main and watch Auto DevOps deploy to production using an incremental canary strategy.
1. Merge into main and Trigger Production Pipeline
Once the Merge Request is accepted, GitLab triggers a new pipeline on the protected main branch. This pipeline adds deployment stages on top of the build, test, DAST and performance jobs.
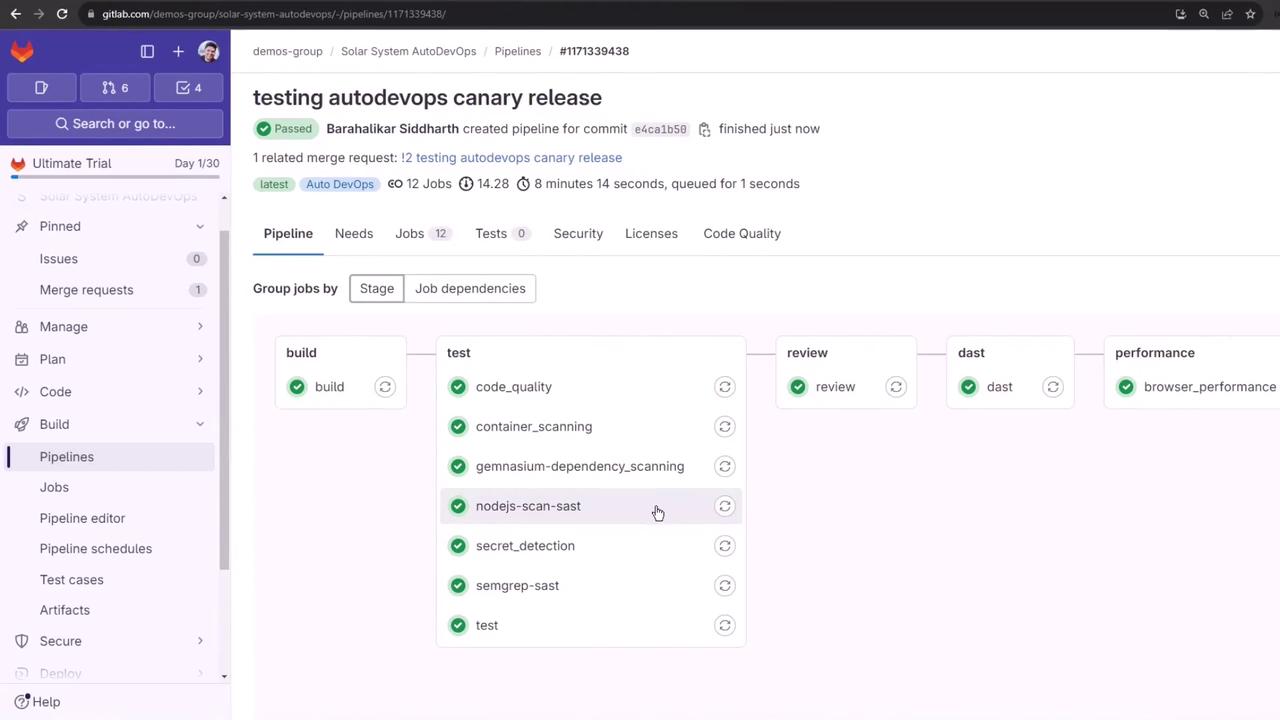
- build
- test
- review (DAST)
- staging
- production rollout (10%, 25%, 50%, 100%)
