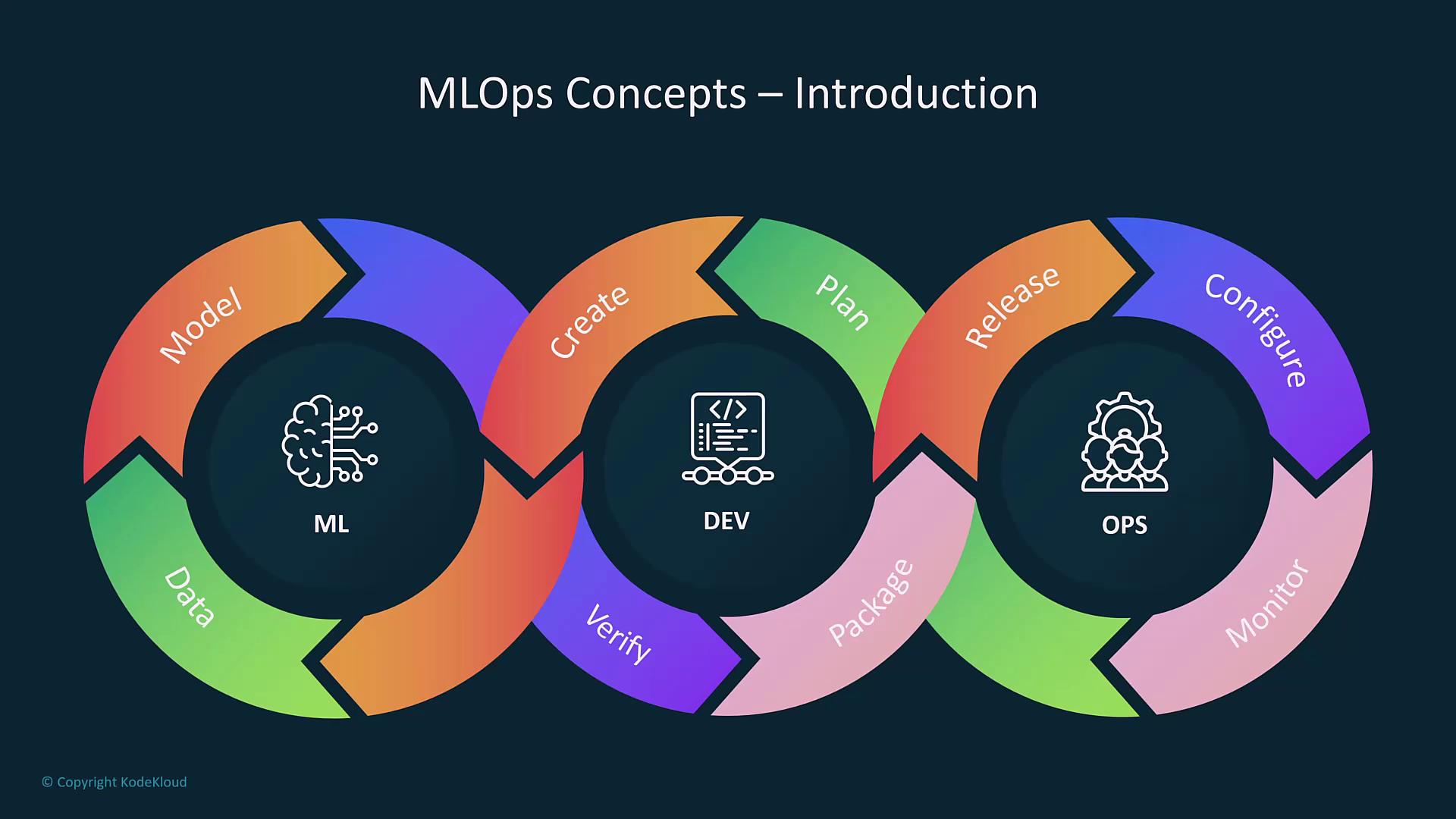
Pipelines and Automation
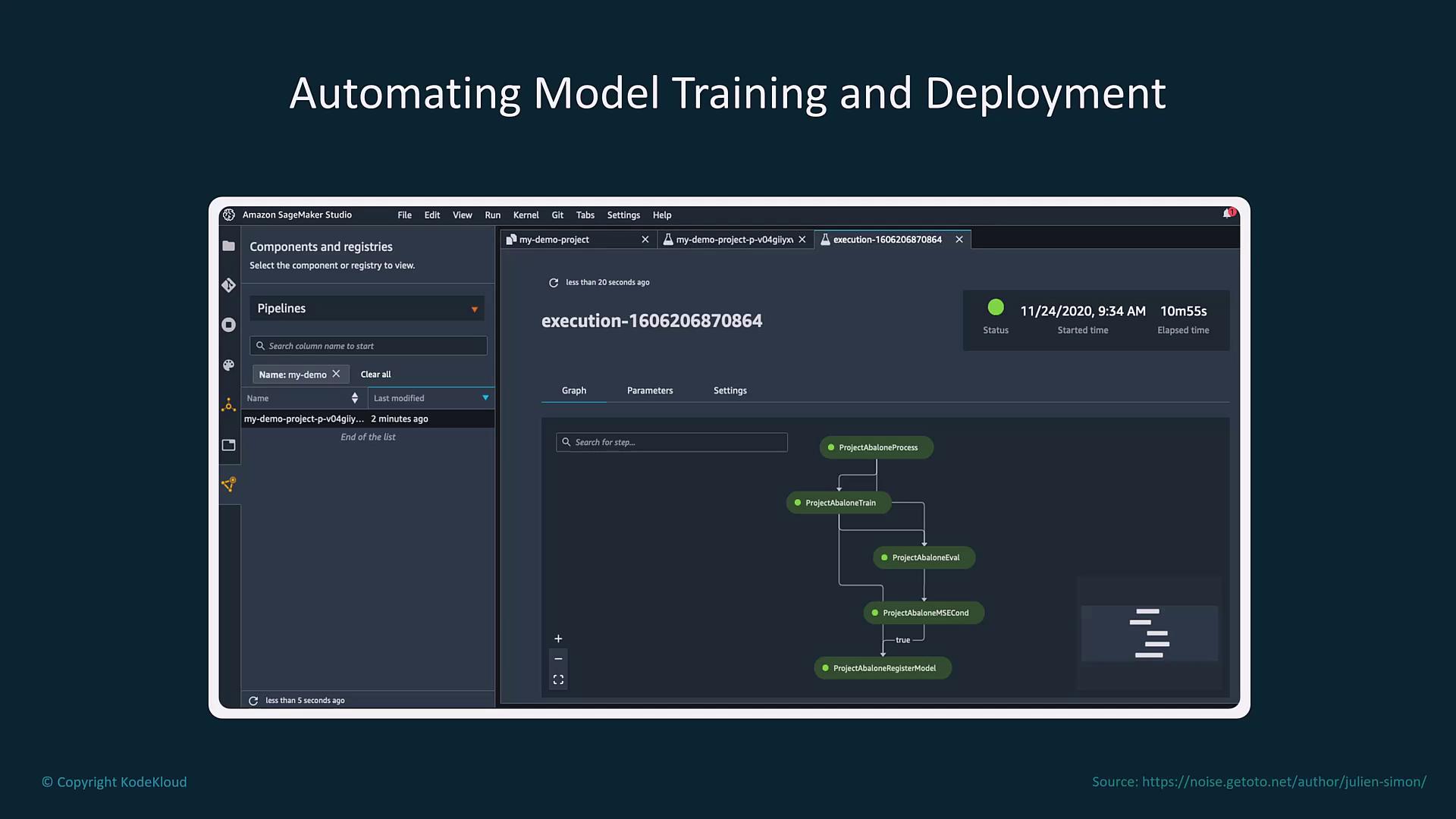
MLOps pipelines automate all phases of the machine learning workflow—including data collection, model training, validation, testing, deployment, evaluation, and continuous monitoring. For instance, Amazon SageMaker Pipelines employs a CI/CD-style methodology to streamline these processes. Moreover, tools like Apache Airflow (or its managed AWS service) enable the orchestration of complex data processing tasks.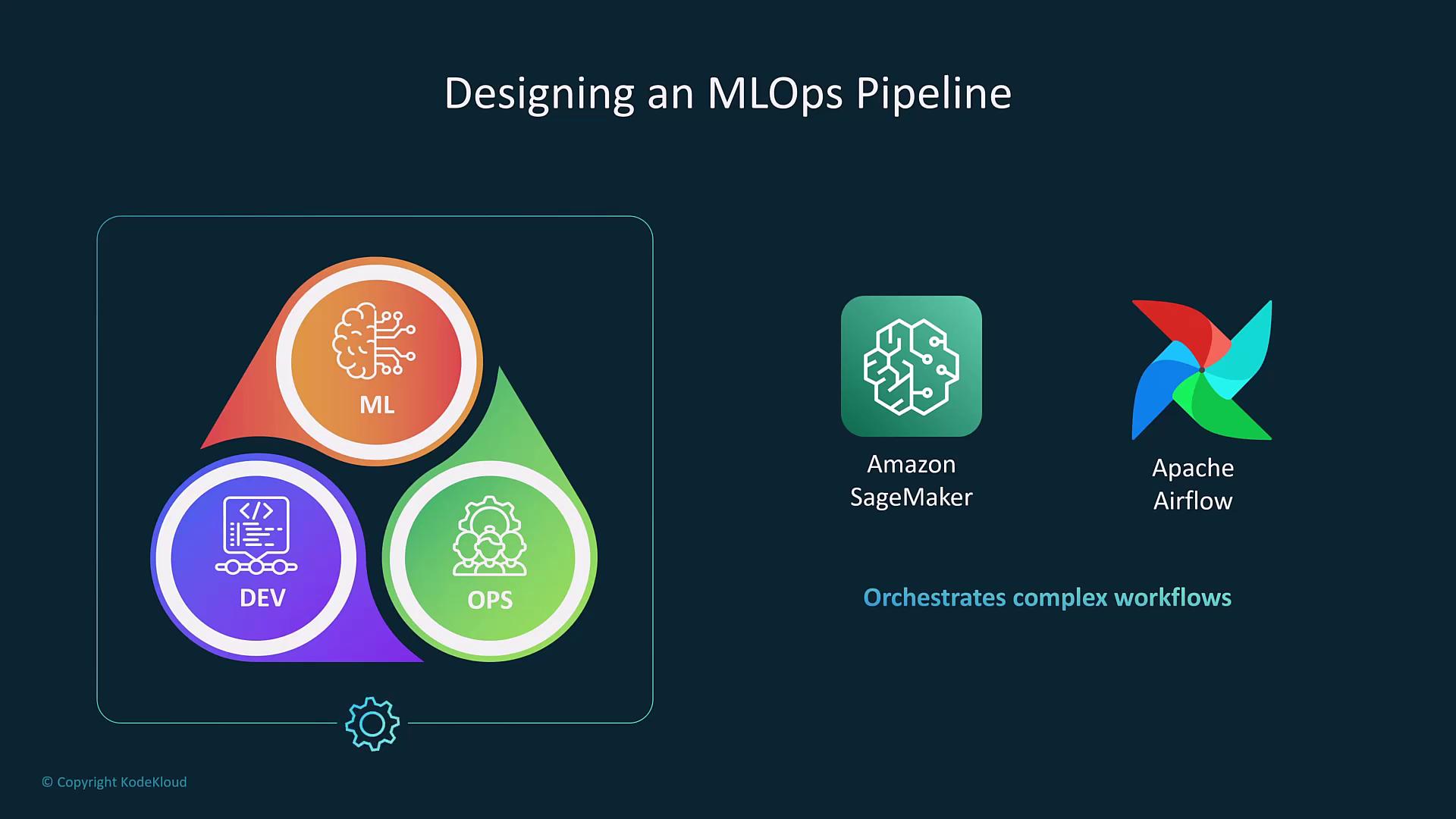
Automated pipelines free up data scientists to focus on experimentation and model optimization, rather than on the underlying orchestration and integration challenges.
Infrastructure Provisioning and Version Control
A critical aspect of MLOps is the setup of reliable infrastructure and robust version control. Key activities include:- Establishing a Git repository.
- Building and managing artifacts.
- Storing Docker containers using Amazon ECR.
- Triggering AWS Lambda functions via API calls.
