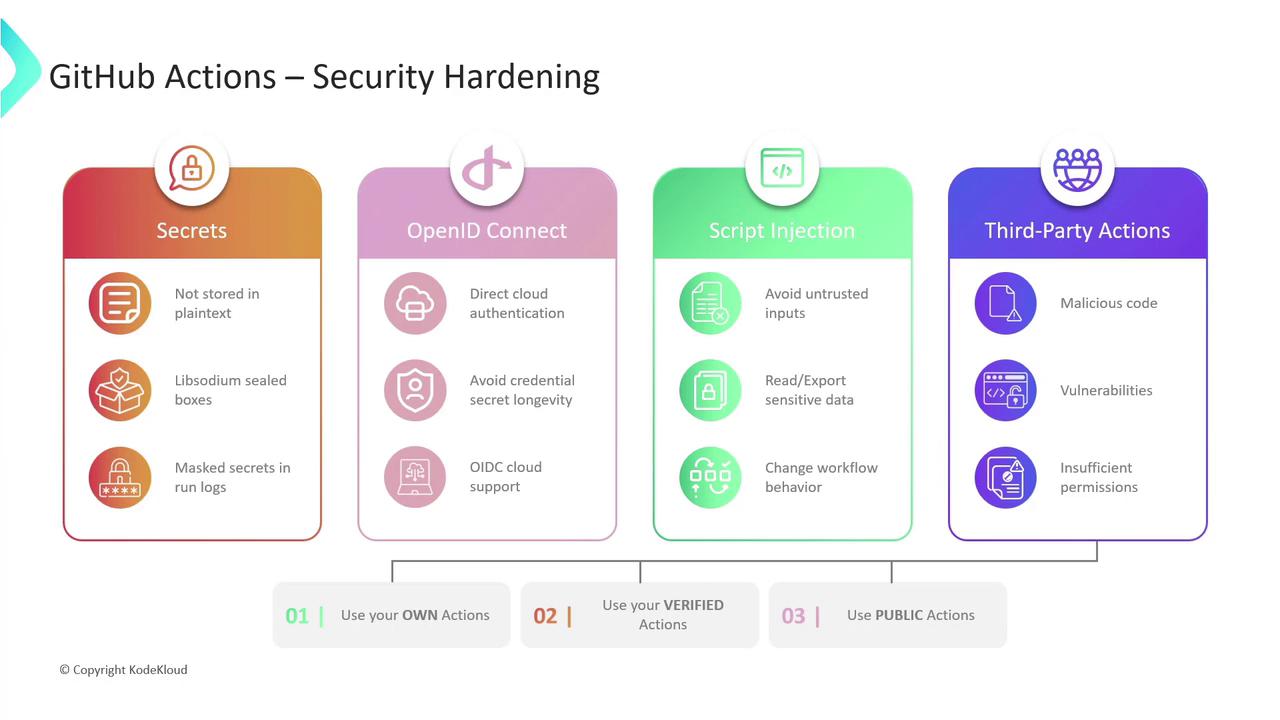
- Secrets Management
- OpenID Connect (OIDC)
- Mitigating Script Injection
- Third-Party Actions
1. Secrets Management
Storing credentials, tokens, and other sensitive information directly in workflows is a critical security risk. GitHub provides a robust secrets management system:- Encrypted storage
Secrets are encrypted client-side with Libsodium sealed boxes before being sent to GitHub. - Scoped access
You can define secrets at the organization, repository, or environment level. - Masked output
Any secret that appears in logs is automatically redacted.
Regularly rotate your secrets and remove any unused credentials to limit blast radius.
2. OpenID Connect (OIDC)
Instead of long-lived cloud credentials, leverage short-lived tokens via OIDC. This eliminates static secrets and reduces credential exposure.-
Trust GitHub’s issuer
Configure your cloud provider to trusthttps://token.actions.githubusercontent.comas an OIDC identity provider. -
Grant OIDC permissions
In your workflow, request theid-tokenpermission: -
Configure credentials with an action
For AWS, you can use the official AWS OIDC action:
Short-lived tokens automatically expire, minimizing the risk of credential theft or misuse.
3. Mitigating Script Injection
When workflows process external or user-supplied data, attackers may inject malicious commands. Protect your runners by following these best practices:- Never concatenate untrusted input into shell commands.
- Use action inputs or parameterized APIs instead of manually building commands.
- Validate and sanitize all external data.
- Prefer official or well-audited actions for complex processing.
Running unchecked user input in a shell step can expose secrets, corrupt workflows, or allow remote code execution.
4. Third-Party Actions
Community actions speed up development but can also introduce vulnerabilities or excessive permissions. Evaluate and manage third-party risks with this matrix:| Action Type | Risk | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Community/Public | Malicious code, supply-chain attacks | Pin to a specific commit SHA; review source code |
| GitHub-Verified | Lower risk but still subject to updates | Check blue-verified badge; grant least privilege |
| Custom (Own) | You control code integrity | Maintain under version control; audit permissions |
- Pin actions to a commit SHA instead of a floating tag.
- Limit the
permissionsscope to the bare minimum (principle of least privilege). - Periodically review third-party code for updates or security advisories.