- performance
- cleanup
Cancelling Unneeded Jobs
If you need to skip rerunning certain tests, you can:- Manually cancel jobs in the GitLab UI
- Disable specific jobs via Settings > CI/CD
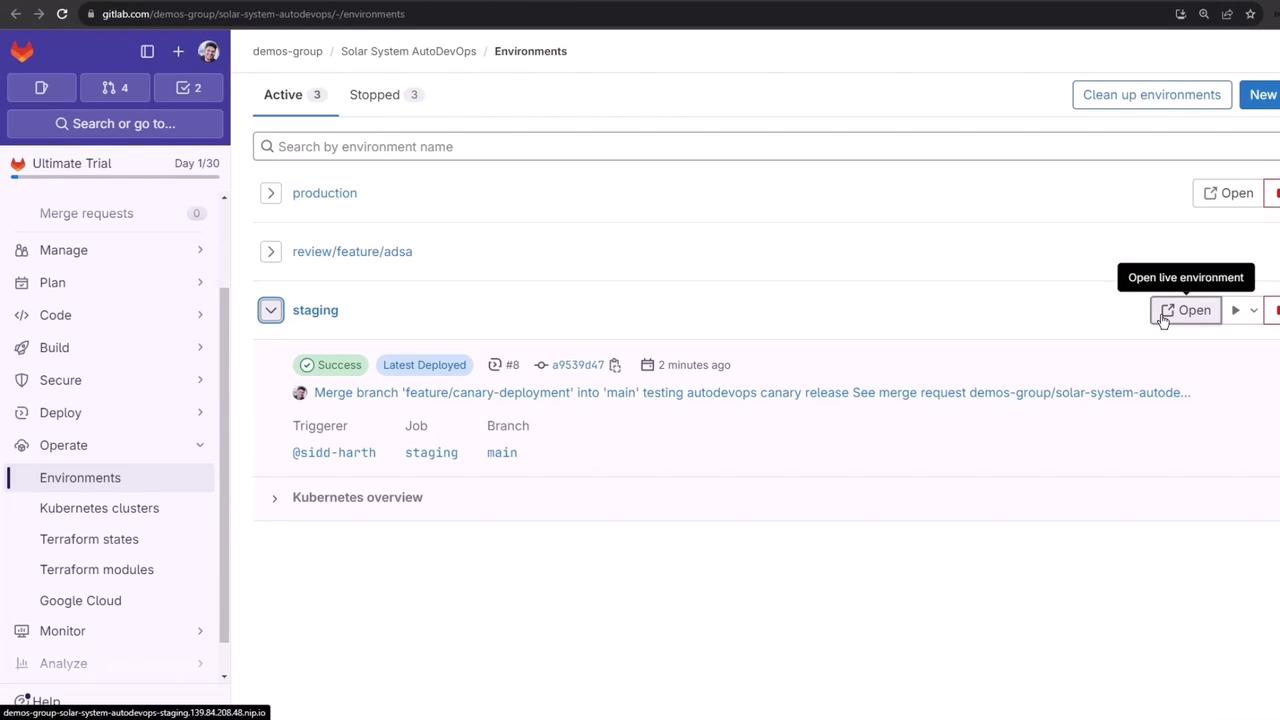
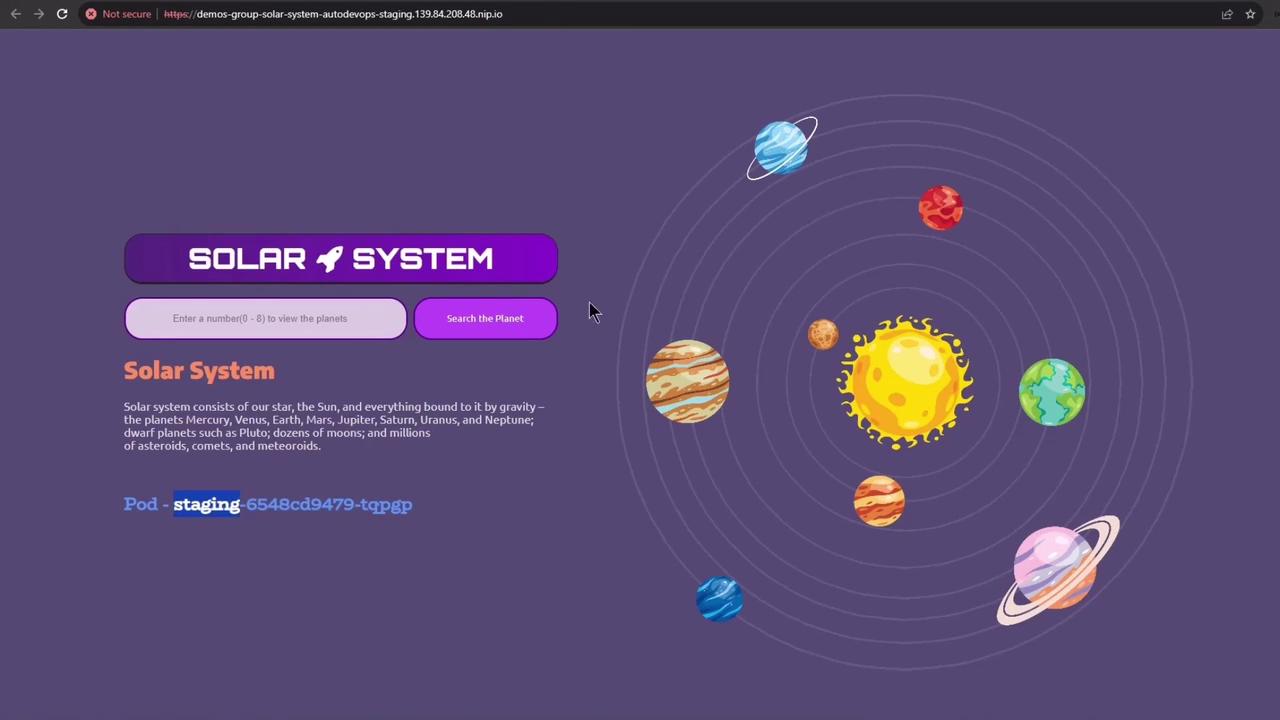
2. Staging Deployment
After build, test, and DAST succeed, thestaging job deploys to the staging namespace and then waits for the production approval.
