Why Centralized Secrets Matter
GitHub supports two secret scopes:| Scope | Versioning | Management Overhead | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repository-level | No | High (per repo) | Single-repo deployments |
| Environment-level | No | High (per env) | Environment-specific workflows |
| Vault Secrets (HCP) | Yes | Low (centralized) | Multi-repo CI/CD pipelines |
1. Reviewing GitHub Repository Secrets
Most teams start by defining secrets directly in GitHub. You’ll find them at Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions.
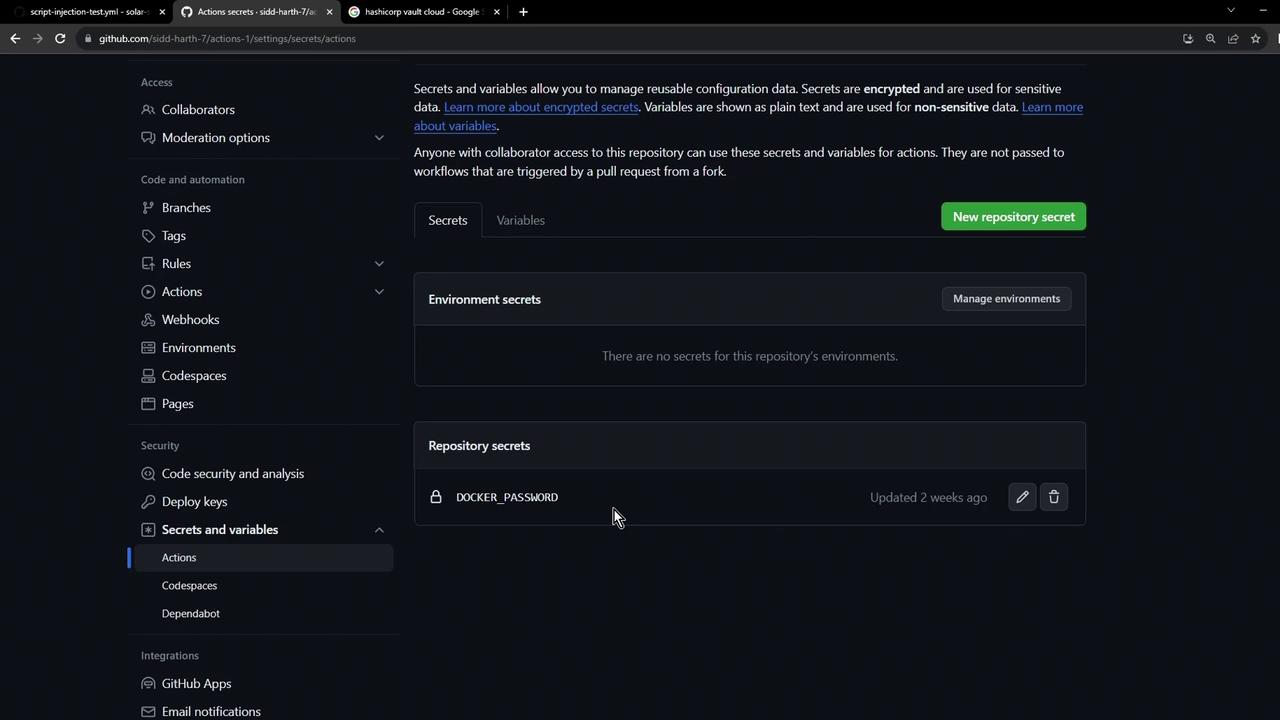
Repository-level secrets are not versioned. Managing them individually across many repos can quickly become tedious and error-prone.
