Optimize your CI/CD workflow by integrating GitLab’s Code Quality analysis. This component scans your source code for complexity, duplication, style issues, and maintainability risks—helping your team merge only high-quality changes.
Why Code Quality Matters
Detects potential bugs and anti-patterns early
Tracks complexity and duplication over time
Enforces coding standards and style guidelines
Integrates seamlessly with merge requests for inline review
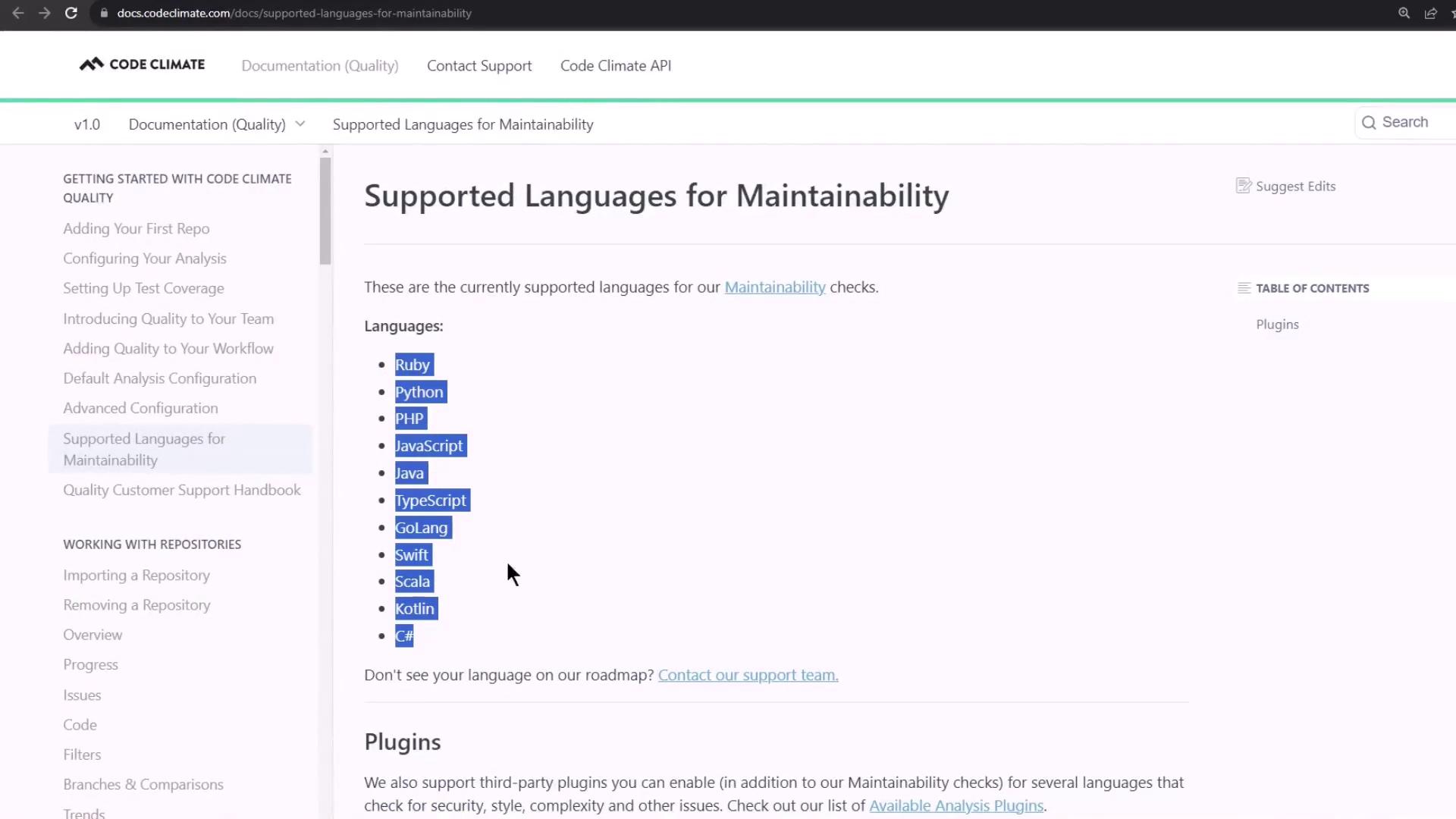
How It Works GitLab’s built-in Code Quality template leverages the open-source Code Climate engine plus additional scanners. It produces a JSON (or HTML) report consumed by GitLab to annotate merge requests and pipeline views.
Verify your project’s language is supported by Code Climate before enabling the component.