By default, Auto DevOps deploys to staging before production. To skip staging and deploy directly to production, set the CI/CD variable:
3. Manual Production Deployment
Production is a protected environment requiring manual approval. Before rolling out, inspect current production workloads: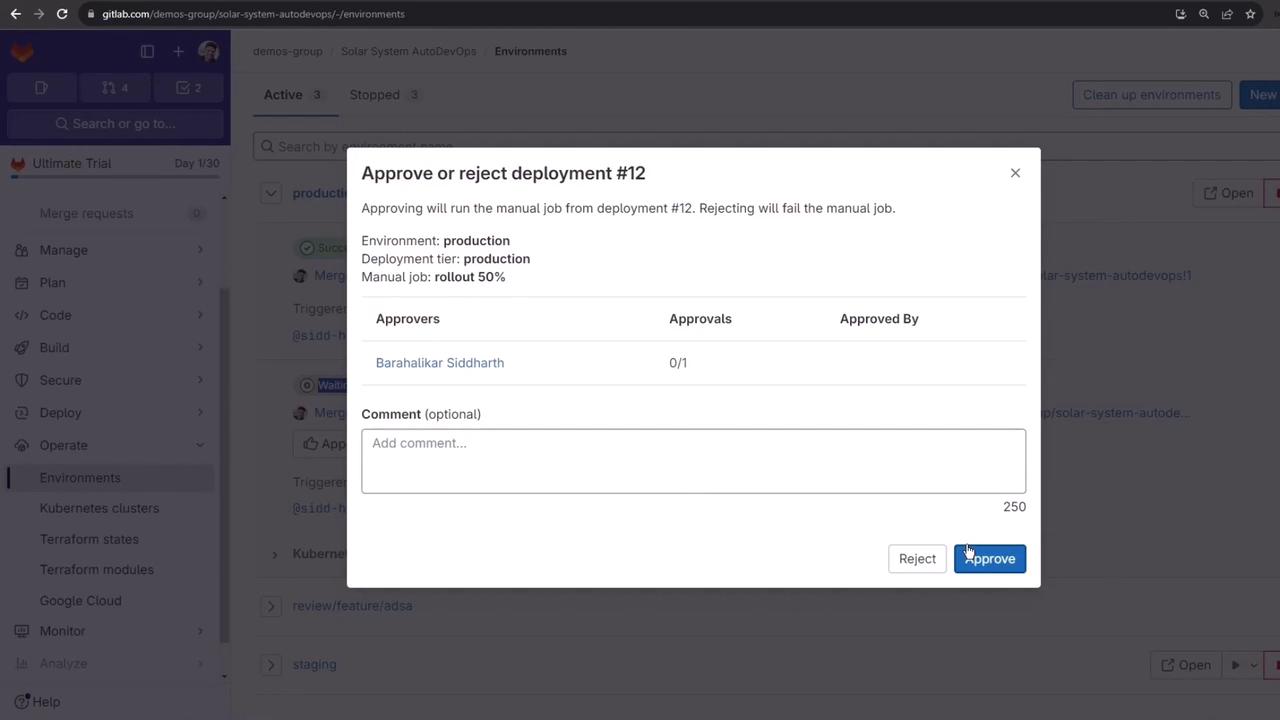
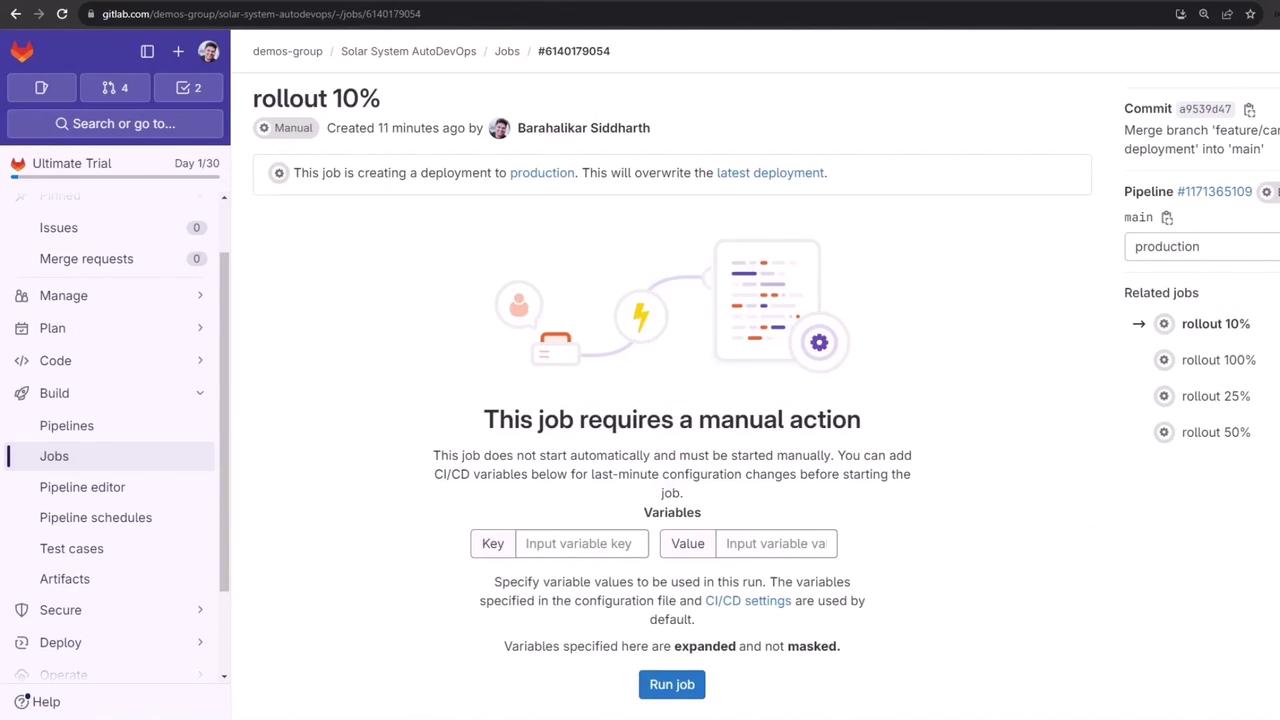
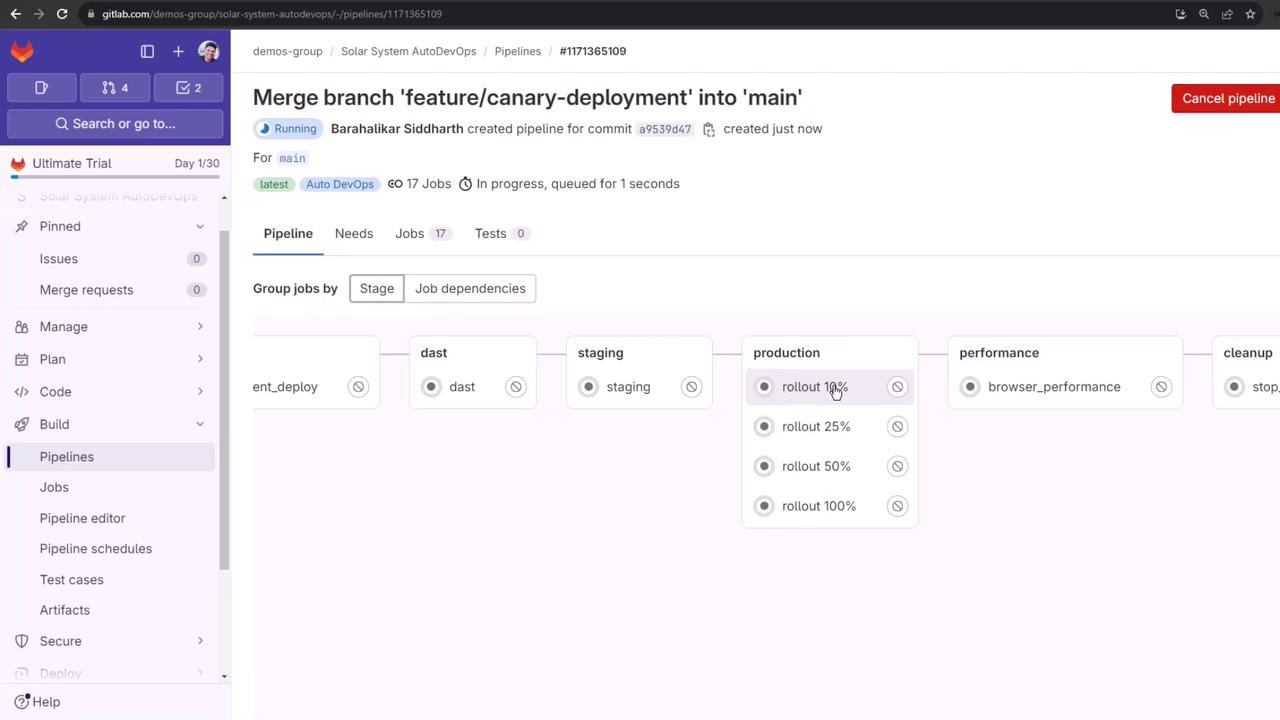
4. Canary Rollouts
