Learn how to debug custom JavaScript GitHub Actions step by step. We’ll use workflow commands and the @actions/core toolkit to inspect annotations, logs, summaries, and properly handle failures. By the end, you’ll be able to:
Read inputs and set outputs
Log at different levels (info, notice, warning, error)
Mask secrets and export environment variables
Generate job summaries
Fail actions with descriptive exit codes
Table of Contents
Importing and Cloning the Repository Reviewing action.yaml Examining package.json Business Logic in index.js Building the Action Testing with a Workflow Enabling Actions and Running the Workflow Viewing Annotations Inspecting Logs Error Scenario: Invalid Phone Number Setting Failure Exit Codes Conclusion Links & References
1. Importing and Cloning the Repository First, import the sample project into your GitHub account. Choose TroubleshootingJS-Actions , set visibility to Public, and click Import .
Then clone it locally:
git clone https://github.com/your-org/TroubleshootingJS-Actions.git cd TroubleshootingJS-Actions
2. Reviewing action.yaml Open action.yaml , the manifest that defines inputs, outputs, and runtime:
name : 'Demo - Troubleshooting Custom JavaScript Actions' description : 'Use @actions/core methods for logging, secrets, and summaries' inputs : name : description : 'User name' required : true default : 'Siddharth' phone : description : 'User phone number' required : true default : '0123456789' country : description : 'User country' required : true default : 'india' outputs : customized_greeting : description : 'Greeting passed to next steps' runs : using : 'node20' main : 'dist/index.js'
Section Purpose inputs Define user-provided values (name, phone, country) outputs Pass data to downstream steps runs Specify Node.js version and bundled entrypoint
3. Examining package.json The package.json file lists dependencies for your action bundle:
{ "name" : "troubleshooting-custom-action" , "version" : "1.0.0" , "main" : "index.js" , "scripts" : { "test" : "echo \" Error: no test specified \" && exit 1" }, "dependencies" : { "@actions/core" : "^1.10.0" , "@vercel/ncc" : "^0.38.0" } }
@actions/core : Toolkit for inputs, outputs, logging, secret masking@vercel/ncc : Bundles your JavaScript into a single file
Refer to the actions toolkit documentation for examples such as:
const core = require ( '@actions/core' ); core . getInput ( 'name' , { required: true }); core . setOutput ( 'customized_greeting' , 'Hello World' ); core . exportVariable ( 'ENV_VAR' , 'value' );
4. Business Logic in index.js The main script reads inputs, logs messages, masks secrets, exports variables, and builds a summary:
const core = require ( '@actions/core' ); try { // 1. Read inputs const nameInput = core . getInput ( 'name' , { required: true }); const phoneInput = core . getInput ( 'phone' , { required: true }); const country = core . getInput ( 'country' , { required: true }); // 2. Debug logging if ( core . isDebug ()) { core . info ( 'Running in debug mode' ); core . debug ( 'Debug-level message' ); } core . info ( '---------- START ----------' ); // 3. Prepare greeting const greeting = `Hello ${ nameInput } , your phone number is ${ phoneInput } ` ; // 4. Log at different levels core . info ( `Info: ${ greeting } ` ); core . notice ( `Notice: ${ greeting } ` ); core . warning ( `Warning: ${ greeting } ` ); core . error ( `Error: ${ greeting } ` ); core . info ( '---------- END ------------' ); // 5. Set output core . setOutput ( 'customized_greeting' , greeting ); // 6. Validate phone and export variable if ( phoneInput . length !== 10 ) { core . error ( `Invalid phone number: ${ phoneInput } ` ); // core.setFailed('Invalid phone number provided!'); } else { const prefix = country . toLowerCase () === 'india' ? '+91' : country . toLowerCase () === 'canada' ? '+1' : '' ; core . exportVariable ( 'JS_ACTION_PHONE_VAR' , ` ${ prefix }${ phoneInput } ` ); } // 7. Mask secret and write summary core . setSecret ( phoneInput ); core . summary . addHeading ( 'Action Summary' ) . addCodeBlock ( "const core = require('@actions/core');" , 'js' ) . addTable ([ [{ data: 'Name' , header: true }, { data: 'Country' , header: true }, { data: 'Phone' , header: true }], [ nameInput , country , phoneInput ] ]) . addQuote ( 'Phone number has been masked' ) . addLink ( 'View Repository' , 'https://github.com/sidd-harth/troubleshooting-actions' ) . write (); } catch ( error ) { core . setFailed ( error . message ); }
The core.setSecret() method masks sensitive values in logs. Use it whenever you log or store secrets.