- Deploying resources with CloudFormation.
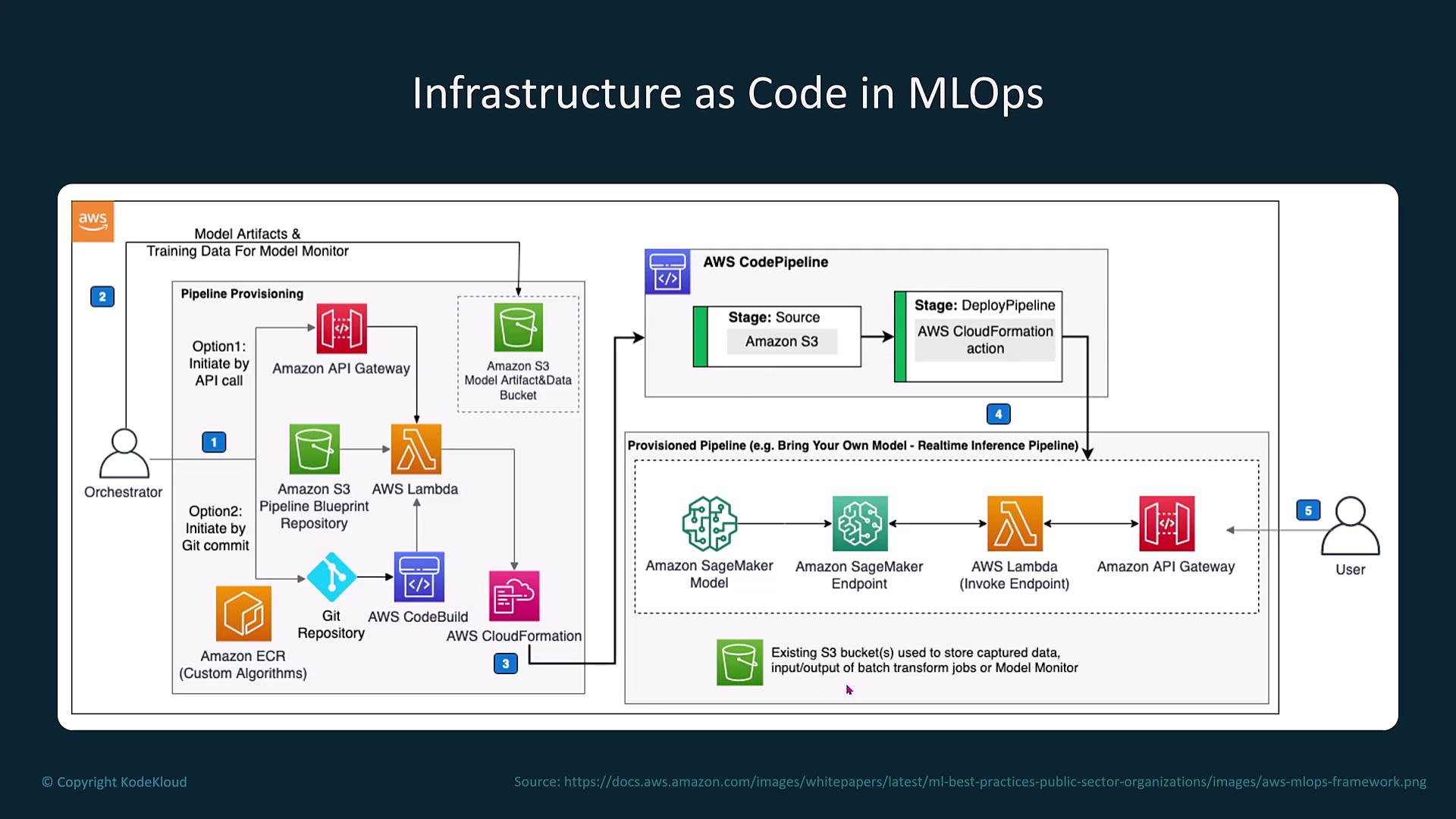
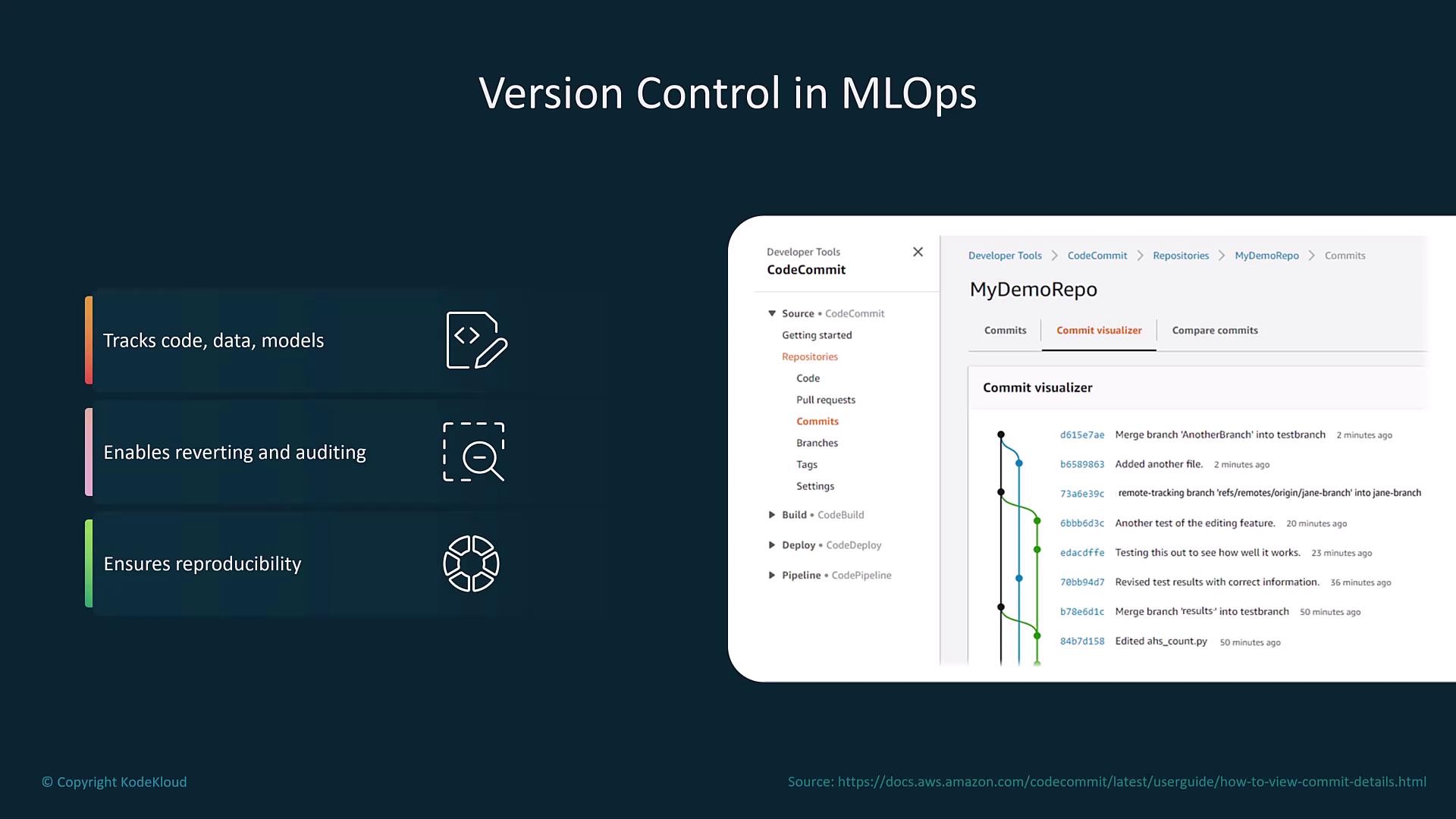
Model Monitoring and Automated Retraining
Continuous monitoring is vital to ensure models perform as expected over time. Tools such as Amazon CloudWatch and SageMaker Model Monitor track performance metrics