• The
• The field
• The
affinity key under spec introduces the nodeAffinity configuration.• The field
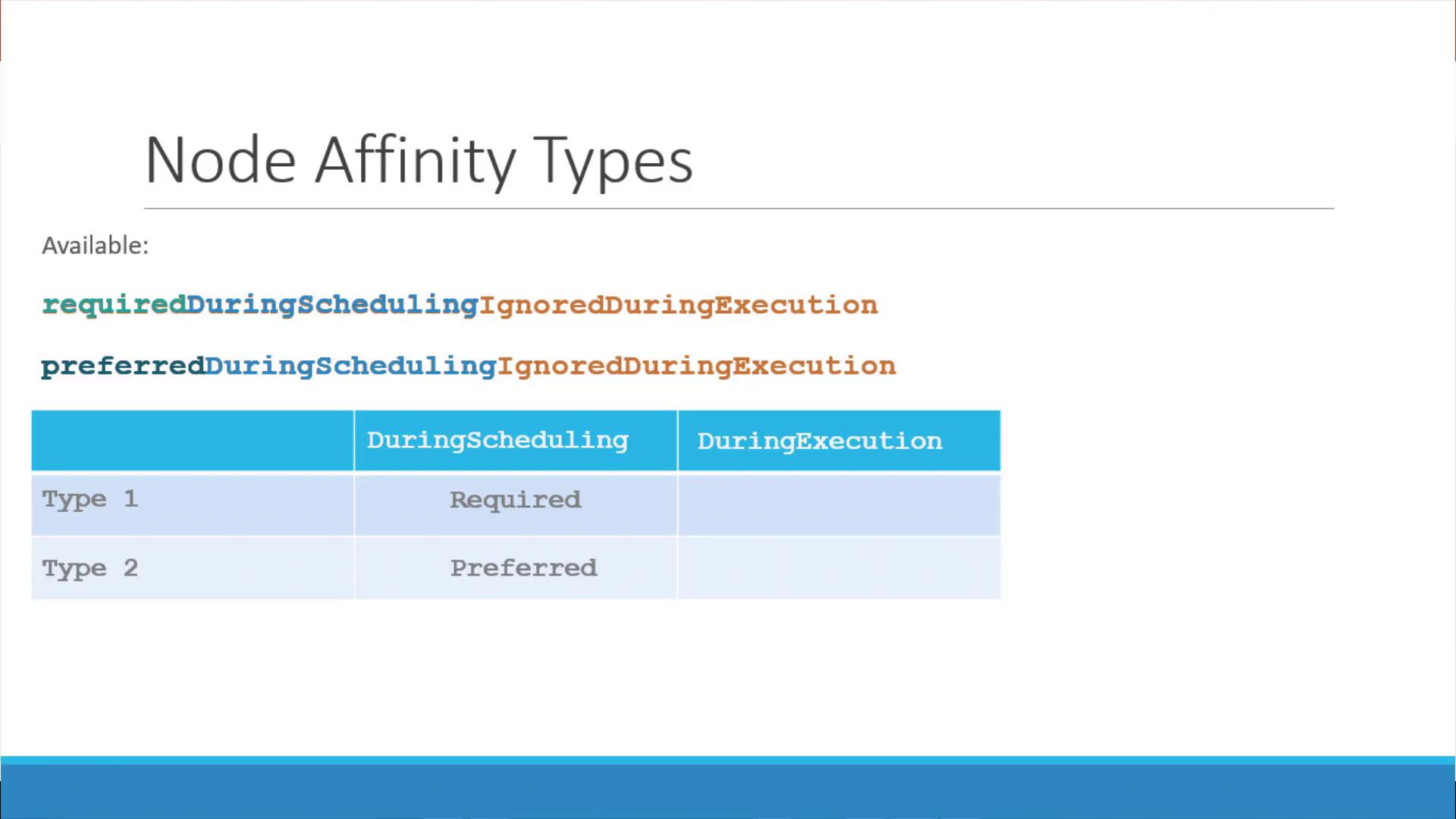
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution indicates that the scheduler must place the pod on a node meeting the criteria. Once the pod is running, any changes to node labels are ignored.• The
nodeSelectorTerms array contains one or more matchExpressions. Each expression specifies a label key, an operator, and a list of values. Here, the In operator ensures that the pod is scheduled only on nodes where the label size includes ‘Large’.NotIn operator to explicitly avoid placing a pod on nodes with specific labels. For example, to avoid nodes labeled as small:
Exists operator is useful. When using Exists, you do not provide a list of values:
Once a pod is scheduled using node affinity rules, these rules are only evaluated during scheduling. Changes to node labels after scheduling will not affect a running pod due to the “ignored during execution” behavior.