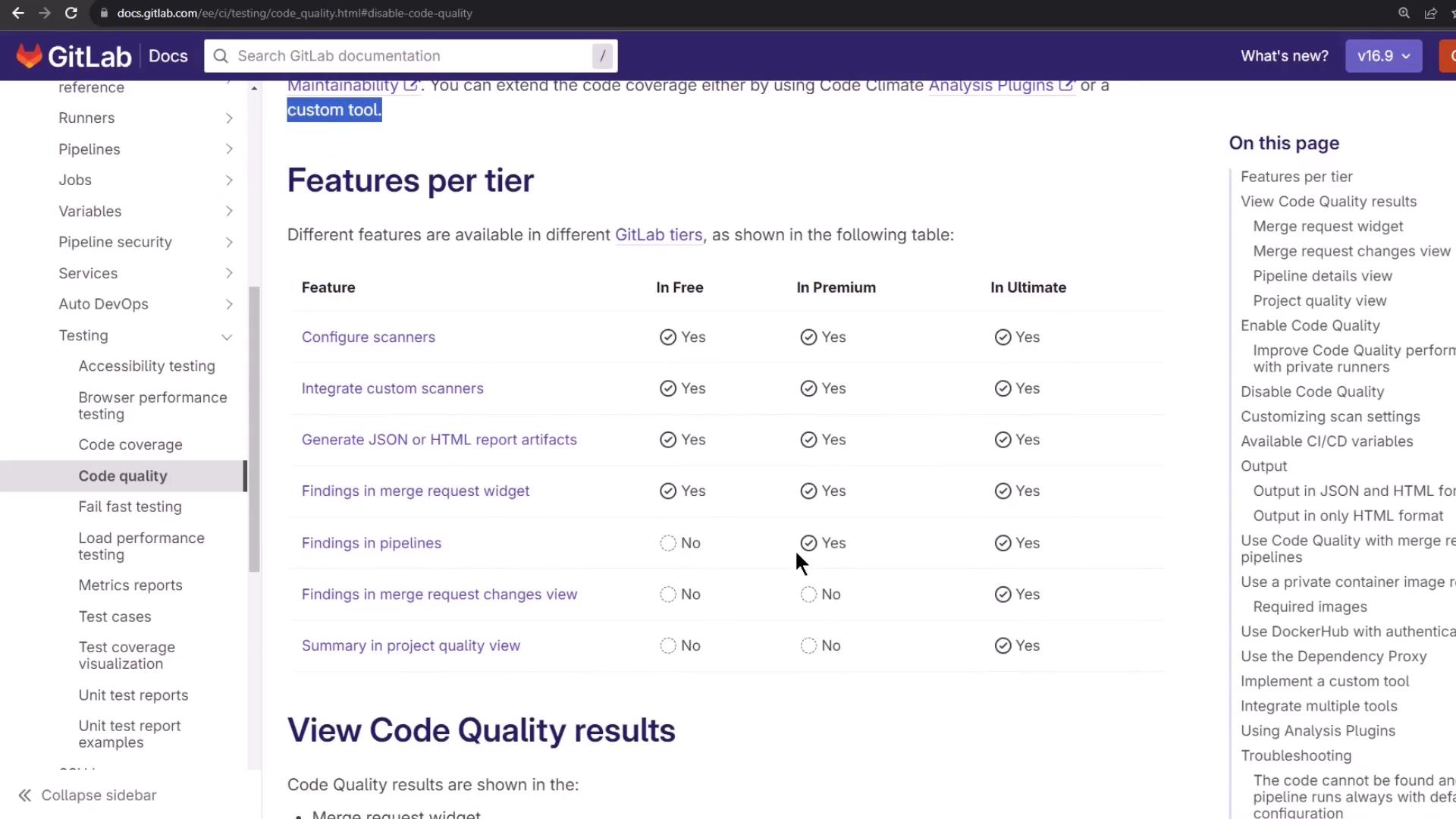
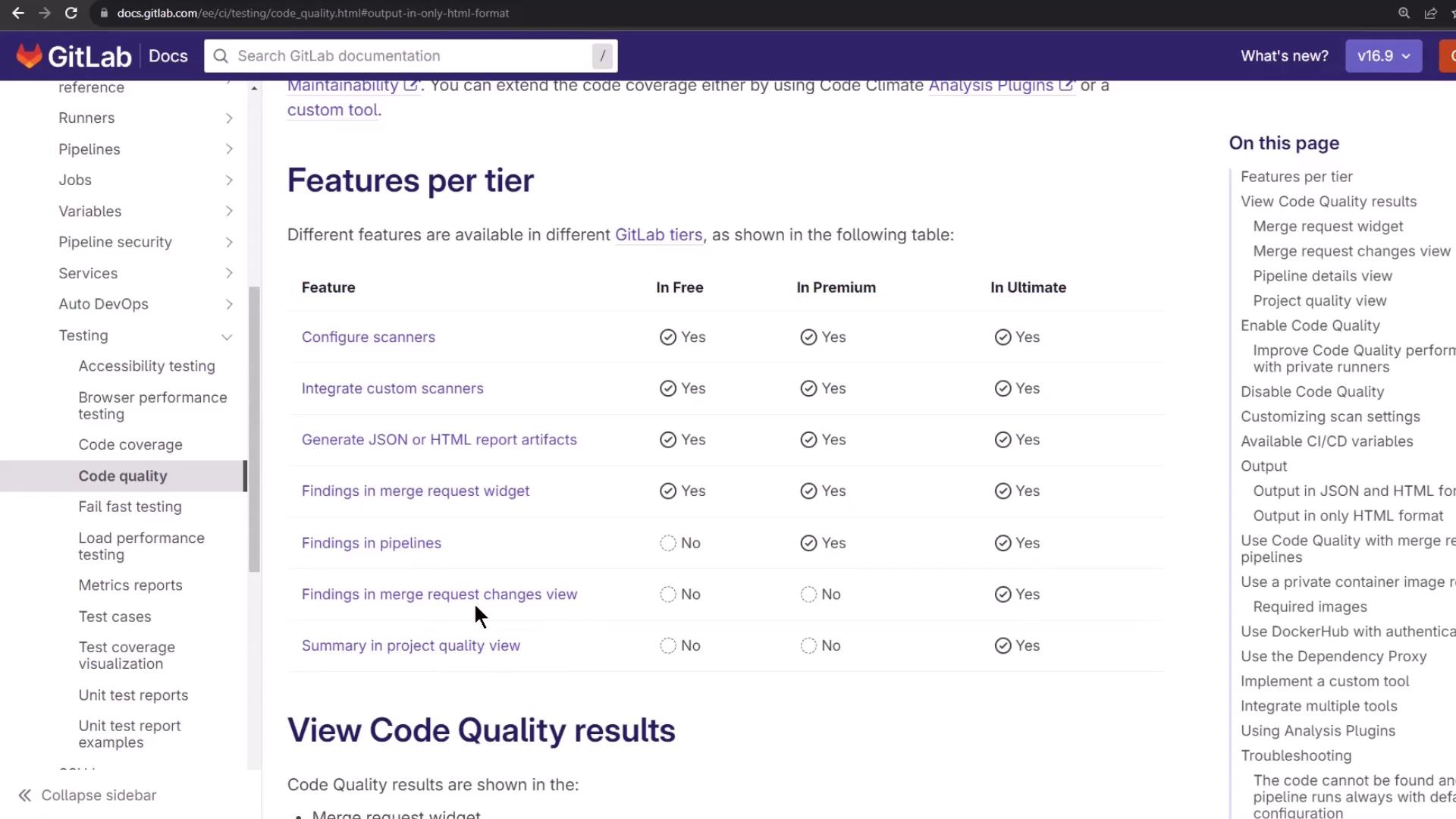
Feature Comparison by GitLab Tier Different GitLab subscriptions unlock advanced Code Quality capabilities:
GitLab Tier Key Features Free Basic maintainability and style checks Premium Custom scanner configuration, report artifacts Ultimate Quality dashboard, advanced analytics, MR insights
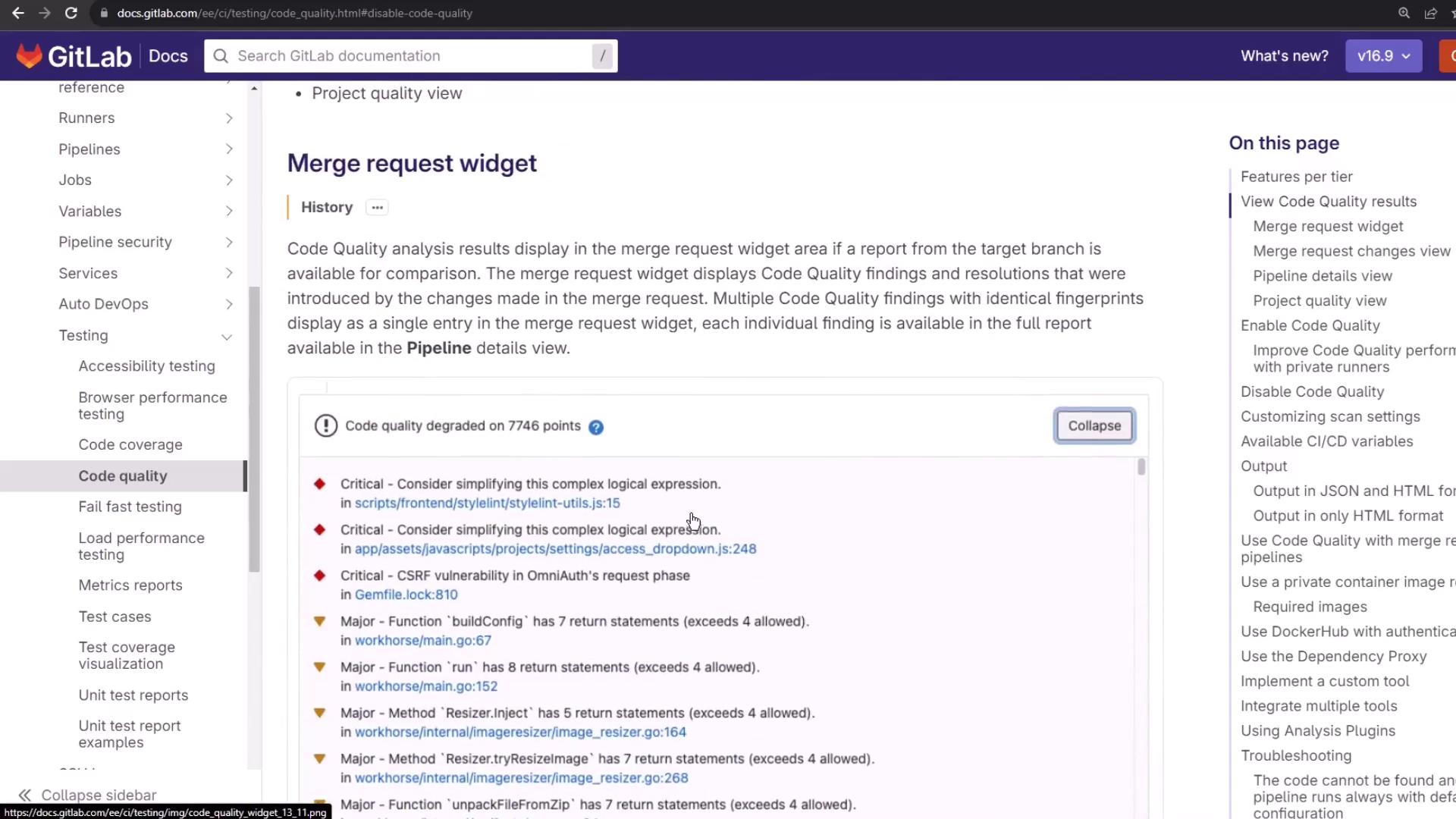
Merge Request Inline Reports Once enabled, Code Quality issues surface directly in the Merge Request widget—categorized by severity and file location.