like error rate, latency, and accuracy. When these metrics exceed predefined thresholds, automated retraining is initiated to update the model with new data.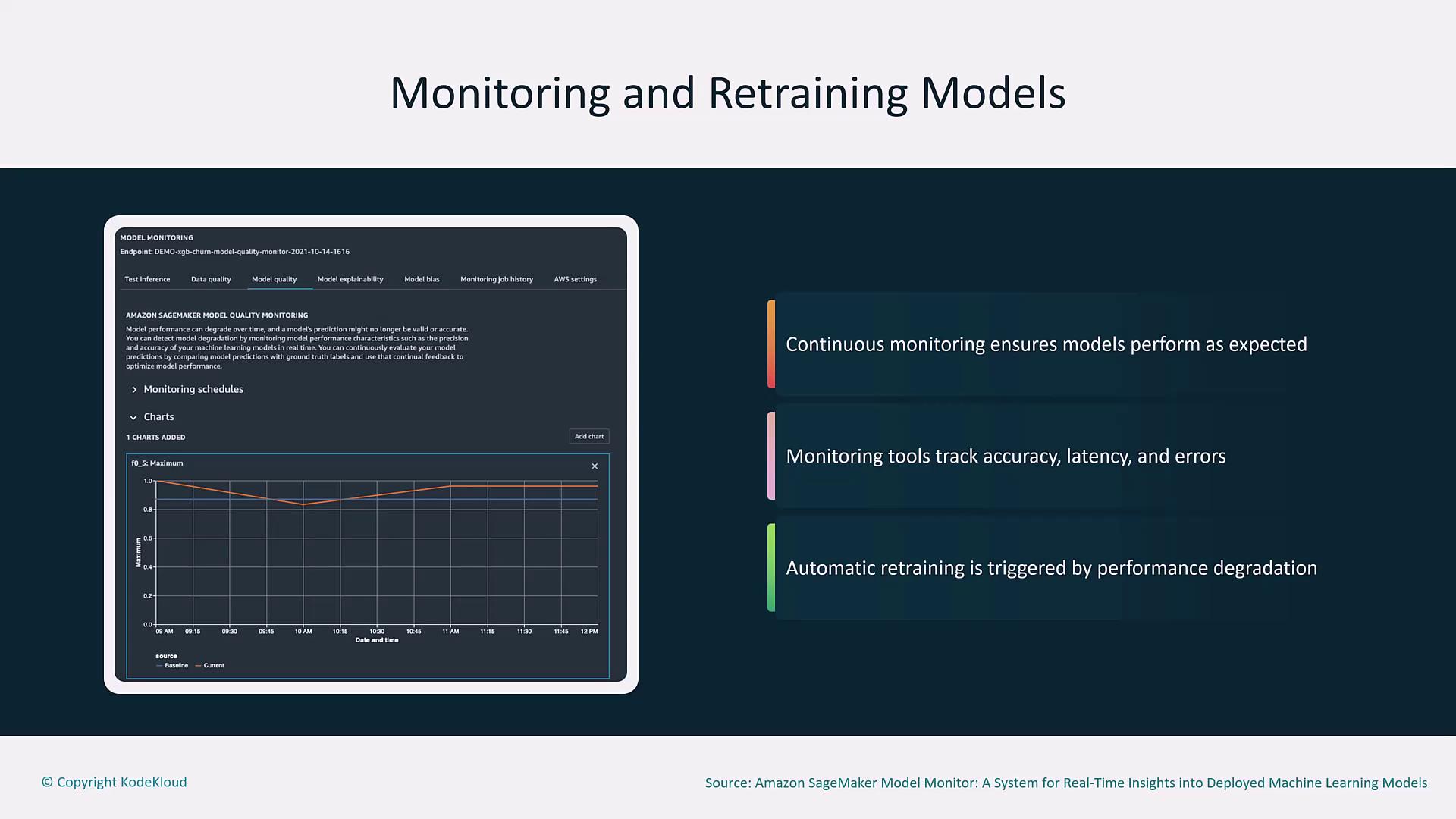
Ensure that the thresholds for triggering retraining are carefully set to avoid unnecessary model updates or performance degradation.
