Why Use Replication Controllers?
Running a single Pod is risky—if it crashes, your application goes offline. A ReplicationController (RC) maintains a specified number of identical Pods, ensuring high availability and load distribution.- High availability: If one Pod fails, others continue serving traffic.
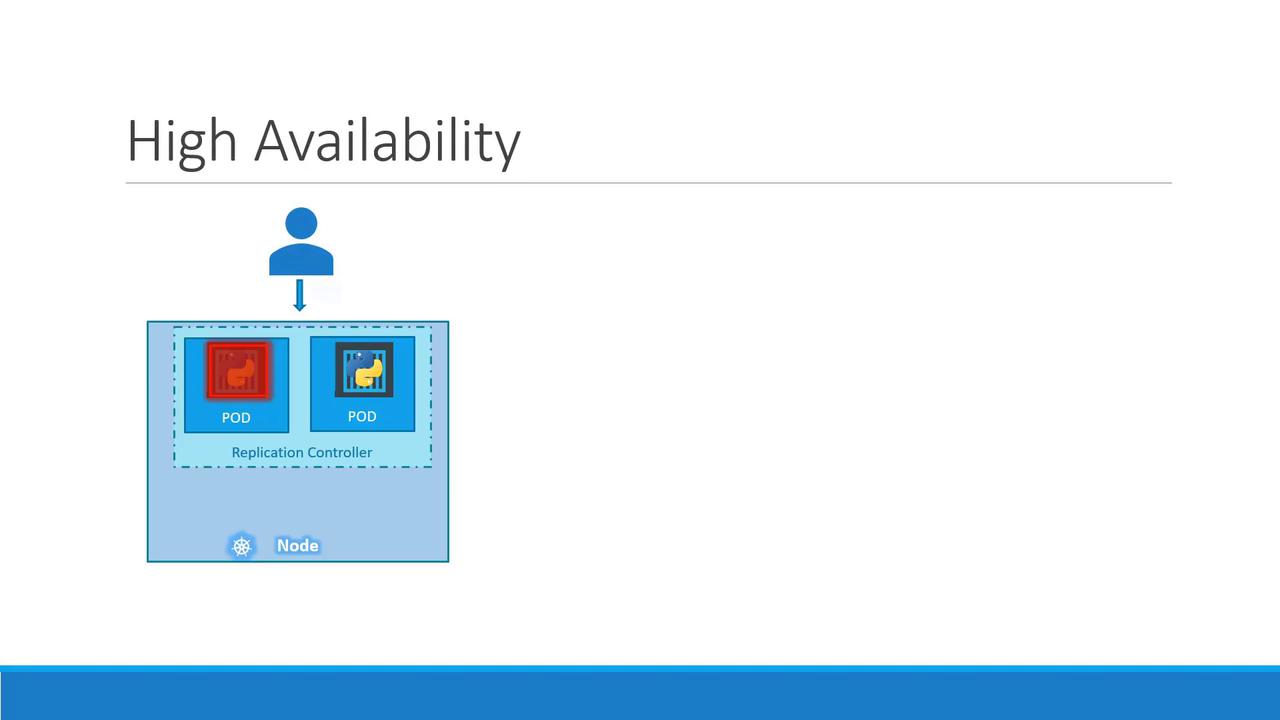
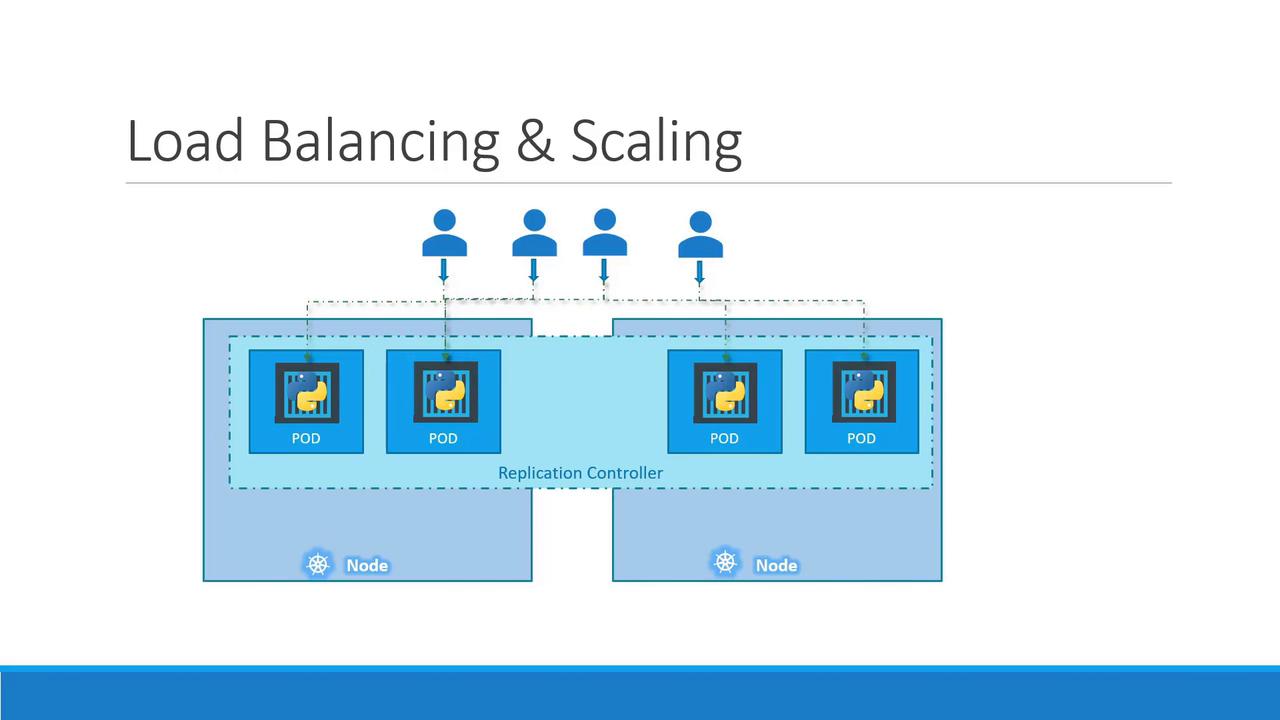
- Redundancy and load balancing across nodes:

- Scaling across nodes to meet growing demand:
ReplicationController vs. ReplicaSet
While both controllers maintain a set of Pod replicas, ReplicaSet (RS) is the modern API (apps/v1) and supports set-based label selectors. ReplicationController (v1) is older and has fewer selector capabilities. We recommend using ReplicaSets for new deployments.
| Feature | ReplicationController (v1) | ReplicaSet (apps/v1) |
|---|---|---|
| API Version | v1 | apps/v1 |
| Selector Support | Equality-based labels only | Equality & set-based label match |
| Recommended for Usage | Deprecated | Yes |
Creating a ReplicationController
-
Define
rc-definition.yaml: -
Apply the manifest and verify:
Example output:
-
List Pods managed by the RC:
Introducing ReplicaSets
A ReplicaSet manifest closely mirrors an RC, with two key differences:- apiVersion:
apps/v1 - selector: Required to match Pods
Labels and Selectors
Labels are key/value pairs attached to objects. A ReplicaSet’sspec.selector.matchLabels determines which Pods it manages—even pre-existing ones.
Example Pod with labels:
Scaling a ReplicaSet
You can adjust replica counts by editing the YAML or usingkubectl scale:
Option 1: Update replicas in replicaset-definition.yaml and apply:
Using
For automatic scaling based on metrics, see the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler.
kubectl scale updates in-memory replica counts but does not modify your source YAML file.For automatic scaling based on metrics, see the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler.
Command Cheat Sheet
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl create -f <file> | Create any Kubernetes object |
kubectl get <resource> | List resources (e.g., pods, rs) |
kubectl delete <resource> <name> | Delete a resource by name |
kubectl replace -f <file> | Update by replacing the manifest |
kubectl scale —replicas=<n> -f <file> | Scale replicas from the command line |