For example, a simple JavaScript function:
function init () { return 'foo' ; debugger ; }
Code Climate flags the unused debugger; statement as an issue.
1. Enable Code Quality in Your CI Configuration Add the official GitLab CI/CD component at the top of your .gitlab-ci.yml:
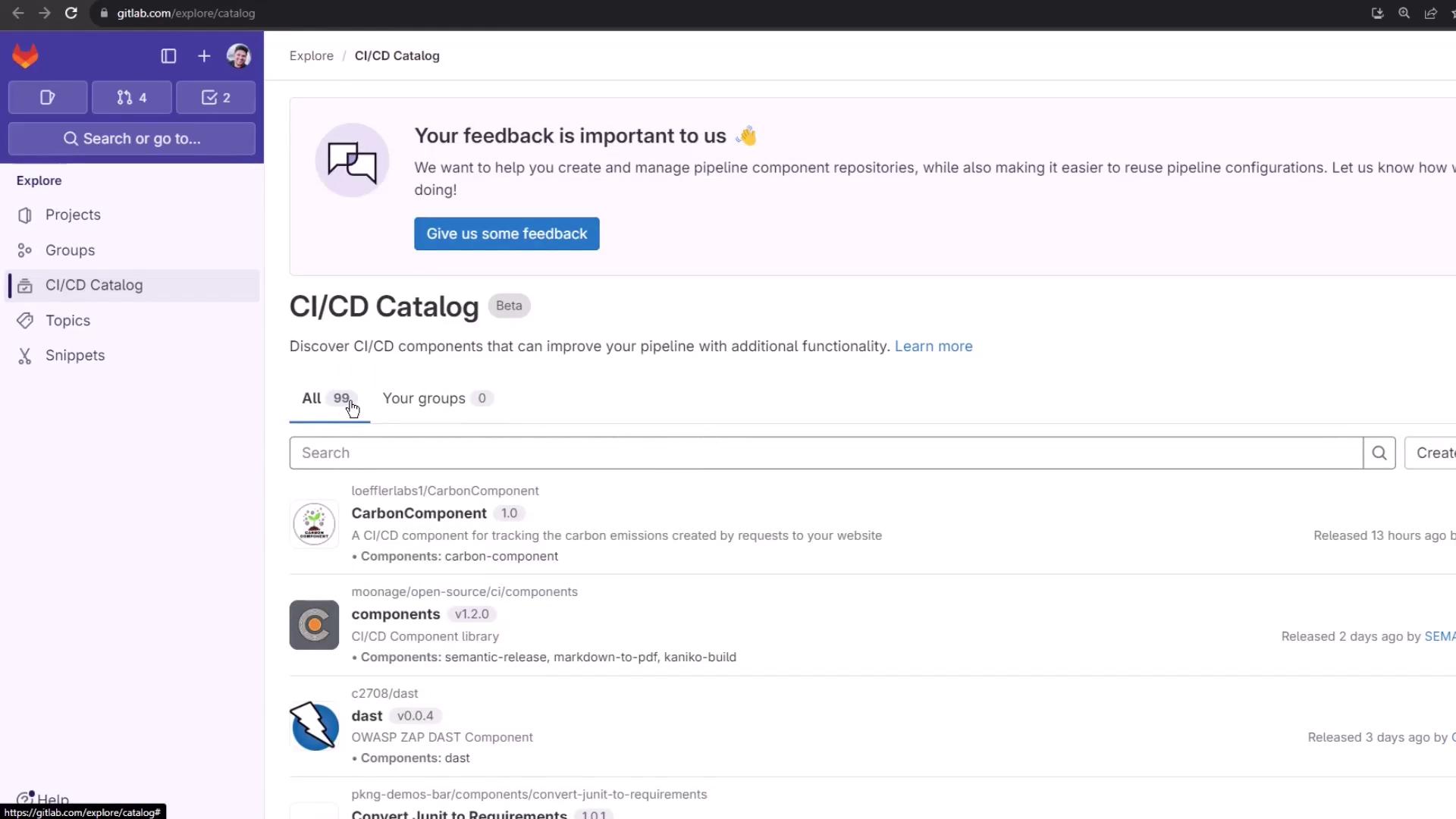
GitLab CI/CD components are reusable jobs and templates. Browse the CI/CD Catalog (beta) to discover 99 components.
In the Pipeline Editor, search for code-quality :
workflow : … stages : … variables : … unit_testing : … docker_build : … # … other jobs …
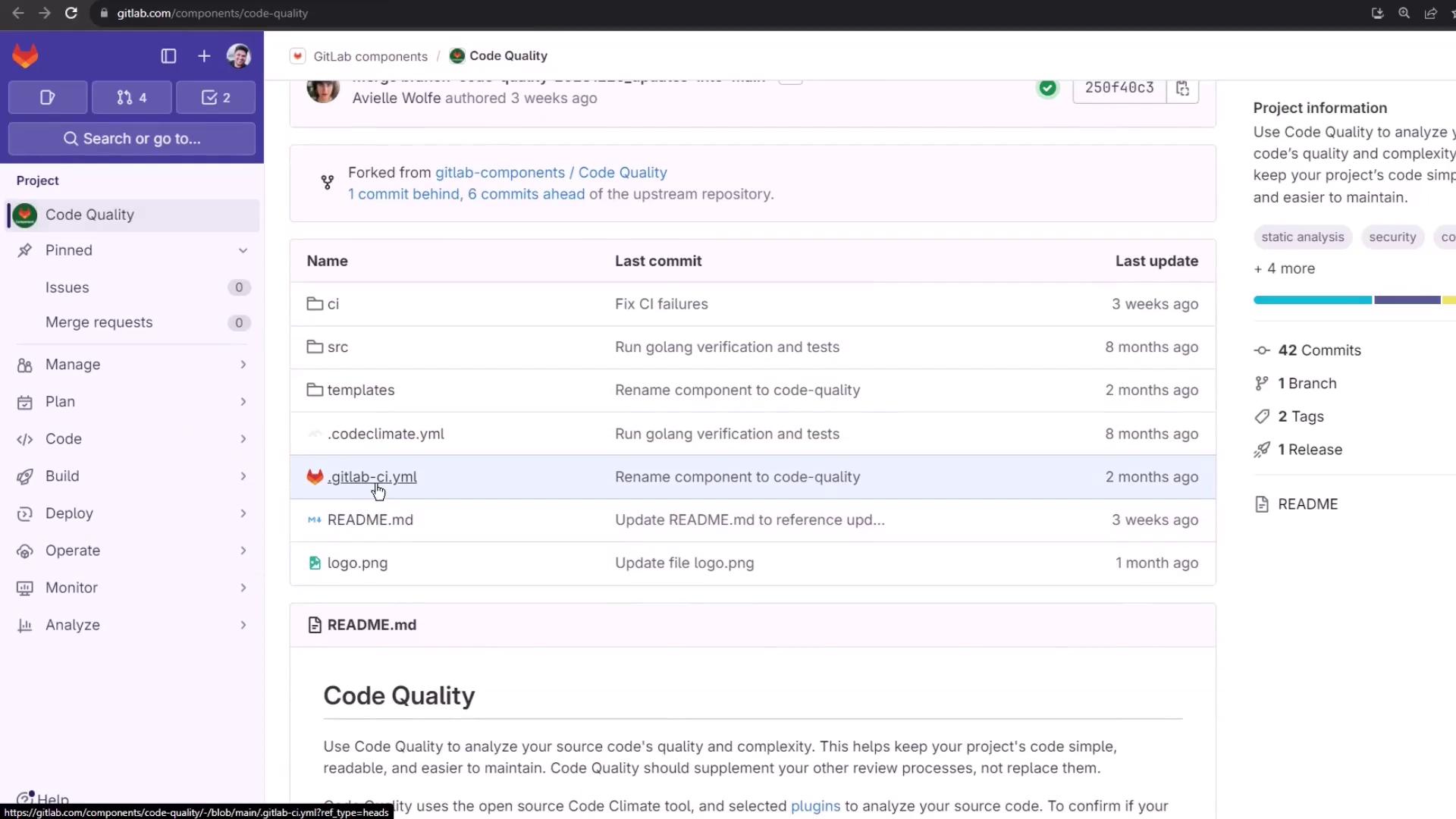
Click code-quality to view usage details and inspect its repository files:
Snippet from the component’s template:
code_quality : artifacts : paths : - gl-code-quality-report.json rules : - if : $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_ID || $CI_COMMIT_TAG || $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH
2. Add Code Quality to Your Pipeline Start with a basic Node.js pipeline:
stages : - test .prepare_nodejs_environment : & prepare_nodejs image : node:14 before_script : - npm install unit_testing : stage : test extends : * prepare_nodejs script : - npm test artifacts : when : always expire_in : 3 days reports : coverage_report : coverage_format : cobertura path : coverage/cobertura-coverage.xml
Include the Code Quality component before defining your jobs:
include : - component : gitlab.com/gitlab-components/code-quality/[email protected] stages : - test # … your existing jobs … #
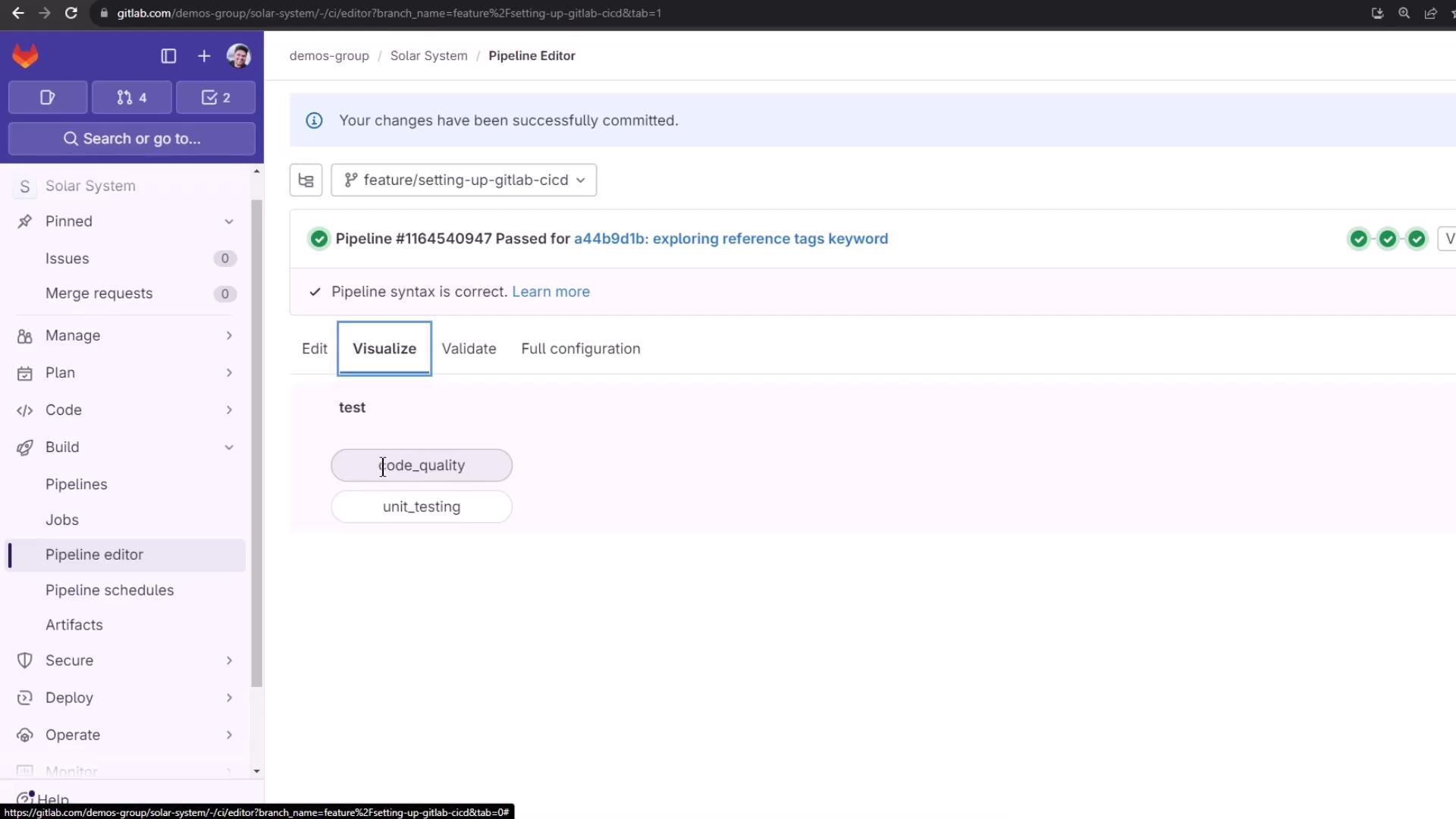
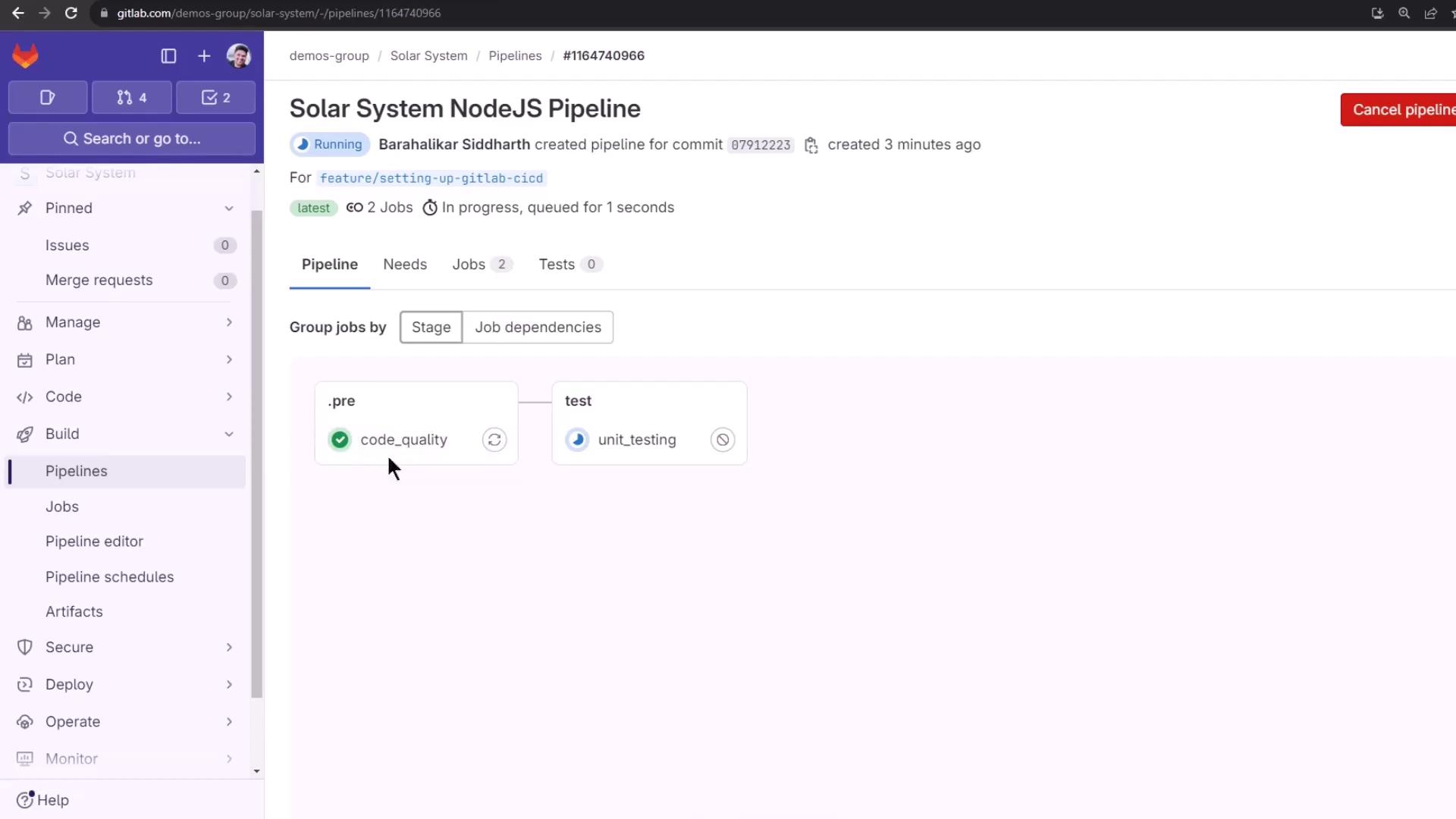
Once committed, the pipeline adds a code_quality job automatically:
View the Merged Configuration Click View full config in the pipeline editor to see how your .gitlab-ci.yml merges with the Code Quality template:
code_quality : stage : test image : docker:20.10.12 allow_failure : true services : - name : docker:20.10.12-dind command : [ "--tls=false" , "--host=tcp://0.0.0.0:2375" ] variables : DOCKER_DRIVER : overlay2 DOCKER_TLS_CERTDIR : "" script : - export SOURCE_CODE=$PWD - docker pull -q $CI_TEMPLATE_REGISTRY_HOST/gitlab-org/ci-cd/codequality:0.96.0 - docker run --rm \ --volume "$SOURCE_CODE":/code \ --volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ $CI_TEMPLATE_REGISTRY_HOST/gitlab-org/ci-cd/codequality:0.96.0 /code artifacts : reports : codequality : - gl-code-quality-report.json expire_in : 1 week rules : - if : '$CI_COMMIT_TAG || $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH' when : always
By default, allow_failure: true ensures Code Quality issues don’t block merges.
GitLab supports two special stages: .pre and .post. Assign code_quality to .pre for early feedback:
stages : - ".pre" - test - build - deploy - ".post" include : - component : gitlab.com/gitlab-components/code-quality/[email protected] code_quality : stage : ".pre"
To generate an HTML report instead of JSON:
code_quality : stage : ".pre" variables : REPORT_FORMAT : html artifacts : paths : - gl-code-quality-report.html reports : codequality : []
This stores gl-code-quality-report.html as a job artifact.
4. Pipeline Run & Artifacts Triggering a commit runs both code_quality and unit_testing jobs:
Inspect logs to see the analysis steps:
$ export SOURCE_CODE= $PWD $ docker pull -q $CI_TEMPLATE_REGISTRY_HOST /gitlab-org/ci-cd/codequality:0.96.0 $ docker run --rm \ --volume " $SOURCE_CODE ":/code \ --volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ ...
Browse the HTML or JSON report via the job’s Browse link. The report groups findings by:
Bug Risk
Complexity
Duplication
Style
For inline MR annotations, GitLab uses the JSON report.
Example Findings Bug Risk throw new Error ( 'Request failed.' ); }). catch ( function ( error ) { alert ( "Ooops, We have 8 planets. \n Select a number from 0 - 8" ); console . log ( error ); })
Duplication describe ( 'Fetching Planet Details' , () => { it ( 'should fetch Mercury' , ( done ) => { const payload = { id: 1 }; chai . request ( server ) . post ( '/planet' ) . send ( payload ); . end (( err , res ) => { res . should . have . status ( 200 ); res . body . should . have . property ( 'name' ). eql ( 'Mercury' ); done (); }); }); });
Additional Code Quality Features Top-tier GitLab plans unlock more advanced tools:
Feature Availability Pipeline view inline annotations Premium & above Project Quality Dashboard summaries Ultimate Merge Request Changes view Ultimate
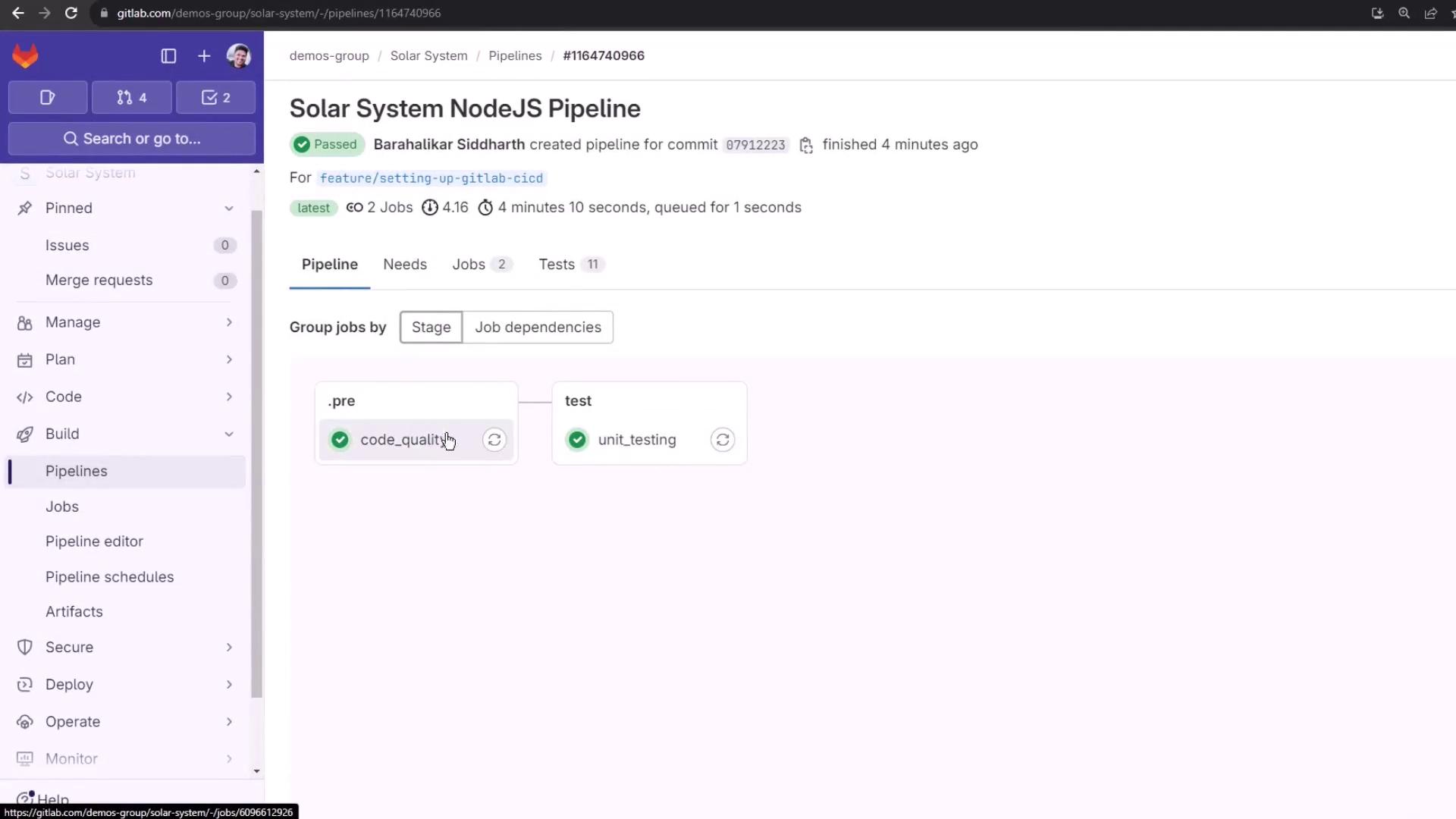
After review, your pipeline completes successfully:
That’s it! You’ve integrated and customized GitLab’s Code Quality component to elevate your CI/CD standards.
Links and References