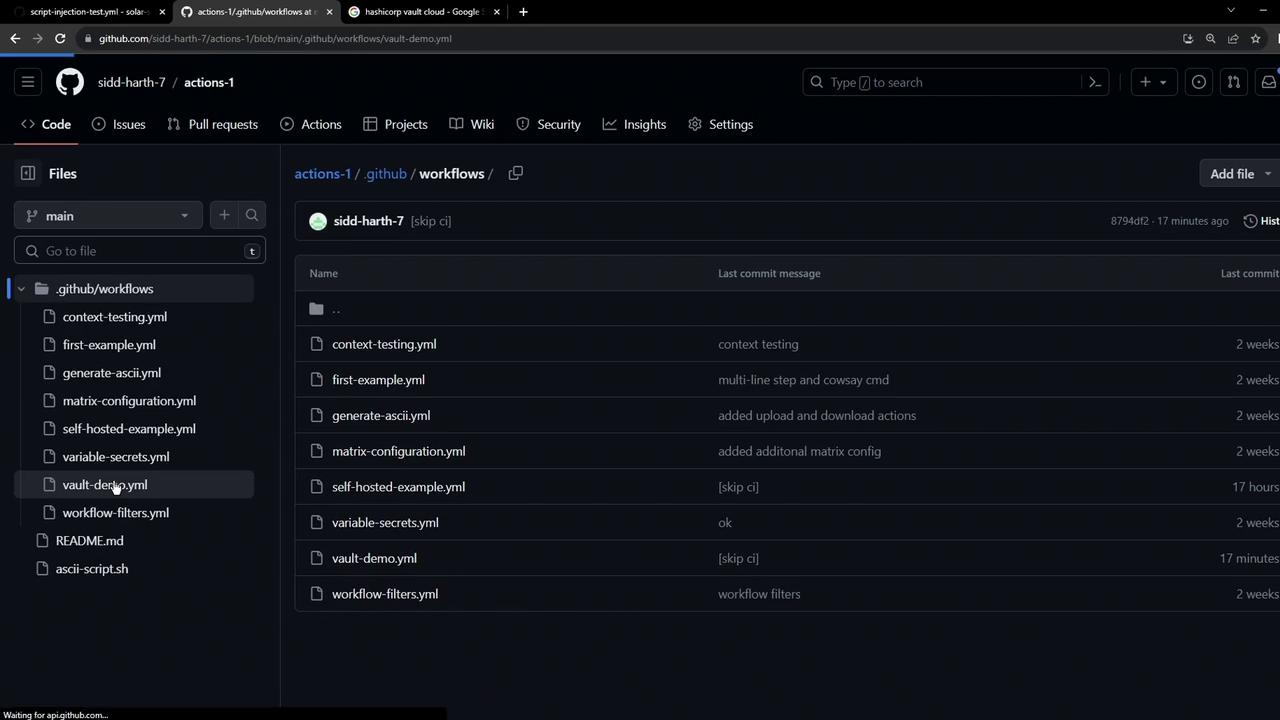
2. Setting Up a Simple Vault‐Demo Workflow
Create a workflow file at.github/workflows/vault-demo.yml:
3. Storing a Secret in HashiCorp Vault
- Sign in to the HashiCorp Cloud Platform and select Vault:

- In the HCP dashboard, click Vault Secrets to open the managed secrets service:
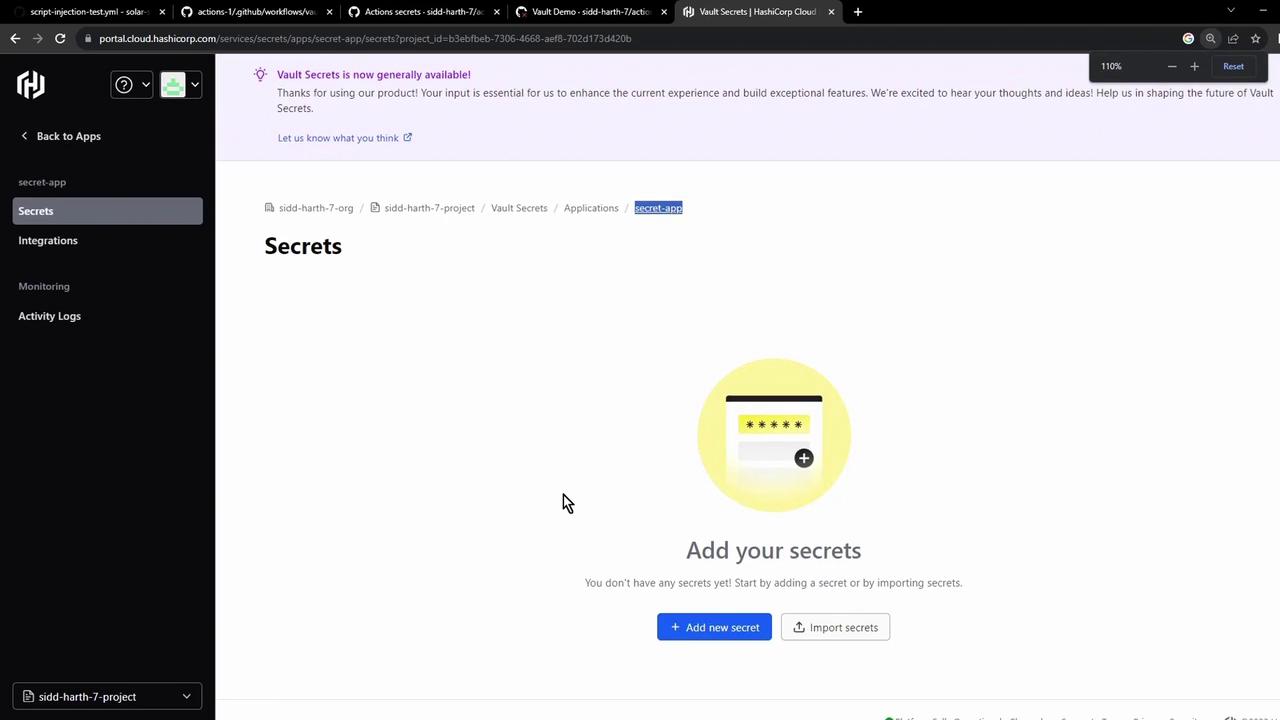
- Create an application (e.g., Secret App), then add a key
AWS_API_KEYwith your value:
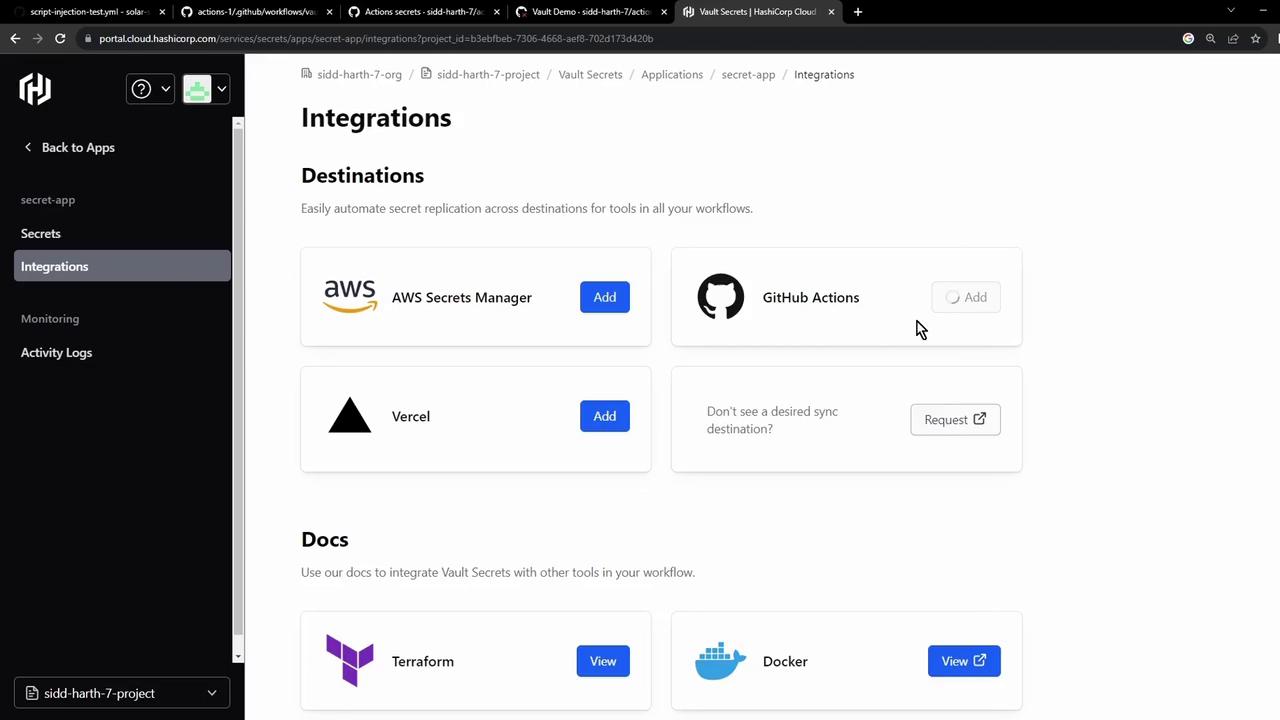
4. Integrating Vault Secrets with GitHub Actions
- In the Vault UI, go to Integrations → GitHub Actions, then authorize the GitHub App on your organization or account:
