Key Components
Docker Engine consists of three primary parts that work together to build, ship, and run containers:- Docker Daemon (
dockerd)
The background service that manages images, containers, networks, and volumes on your host. - REST API
A set of HTTP endpoints that expose the daemon’s functionality to clients and automation tools. - Docker CLI (
docker)
The command-line interface that sends commands to the REST API.
From LXC to Libcontainer
When Docker launched in 2013, it used Linux Containers (LXC) to isolate processes via namespaces and cgroups. By version 0.9, Docker introduced Libcontainer, a Go library that interfaces directly with kernel primitives—eliminating the LXC dependency and simplifying container management.The Open Container Initiative (OCI)
Before 2015, container formats and runtimes were fragmented. Docker, CoreOS, and other industry leaders formed the Open Container Initiative (OCI) to standardize:- Runtime Specification
Defines lifecycle operations (create,start,delete, etc.). - Image Specification
Specifies how container images are formatted and distributed.
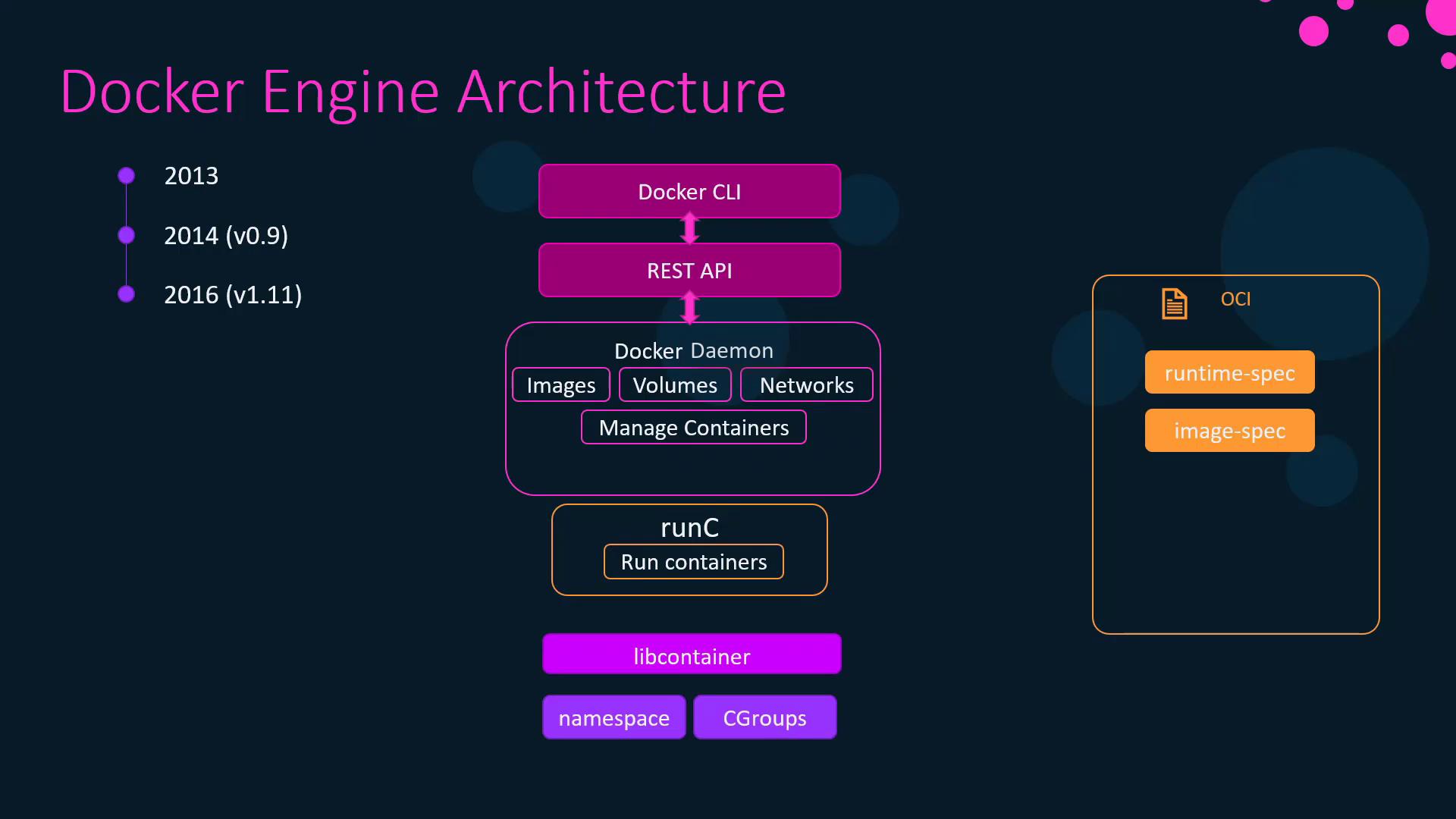
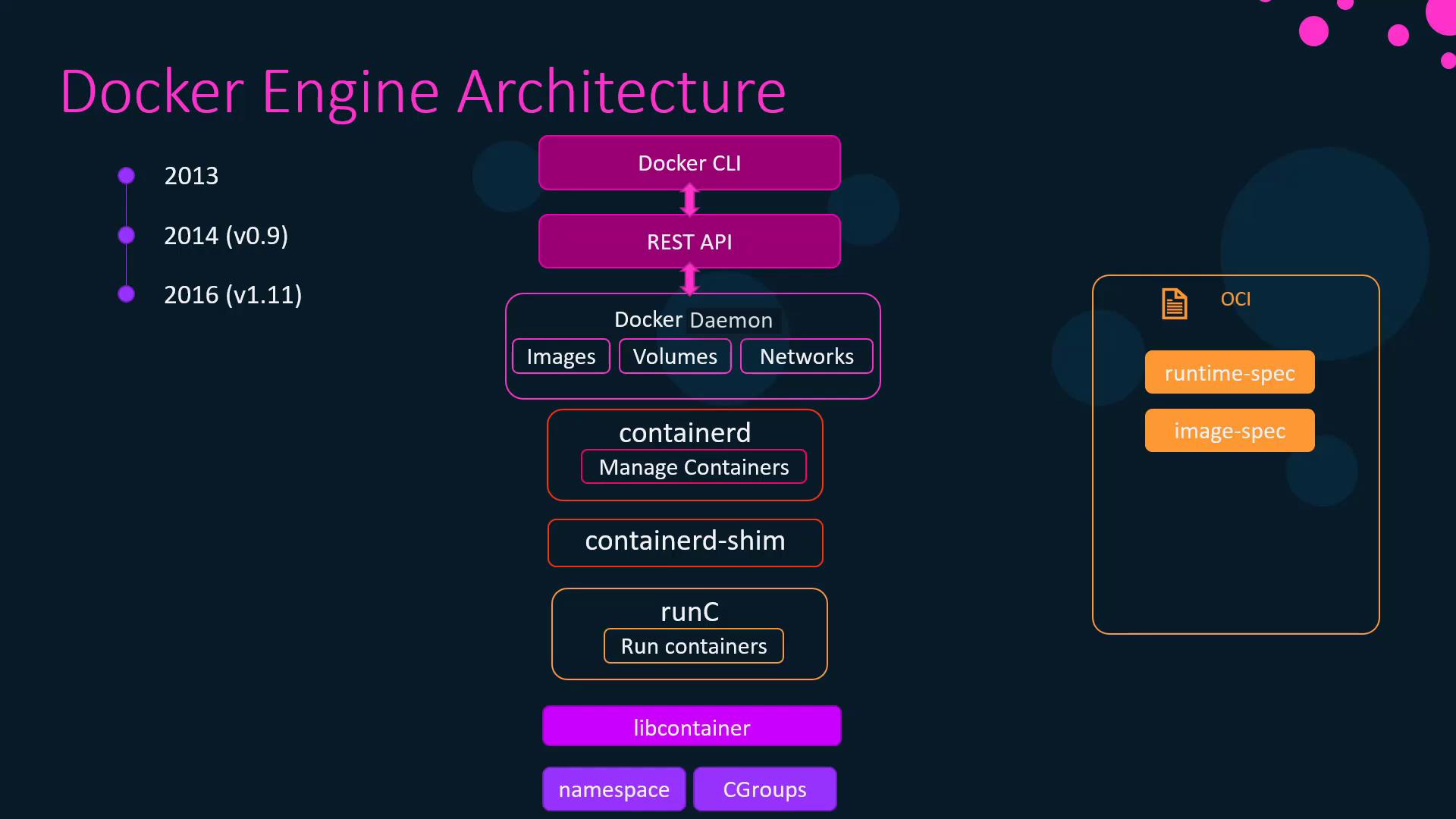
- runC
The OCI-compliant runtime that handles low-level container operations. - containerd
A daemon responsible for managing runC instances, image transfer, and storage. - containerd-shim
Allows containers to keep running independently of containerd, ensuring resilience if the daemon restarts.
Core Docker Objects
Docker Engine manages four primary resource types:| Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Images | Read-only templates composed of layered filesystem snapshots and metadata. |
| Containers | Instances of images providing a writable layer and running processes. |
| Networks | Virtual networks enabling container-to-container and external communication. |
| Volumes | Persistent storage volumes decoupled from container lifecycles. |
Docker Registry
A registry is a service for storing and distributing Docker images:- Docker Hub (default public registry)
- Private Registry (self-hosted)
- Docker Trusted Registry (DTR) (enterprise-grade, on-premises)
Container Creation Flow
When you rundocker run, Docker follows a series of steps:
- CLI to API
The Docker CLI translates your command into a REST API call. - Daemon Processing
The daemon checks for the image locally or pulls it from the registry. - containerd
Converts the image into an OCI bundle. - containerd-shim
Hands off the bundle to runC and monitors the container’s lifecycle. - runC
Uses kernel namespaces and cgroups to spawn and isolate the container.