Enhancing and Evaluating Model Quality
Improving model quality is an iterative process that involves rigorous experimentation, performance tracking, and bias detection. Amazon SageMaker Studio provides an integrated development environment for experimenting with models and analyzing a variety of metrics, including class imbalance and divergence.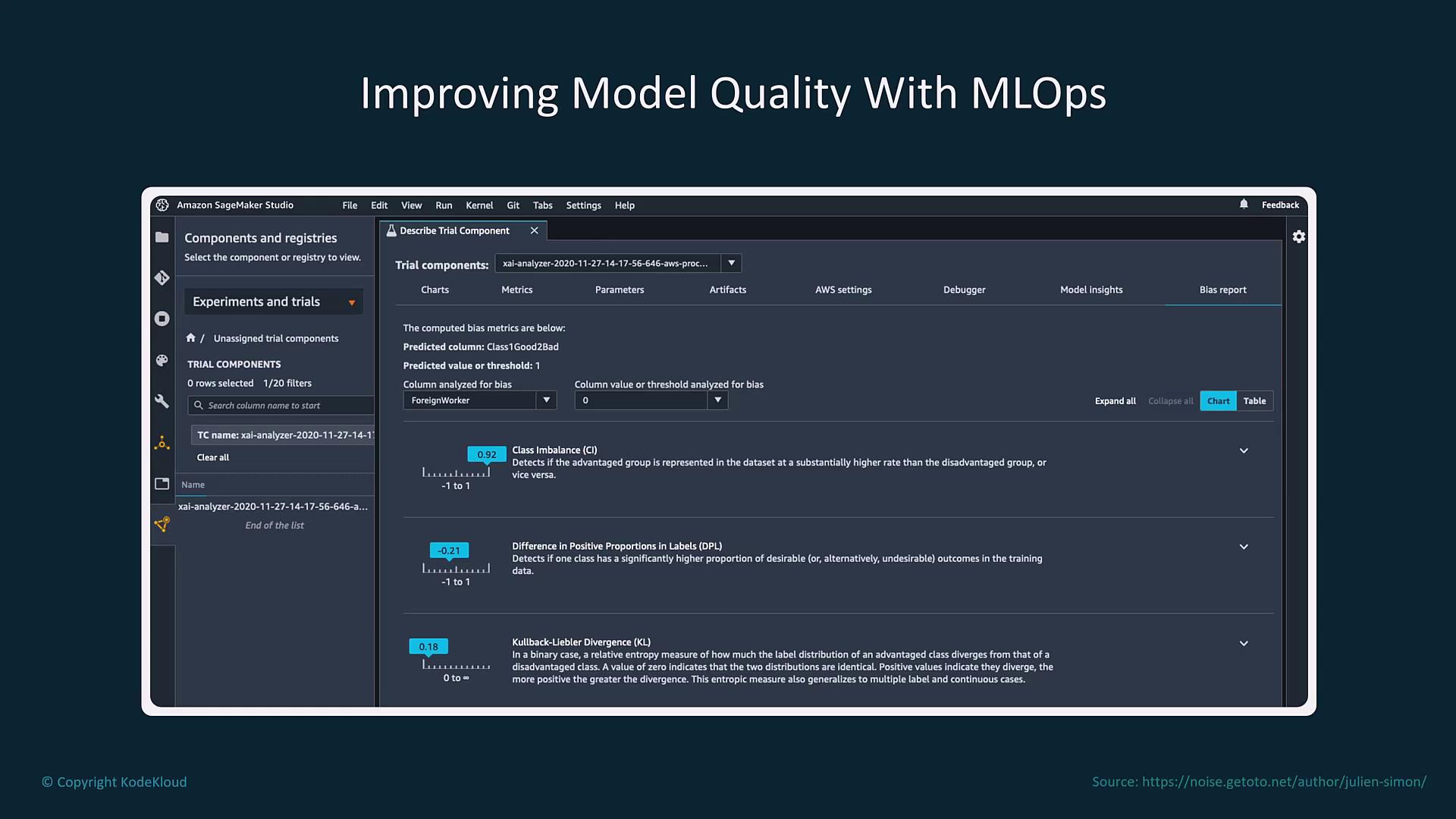


Evaluating Model Performance Metrics
Analyzing model performance is essential to validating and refining your machine learning solutions. Common performance metrics include:| Metric | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