-
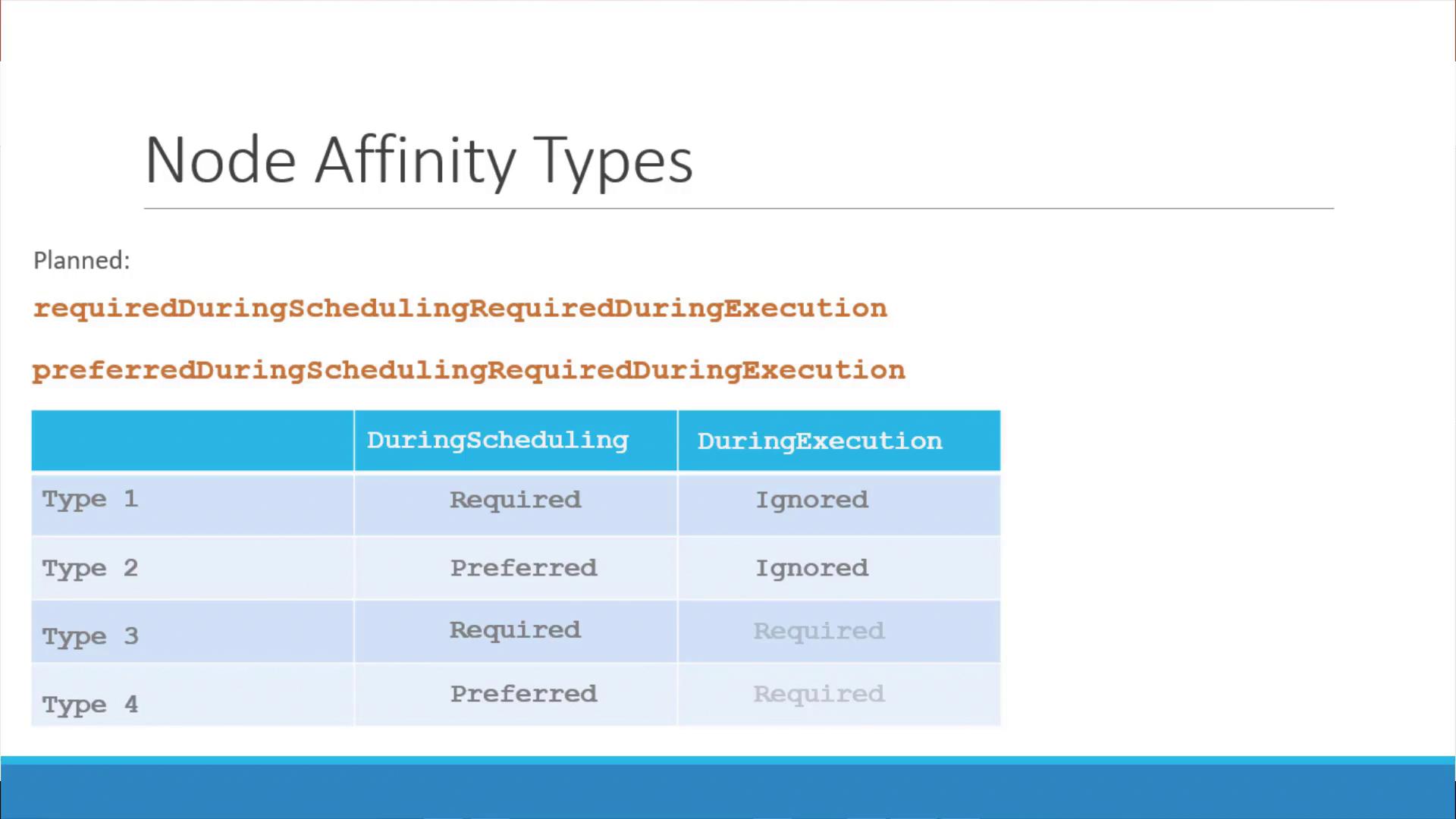
Required During Scheduling, Ignored During Execution
- The pod is scheduled only on nodes that fully satisfy the affinity rules.
- Once running, changes to node labels do not impact the pod.
-
Preferred During Scheduling, Ignored During Execution
- The scheduler prefers nodes that meet the affinity rules but will place the pod on another node if no matching nodes are available.
Summary
Node affinity empowers you to define sophisticated scheduling rules for pod placement based on node labels. Key takeaways include:- Using
nodeSelectorTermswithmatchExpressionsto specify rules. - Leveraging operators such as
In,NotIn, andExistsfor flexible matching. - Understanding the scheduling phases: during scheduling and after deployment (execution), and how they interact.