In this guide, we’ll walk through creating a Kubernetes Secret and deploying application manifests to the development namespace using GitLab CI/CD. You’ll learn how to integrate secret creation into your pipeline and verify a successful deploy.
1. Verify the Development Namespace First, confirm the development namespace is clean:
kubectl -n development get all
No resources found in development namespace.
Always ensure you’re targeting the correct namespace before deploying to avoid unintended changes.
2. Initial CI Job Definition Here’s a basic k8s_dev_deploy job from .gitlab-ci.yml:
k8s_dev_deploy : stage : dev-deploy image : alpine:3.7 dependencies : [] before_script : - wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(wget -q -O - https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl - chmod +x ./kubectl && mv ./kubectl /usr/bin/kubectl - apk add --no-cache gettext - envsubst -V script : - export KUBECONFIG=$DEV_KUBE_CONFIG - kubectl version -o yaml - kubectl config get-contexts - kubectl get nodes - export INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx get service ingress-nginx-controller -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}") - for manifest in kubernetes/manifest/*.yaml; do envsubst < $manifest | kubectl apply -f - done
At this stage, deployment will fail because the application requires a mongo-db-creds secret that doesn’t exist yet.
3. Required Manifests Define the Kubernetes resources for your application. Below are two essential manifest examples:
Ingress apiVersion : networking.k8s.io/v1 kind : Ingress metadata : name : solar-system namespace : ${NAMESPACE} annotations : kubernetes.io/ingress.class : nginx kubernetes.io/tls-acme : "true" spec : rules : - host : solar-system-${NAMESPACE}.${INGRESS_IP}.nip.io http : paths : - path : / pathType : Prefix backend : service : name : solar-system port : number : 3000 tls : - hosts : - solar-system-${NAMESPACE}.${INGRESS_IP}.nip.io secretName : ingress-local-tls
Deployment apiVersion : apps/v1 kind : Deployment metadata : name : solar-system namespace : ${NAMESPACE} spec : replicas : ${REPLICAS} selector : matchLabels : app : solar-system template : metadata : labels : app : solar-system spec : containers : - name : solar-system image : ${K8S_IMAGE} imagePullPolicy : Always ports : - name : http containerPort : 3000 envFrom : - secretRef : name : mongo-db-creds
Resource Purpose Ingress Route HTTP/TLS traffic to the service Deployment Manage pods, replicas, and rolling updates
The mongo-db-creds secret must include:
MONGO_URIMONGO_USERNAMEMONGO_PASSWORD
4. Create Secret and Update CI Job Incorporate secret creation into your pipeline before applying manifests:
k8s_dev_deploy : stage : dev-deploy image : alpine:3.7 dependencies : [] before_script : - wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(wget -q -O - https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl - chmod +x ./kubectl && mv ./kubectl /usr/bin/kubectl - apk add --no-cache gettext - envsubst -V script : - export KUBECONFIG=$DEV_KUBE_CONFIG - INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx get service ingress-nginx-controller -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}") - echo "Ingress IP : $INGRESS_IP" - kubectl -n $NAMESPACE create secret generic mongo-db-creds \ --from-literal=MONGO_URI="$MONGO_URI" \ --from-literal=MONGO_USERNAME="$MONGO_USERNAME" \ --from-literal=MONGO_PASSWORD="$MONGO_PASSWORD" \ --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f - - for manifest in kubernetes/manifest/*.yaml; do envsubst < $manifest | kubectl apply -f - done - kubectl -n $NAMESPACE get all,secret,ingress
Using --dry-run=client -o yaml ensures idempotent secret creation.