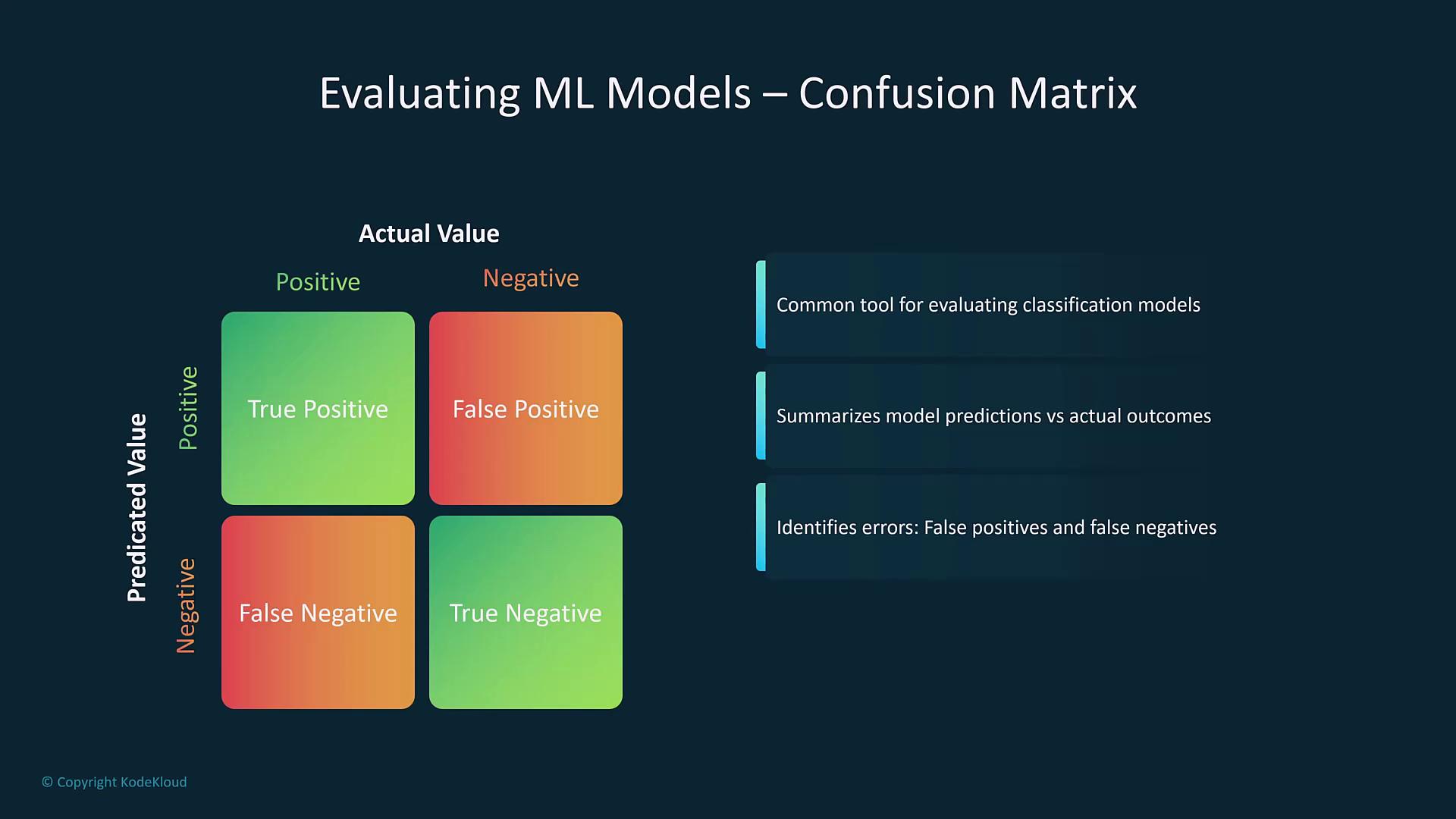
| Confusion Matrix | Summarizes predictions vs. actual outcomes (true positives, false positives, false negatives, true negatives). | Foundation for calculating accuracy, precision, and recall. |
| Accuracy | Ratio of correct predictions to total predictions. | Overall measure of model correctness. |
| Precision | Ratio of true positives to all positive predictions. | Crucial when the cost of false positives is high. |
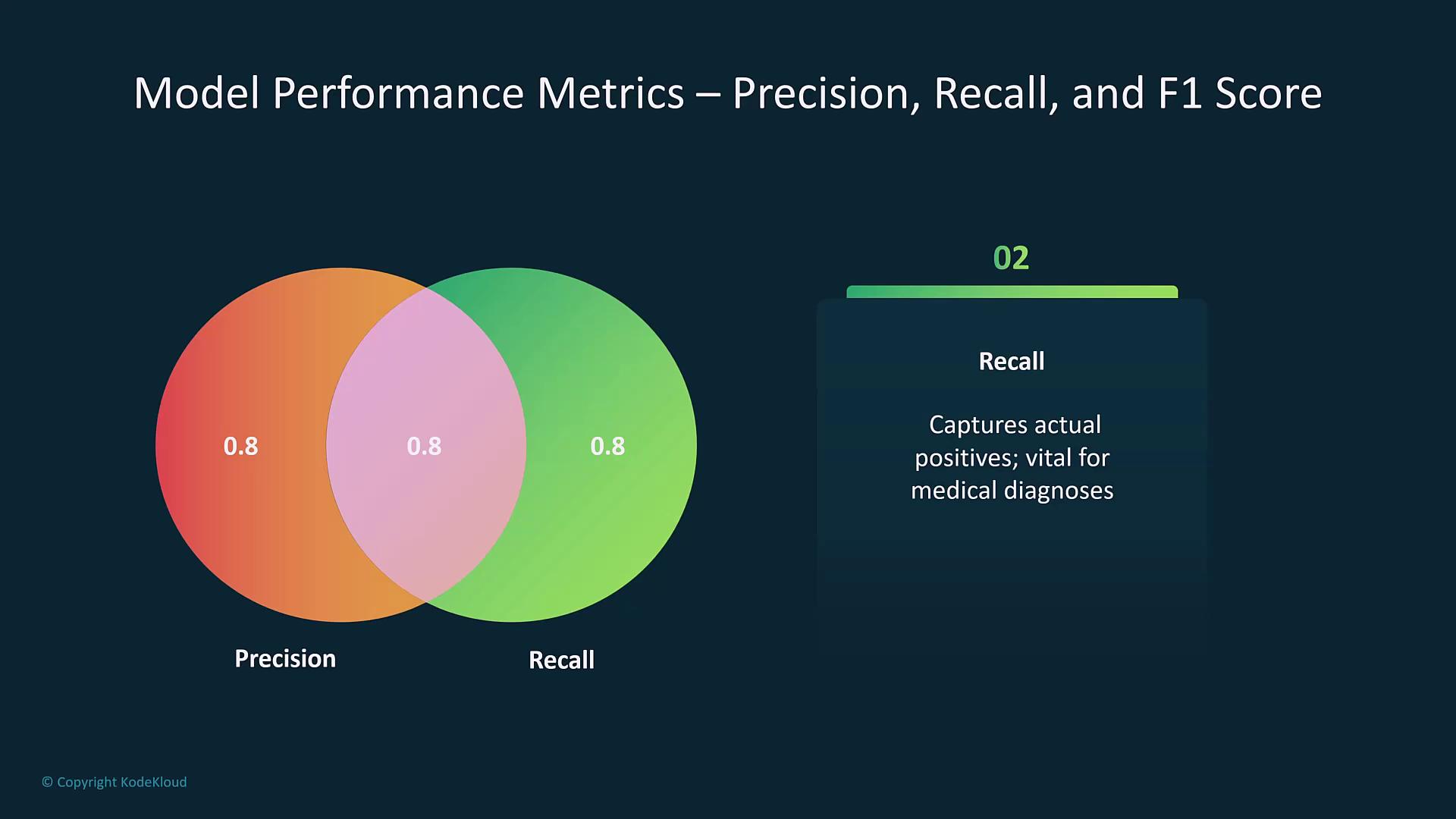
| Recall | Ratio of true positives to actual positives. | Vital when missing positive cases (false negatives) carries significant consequences. |