- Select the repo(s) to sync and install:
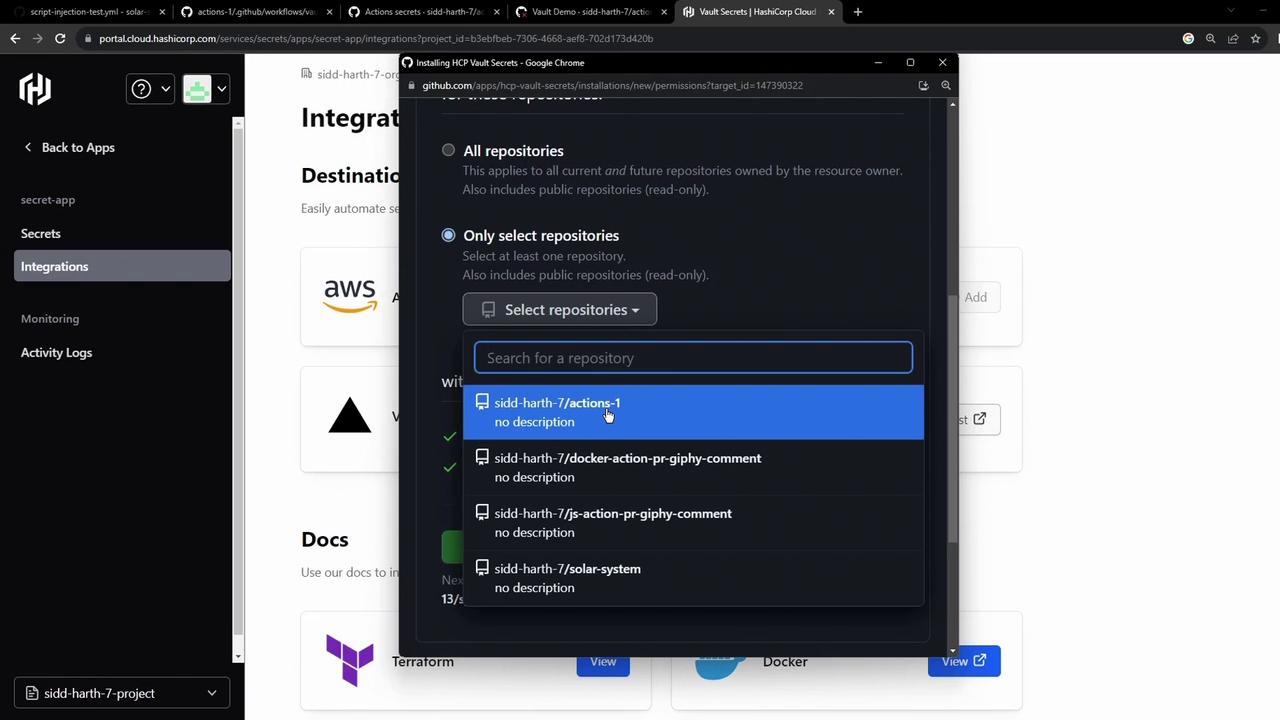
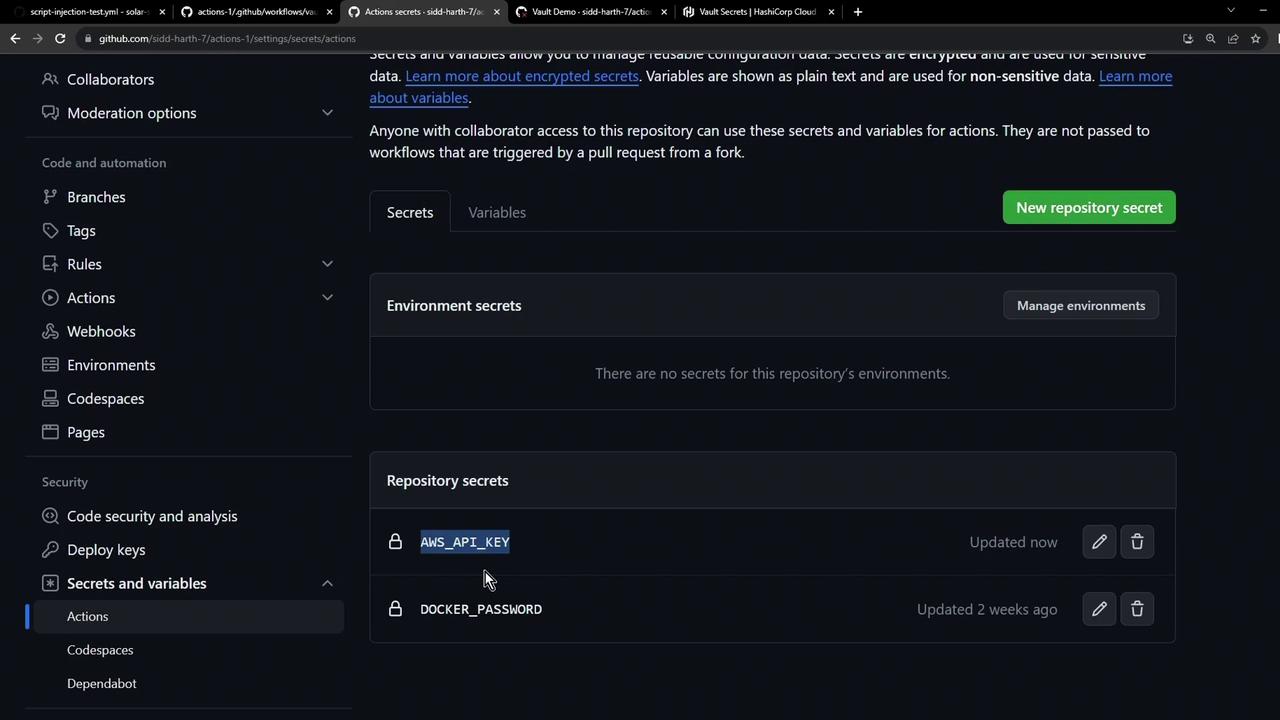
- After installation, Vault Secrets pushes
AWS_API_KEYto your repo. Refresh Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions:
