hostPath and AWS EBS volumes.
Volumes in Docker
Containers created by Docker are ephemeral by design: all data written inside a container is lost when it stops or is removed. To persist data across container restarts or recreations, you attach a volume at creation time.Docker volumes decouple container lifecycles from data lifecycles.
Learn more: Docker Volumes.
Learn more: Docker Volumes.
Volumes in Kubernetes
Kubernetes Pods inherit the same ephemeral behavior: when a Pod is deleted, its filesystem is wiped clean. To preserve data beyond a Pod’s lifecycle, define one or more volumes in the Pod spec and mount them into containers.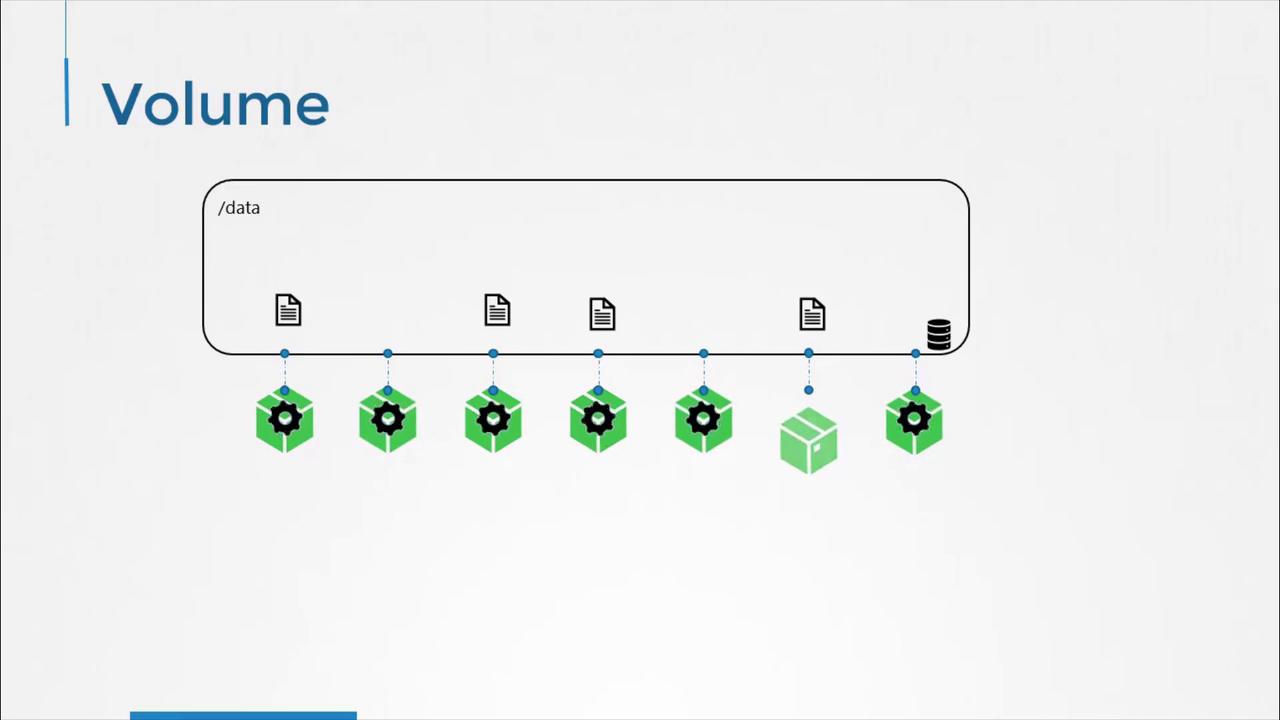
Example: Generating a Random Number with a hostPath Volume
The following Pod manifest demonstrates how to use ahostPath volume. Each time the Pod runs, it appends a random number to /opt/number.out. The underlying directory on the node (/data) retains all generated numbers, even after the Pod is deleted.
hostPath.pathpoints to/dataon the Kubernetes node.- The Pod’s container mounts this directory at
/opt. - Random numbers accumulate in
/data/number.outon the host.
hostPath volumes are bound to a single node’s filesystem and do not provide data sharing or high availability. Avoid using them in multi-node clusters.Storage Options for Kubernetes Volumes
Kubernetes supports a variety of volume types and storage backends. Below is a summary of common volume plugins:| Storage Type | Description | Example Volume Spec |
|---|---|---|
| NFS | Network File System for sharing | nfs.server:port,path |
| AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS) | Block storage in AWS | awsElasticBlockStore: { volumeID, fsType: ext4 } |
| Azure Disk | Managed disks in Azure | azureDisk: { diskName, diskURI, fsType } |
| Google Compute Engine Persistent Disk | Block storage in GCP | gcePersistentDisk: { pdName, fsType } |
| CephFS | Distributed file system | cephfs: { monitors, path, user } |
Example: AWS EBS Volume
To switch from ahostPath volume to AWS EBS, replace the hostPath section with an awsElasticBlockStore definition in your Pod spec: