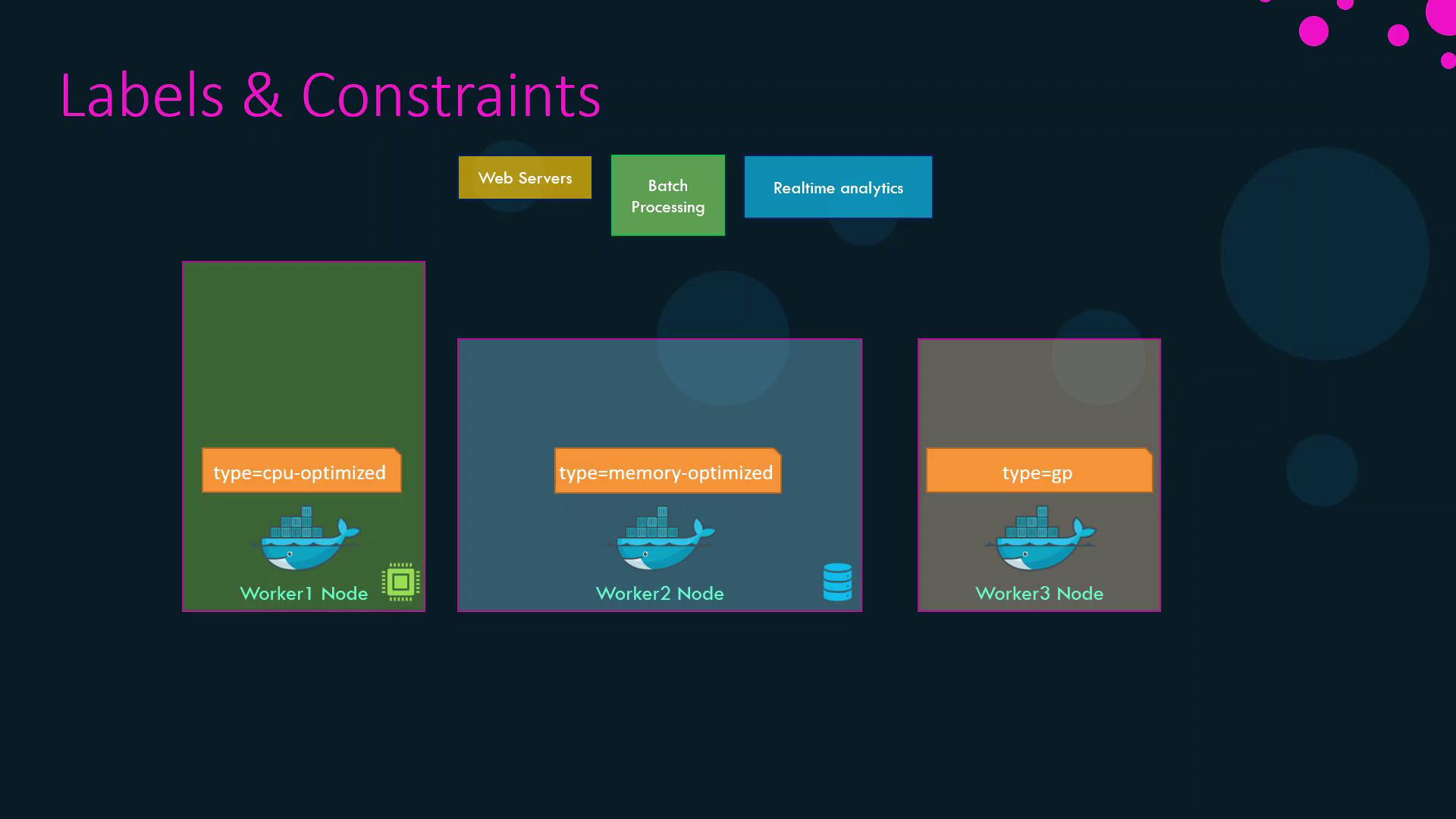
| Node Name | Label | Profile |
|---|---|---|
| worker1 | type=CPU-optimized | CPU-optimized (batch processing) |
| worker2 | type=memory-optimized | Memory-optimized (real-time analytics) |
| worker3 | type=GP | General-purpose (web servers) |
| Service Name | Resource Profile |
|---|---|
| batch-processing | CPU-intensive |
| realtime-analytics | Memory-intensive |
| web | General-purpose |
1. Labeling Nodes
Assign key-value labels to each node to reflect its resource profile:After labeling, confirm with:
2. Applying Placement Constraints
Use the--constraint flag with docker service create to bind services to nodes based on labels or built-in properties.
2.1 Match a Label
Schedule CPU-intensive and memory-intensive services on their respective optimized nodes:2.2 Exclude a Label
Prevent the web service from running on memory-optimized nodes:web is placed on either the CPU-optimized or general-purpose node.
Constraint expressions are case-sensitive and must be enclosed in quotes.
For more options, see the Service Create reference.
For more options, see the Service Create reference.
2.3 Using Built-in Node Properties
You can also constrain by node role. For example, to run a service only on worker nodes (excluding managers):3. Summary of Constraints
| Service Name | Constraint |
|---|---|
| batch-processing | node.labels.type==CPU-optimized |
| realtime-analytics | node.labels.type==memory-optimized |
| web | node.labels.type!=memory-optimized |
| worker-only-service | node.role==worker |