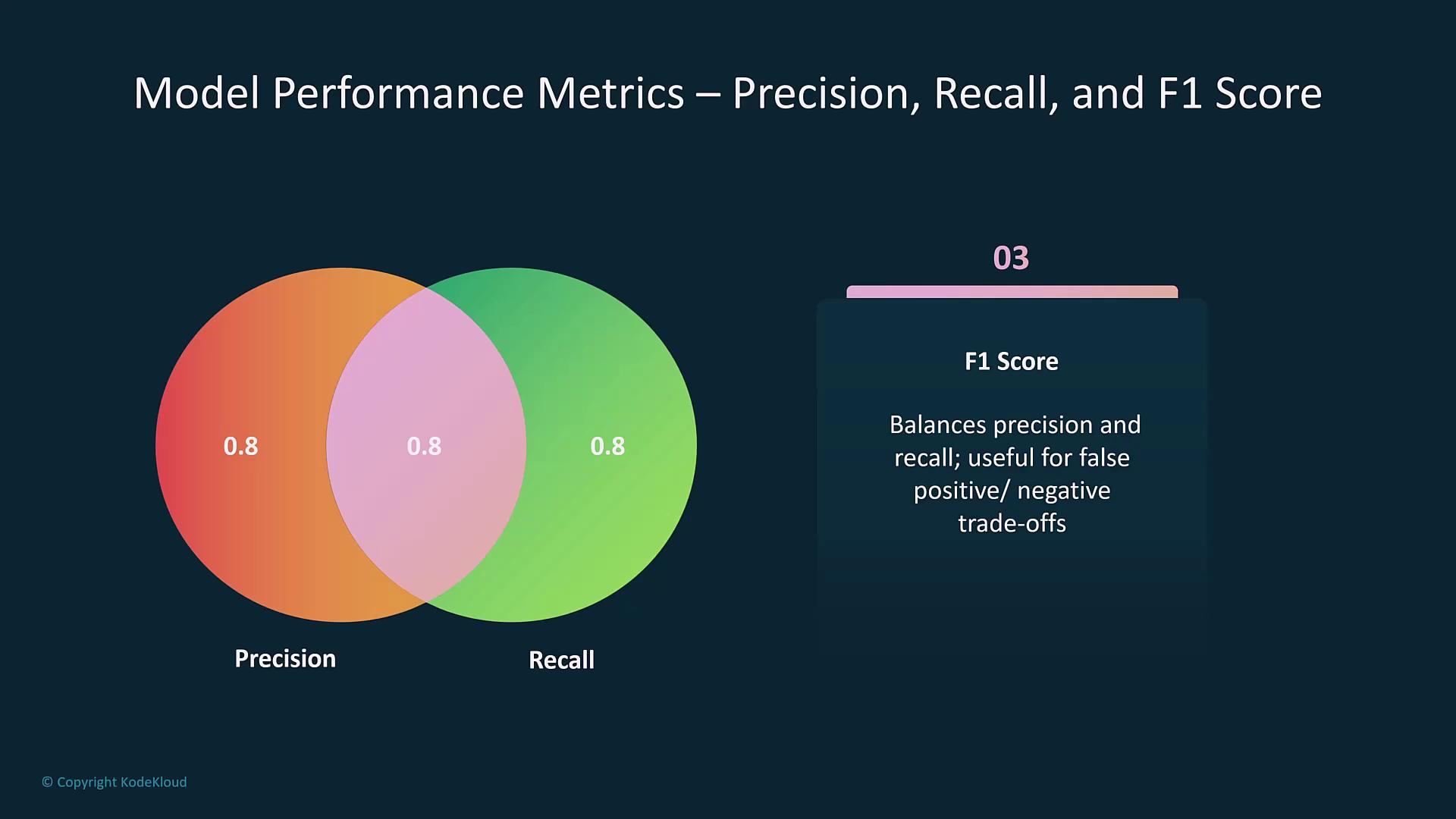
| F1 Score | Harmonic mean of precision and recall. | Balances precision and recall, especially for imbalanced datasets. |
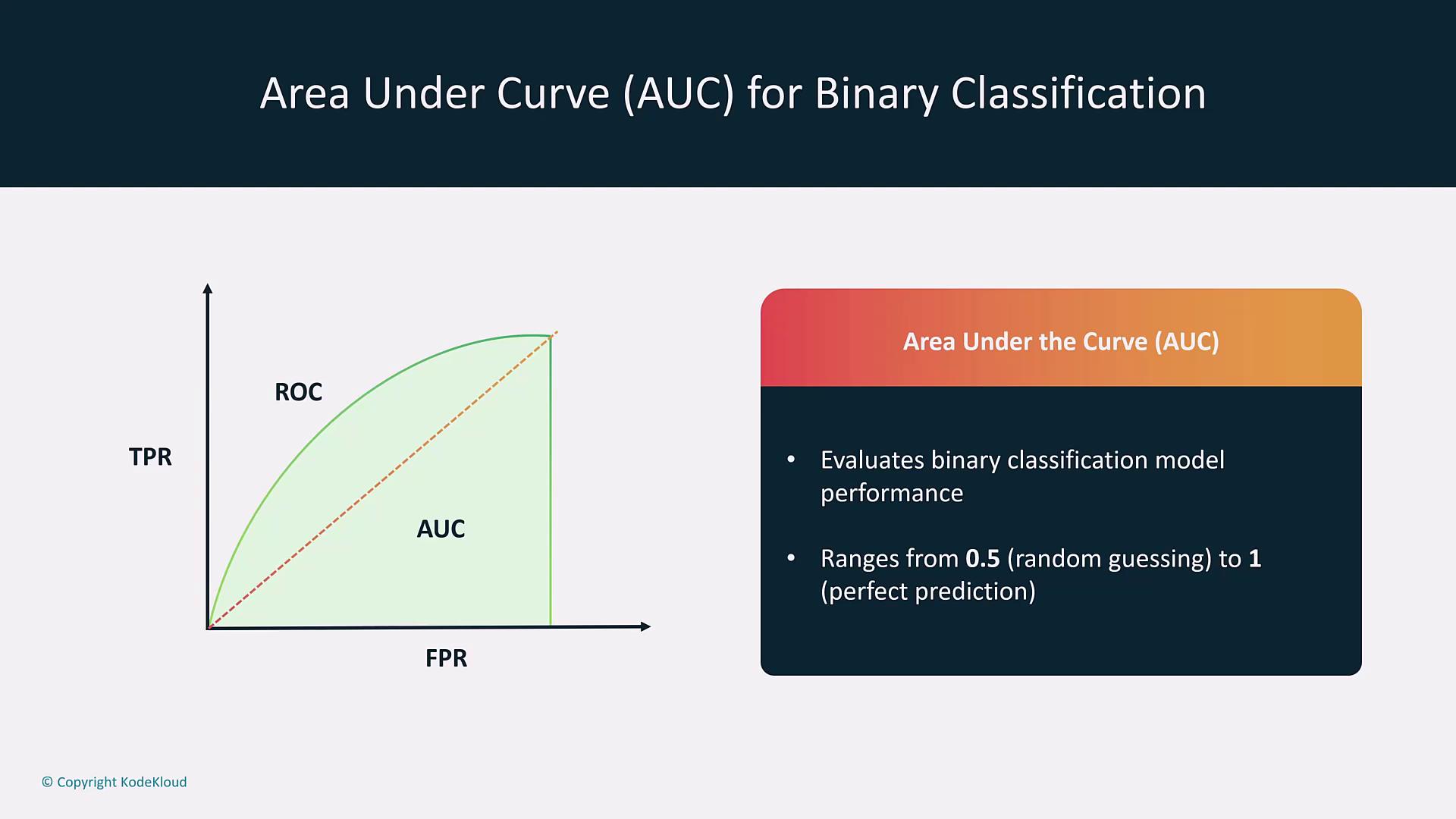
| Area Under the Curve (AUC) | Derived from the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve. | Measures classifier performance from 0.5 (random) to 1 (perfect prediction). |
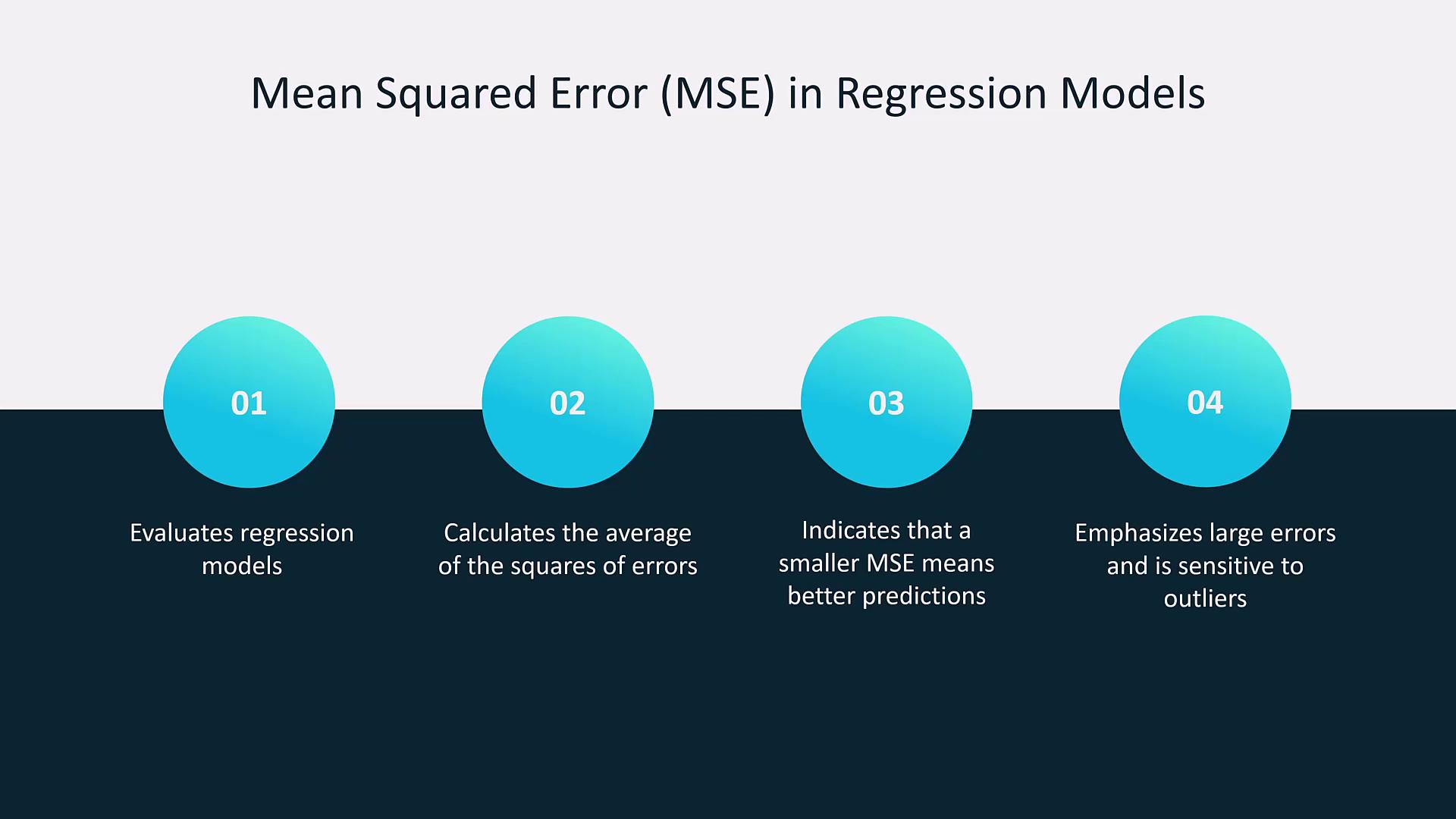
| Mean Squared Error (MSE) / RMSE | MSE: Average of squared differences; RMSE: Square root of MSE, in original units. | Essential for evaluating regression models, with RMSE highlighting large errors. |
Key Visualizations
- Confusion Matrix
- Precision, Recall, and F1 Score
- AUC and ROC Curve
- Mean Squared Error (MSE)/RMSE
Additional Tools for MLOps
MLOps leverages a range of AWS and third-party tools to support model lifecycle management and automation:-
Monitoring & Alerts:
Tools like Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor and Amazon CloudWatch track performance metrics and trigger alerts based on defined thresholds. -
Serverless Orchestration:
AWS Step Functions orchestrate serverless workflows, seamlessly integrating with Lambda functions and automating data processing pipelines.