- Connecting your clusters: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/clusters/agent/
- GitOps with FluxCD in GitLab CI/CD: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/clusters/agent/gitops_with_fluxcd.html
Prerequisites
- A GitLab project with Owner or Maintainer role
kubectlconfigured to target your cluster- Helm 3 installed locally
1. Navigate to Kubernetes Integration
- In your GitLab project, select Operate → Kubernetes clusters.
- Click Connect a cluster (skip the managed-cluster wizard if you already have one).
2. Verify Local Cluster Access
Confirm you can reach the cluster from your terminal:| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
kubectl get nodes | List cluster nodes |
kubectl config get-contexts | Show active context |
kubectl get namespaces | List existing namespaces |
3. Create a New Agent in GitLab
In the Connect a cluster dialog:- Choose Add an agent configuration → Create a new agent.
- Enter a name (for example,
kk-gitlab-agent). - Click Create agent to generate a one-time access token.
Copy and securely store the generated token now—this value is shown only once.
4. Install the Agent via Helm
Add the GitLab Helm repo and deploy the agent chart:- Add and update the GitLab charts repository
- Install (or upgrade) the
kk-gitlab-agentrelease - Create namespace
gitlab-agent-kk-gitlab-agentif it doesn’t exist - Connect to the GitLab Agent Server (KAS) using your token
Verify the Helm Release
5. Inspect Deployed Resources
Check pods, deployments, replica sets, config maps, and secrets:6. Confirm Connection in GitLab
Return to Operate → Kubernetes clusters in your project and refresh.The cluster’s Connection Status should now display Connected and active.
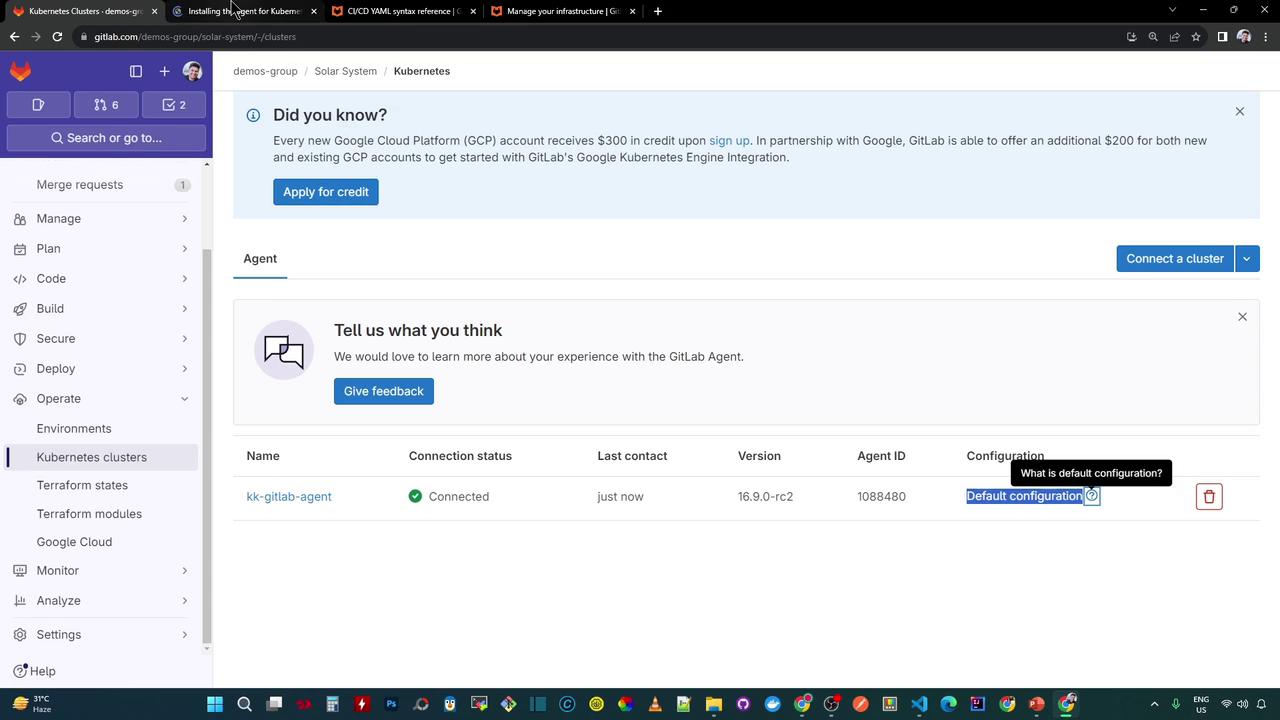
By default, GitLab applies the agent’s built-in config. To customize it, create a file at:Refer to the official documentation for configuration options.
Next Steps
- Define a custom
config.yamlto enable GitOps and environment deployments - Create and annotate environments to surface cluster metrics in the GitLab UI