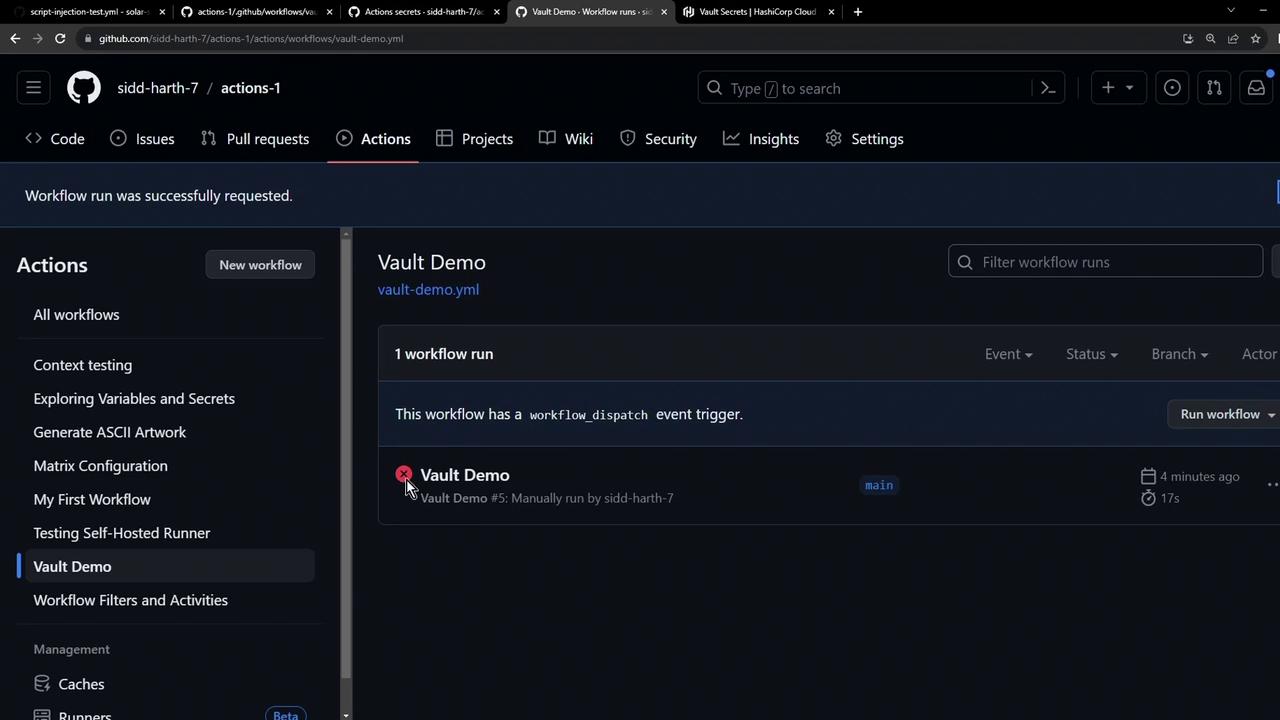
5. Verifying the Pipeline
If you ran the workflow before syncing, you might still see a failed status. Rerun to pick up the new secret.
Further Reading & References
- HashiCorp Vault Documentation
- GitHub Actions Secrets
- HCP Vault Secrets Overview
- Terraform Registry: vault Provider