5. Building the Action Install dependencies and bundle into dist/index.js:
npm install npx ncc build index.js --license licenses.txt
This creates dist/index.js with all required modules included.
6. Testing with a Workflow Create .github/workflows/test.yml to trigger the action manually:
on : workflow_dispatch : inputs : name : description : 'User name' required : true default : 'Sid' phone : description : 'User phone' required : true default : '9876543210' country : description : 'User country' required : true default : 'india' type : choice options : [ india , canada , others ] jobs : custom-action : runs-on : ubuntu-latest steps : - uses : actions/checkout@v3 - name : Run Troubleshooting Action id : action_step uses : ./ with : name : ${{ inputs.name }} phone : ${{ inputs.phone }} country:${{ inputs.country }} - name : Display Outputs run : | echo "Greeting: ${{ steps.action_step.outputs.customized_greeting }}" echo "Phone Var: $JS_ACTION_PHONE_VAR"
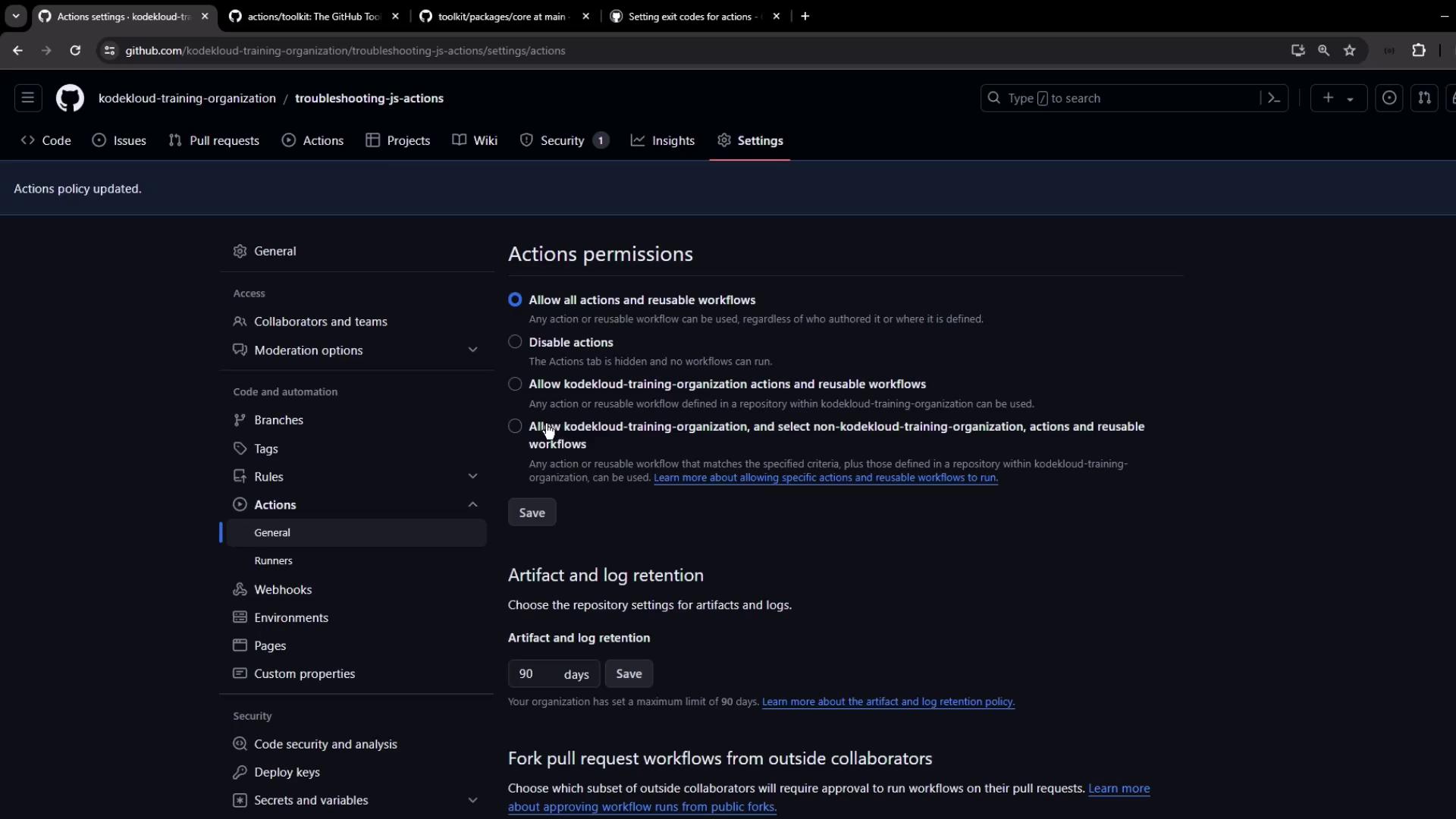
7. Enabling Actions and Running the Workflow Imported repositories have Actions disabled by default. Enable them before running:
Go to Settings → Actions → General
Under Actions permissions , select Allow all actions and reusable workflows
core.error() logs an error but does not fail the step. To stop the job on error, use core.setFailed().