Use incremental percentages to minimize risk. Below is a summary of each stage:| Rollout Stage | Percentage | Verification Command |
|---|---|---|
| Canary | 10% | kubectl -n production get pods |
| Midway | 50% | kubectl -n production get svc |
| Full Release | 100% | kubectl -n production get pods (only primary pods) |
4.1 10% Canary
The job log runs:4.2 50% Midway
Approve and Run job for 50% rollout. After success, the weight updates:
4.3 100% Full Release
Approve and Run job for 100% rollout to merge canary into the primary deployment and remove the canary service: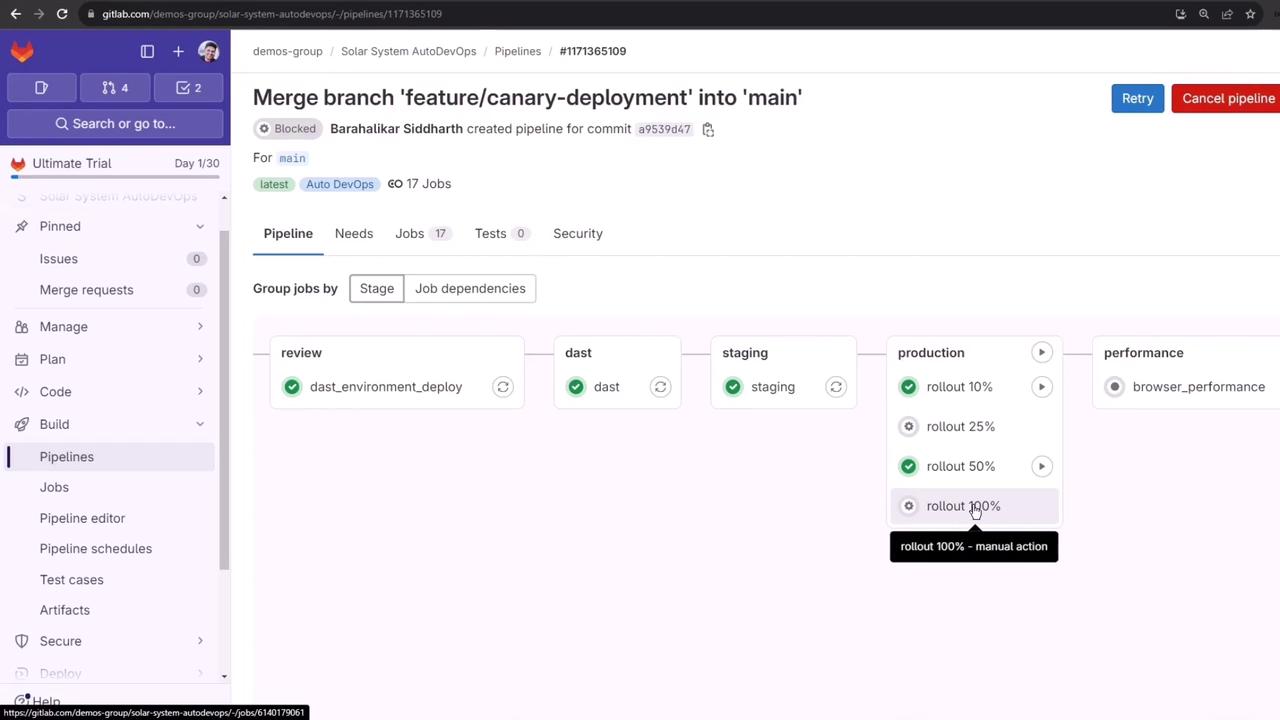
What You Learned
- How Auto DevOps orchestrates staging and production deployments
- Manual approval workflows for protected environments
- Incremental canary rollouts (10%, 50%, 100%) with traffic validation
- Automatic cleanup of canary resources