5. Pipeline Configuration Define the overall GitLab pipeline, stages, and variables:
workflow : name : Solar System NodeJS Pipeline stages : - test - containerization - dev-deploy variables : DOCKER_USERNAME : siddharth67 IMAGE_VERSION : $CI_PIPELINE_ID K8S_IMAGE : $DOCKER_USERNAME/solar-system:$IMAGE_VERSION MONGO_URI : 'mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83ji.mongodb.net/superData' MONGO_USERNAME : superuser MONGO_PASSWORD : $M_DB_PASSWORD
Variable Description DOCKER_USERNAMEDocker Hub username IMAGE_VERSIONImage tag (CI pipeline ID) K8S_IMAGEFull image name for Kubernetes pull MONGO_*MongoDB connection credentials
Include a containerization job if needed:
docker_build : stage : containerization image : docker:24.0.5 services : - docker:24.0.5-dind script : - docker load -i image/solar-system-image:$IMAGE_VERSION.tar - docker login --username=$DOCKER_USERNAME --password=$DOCKER_PASSWORD - docker push $K8S_IMAGE
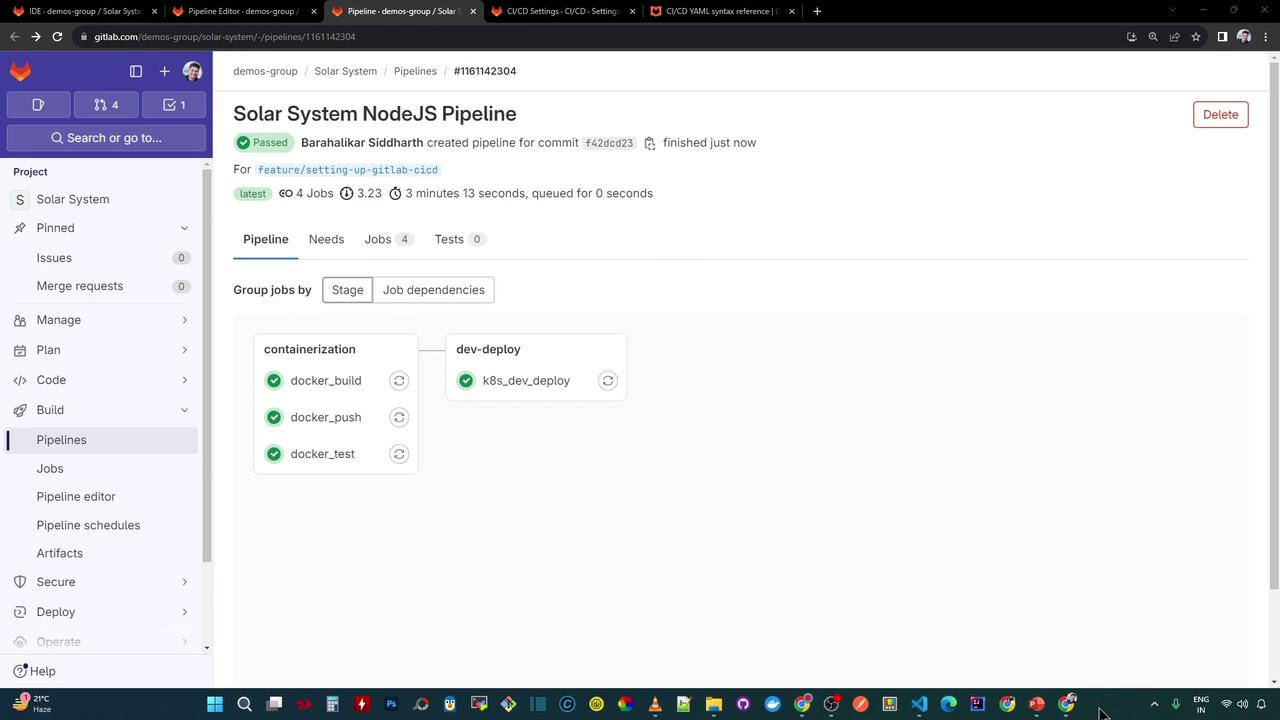
Once pushed, GitLab will visualize the pipeline:
6. Inspect the Dev-Deploy Logs Your dev-deploy job logs should look like this:
$ envsubst -V envsubst (GNU gettext-runtime ) 0.19.8.1 $ export KUBECONFIG= $DEV_KUBE_CONFIG $ kubectl version -o yaml # ClientVersion and ServerVersion details $ kubectl get nodes # Lists nodes $ export INGRESS_IP= 139.48.208.48 $ kubectl -n $NAMESPACE create secret generic mongo-db-creds \ --from-literal=MONGO_URI= $MONGO_URI \ --from-literal=MONGO_USERNAME= $MONGO_USERNAME \ --from-literal=MONGO_PASSWORD= $MONGO_PASSWORD \ --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f - secret/mongo-db-creds created $ for manifest in kubernetes/manifest/ * .yaml ; do envsubst < $manifest | kubectl apply -f - done deployment.apps/solar-system created ingress.networking.k8s.io/solar-system created service/solar-system created $ kubectl -n $NAMESPACE get all,secret,ingress # Pods, services, deployment, secret, and ingress listed
7. Verify Deployment Locally Check all resources in development:
kubectl -n development get all
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/solar-system-86fc65474-5klmr 1/1 Running 0 3m10s pod/solar-system-86fc65474-fcfpq 1/1 Running 0 3m10s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP PORT(S) AGE service/solar-system NodePort 10.102.111.40 3000:30654/TCP 3m5s NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/solar-system 2/2 2 2 3m10s NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/solar-system-86f65474 2 2 2 3m10s
Retrieve the Ingress host:
kubectl -n development get ingress
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE solar-system solar-system-development.139.84.208.48.nip.io 139.84.208.48 80,443 3m33s
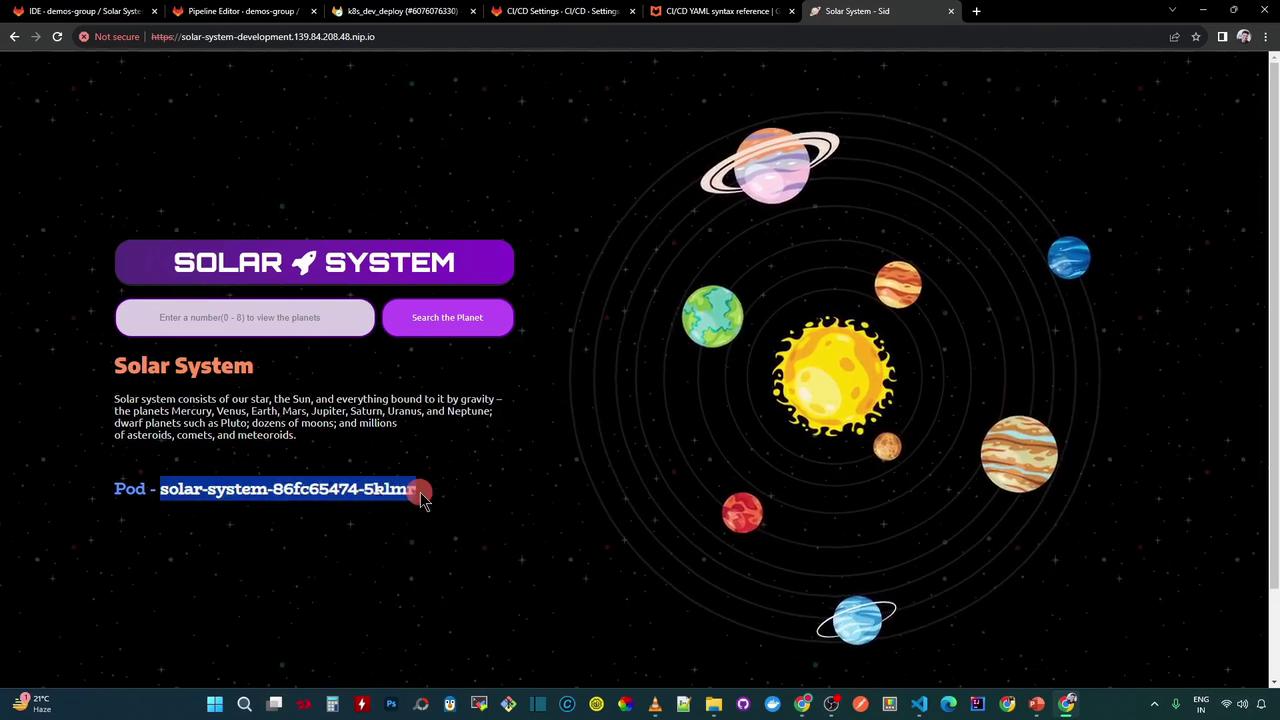
Open the application in your browser (accept the self-signed certificate):
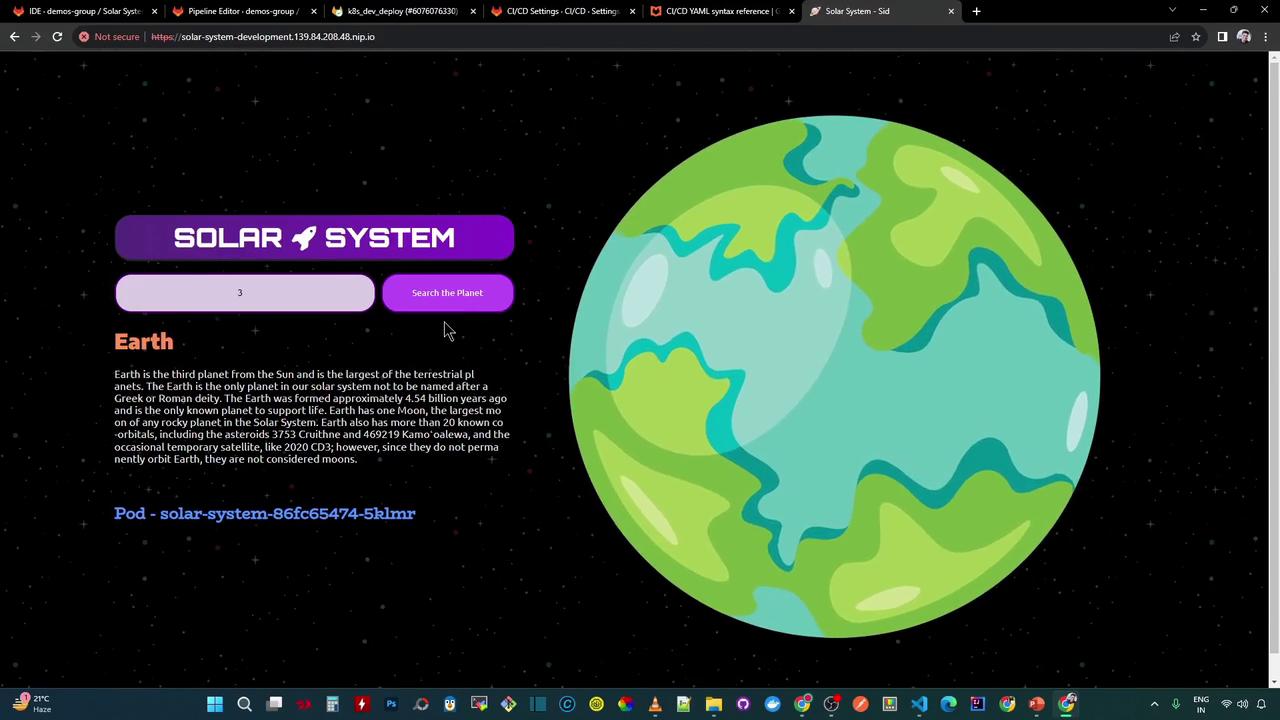
http://solar-system-development.139.84.208.48.nip.io Search for a planet by number (e.g., 3 for Earth):
8. Next Steps To improve reliability, integrate health checks into your pipeline:
GET /live → {"status":"live"}GET /ready → {"status":"ready"}, HTTP 200
These endpoints can be tested with tools like k6 or Postman CLI .
Links and References