Once enabled, trigger the workflow via Actions → Run workflow with default inputs. The job should succeed.
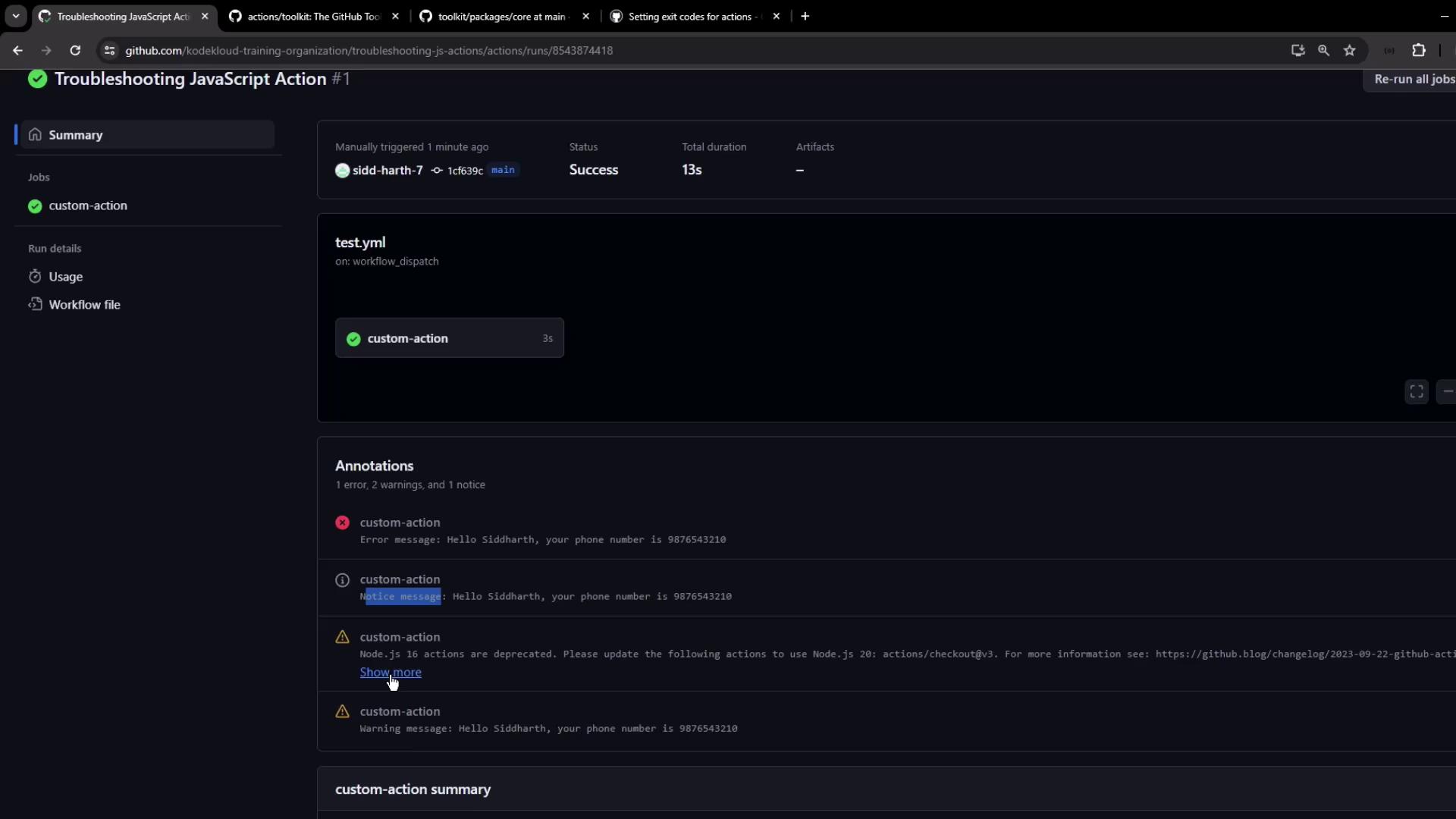
7.1 Viewing Annotations GitHub UI displays annotations from different logging levels:
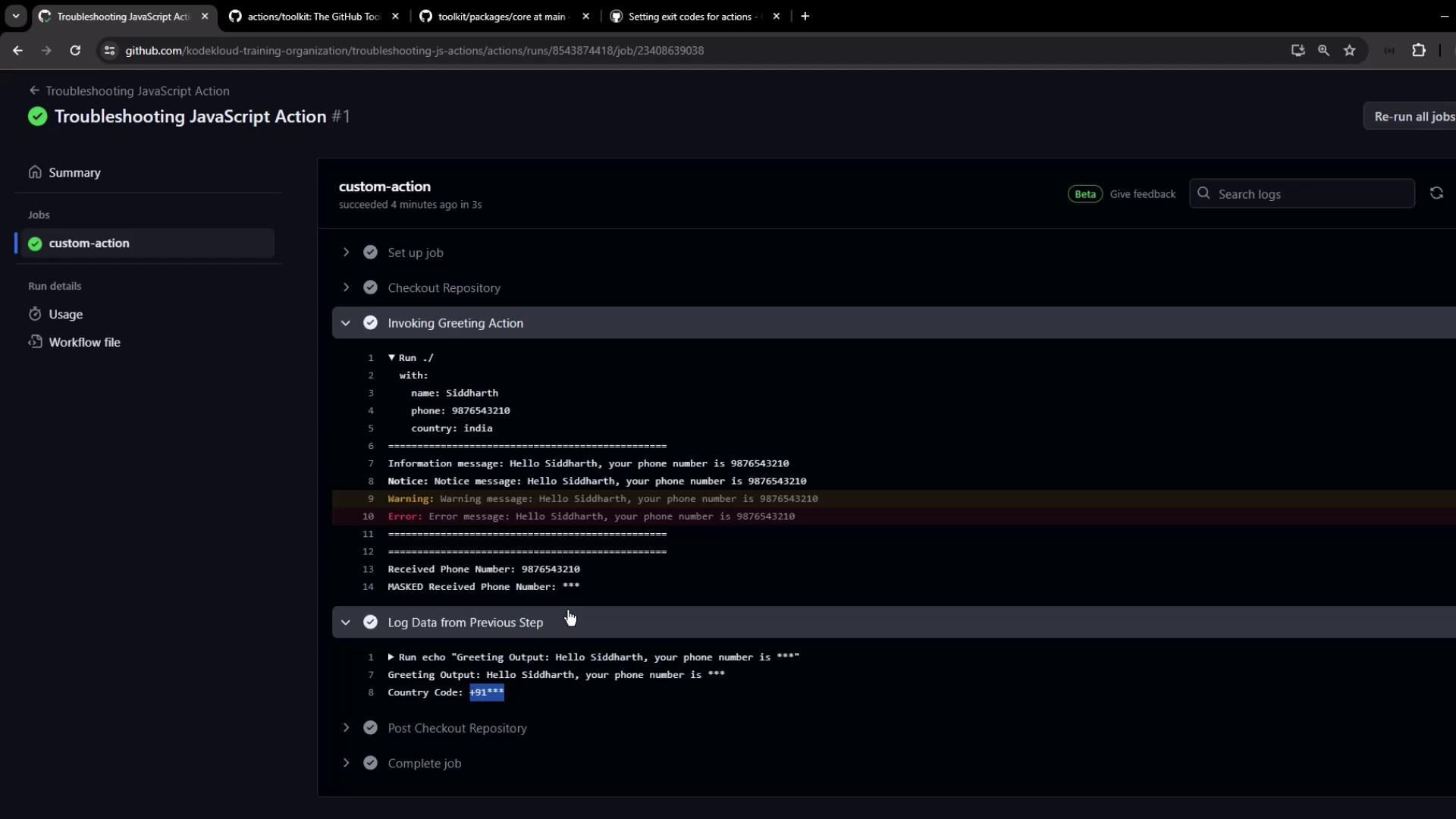
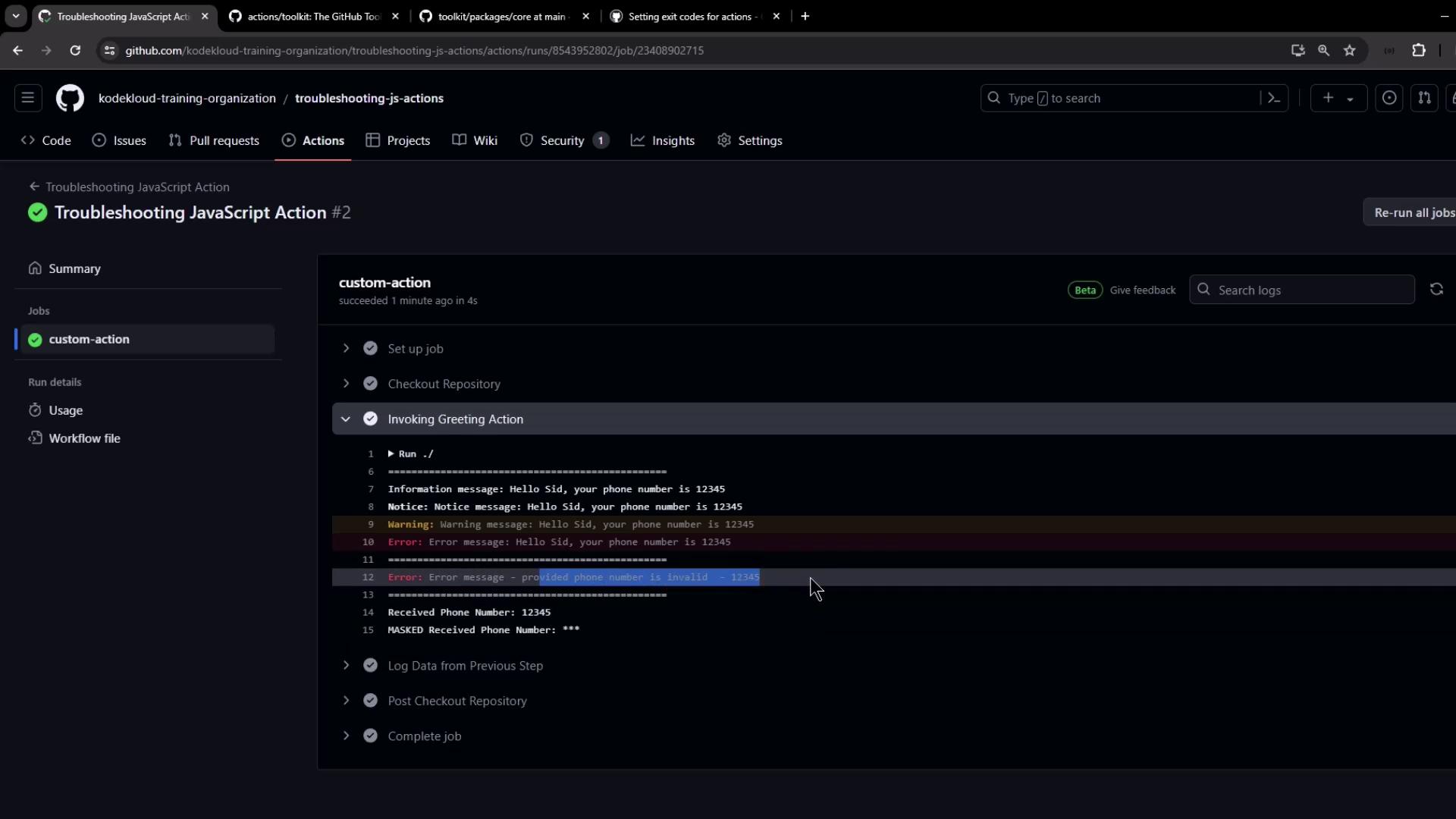
7.2 Inspecting Logs Detailed logs show messages and confirm that secrets are masked:
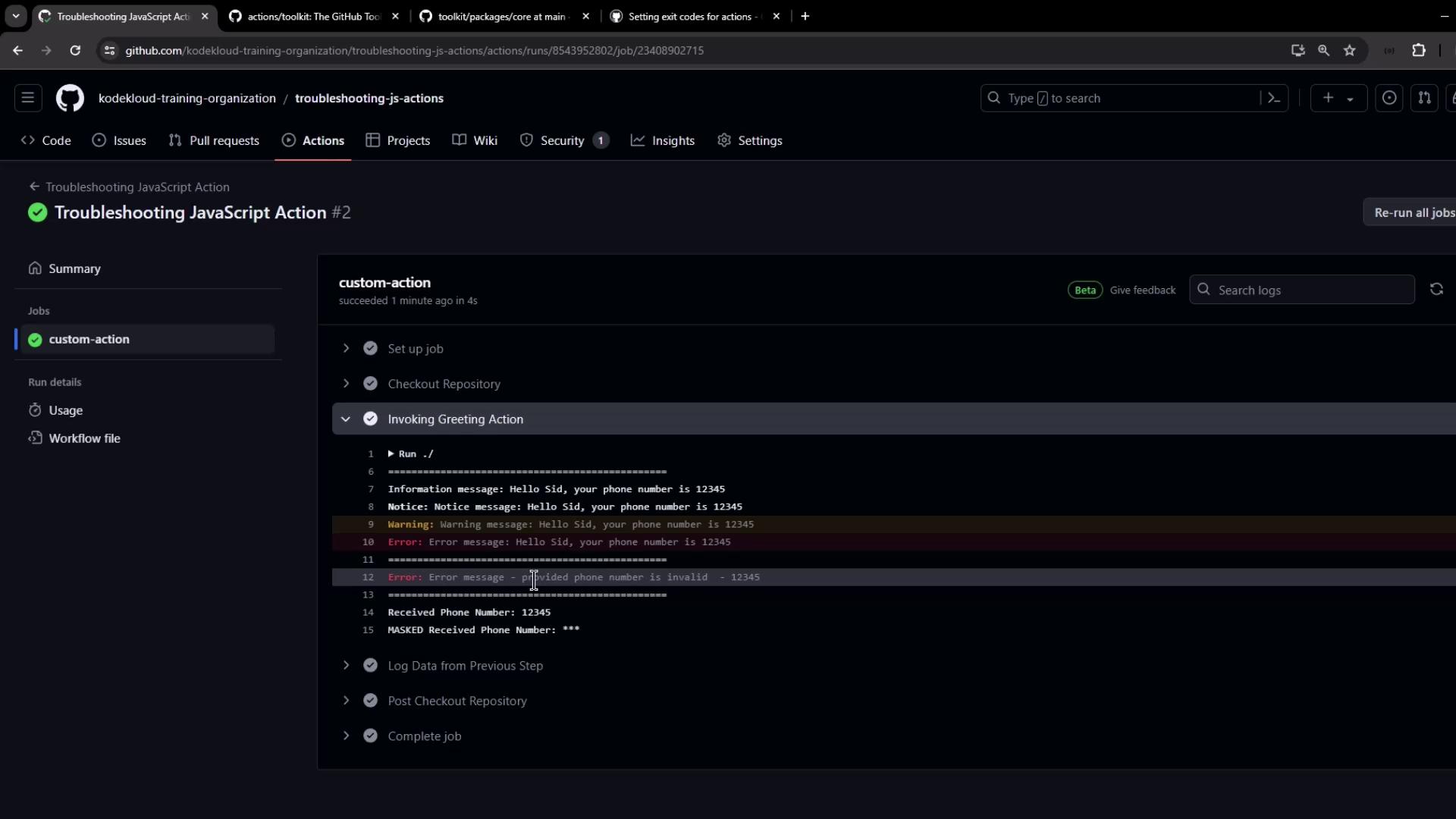
8. Error Scenario: Invalid Phone Number If the phone number is shorter than 10 digits, you’ll see the logged error but the job remains green (until you opt to fail it):
9. Setting Failure Exit Codes To mark the step as failed and stop downstream jobs, uncomment core.setFailed():
if ( phoneInput . length !== 10 ) { core . error ( `Invalid phone number: ${ phoneInput } ` ); core . setFailed ( 'Invalid phone number provided!' ); } else { // Export logic... }
Rebuild and commit, then rerun. A short number now causes the action to fail and skip subsequent steps.
After failure is enabled, the logs will clearly indicate a non-zero exit:
10. Conclusion You’ve covered essential patterns for debugging JavaScript Actions:
Use @actions/core for inputs, outputs, logs, secrets, and summaries
Bundle with ncc for single-file distribution
Write workflows to validate functionality
View annotations and logs directly in the GitHub UI
Fail actions properly with core.setFailed()
Apply these techniques to create maintainable, self-documented, and debuggable GitHub Actions.
11. Links & References