Key Features of API Gateway
AWS API Gateway is a fully managed service, meaning AWS takes care of the underlying infrastructure, scaling, and routine updates. This allows you to concentrate on designing powerful APIs. Some of its core features include:- Built-in Version Management: Easily create and maintain multiple API versions (e.g., v1, v2) without disrupting existing users.
- Support for RESTful APIs and WebSockets: Choose REST APIs for CRUD operations or WebSockets for real-time interactions.
- Throttling and Caching: Configure policies via the AWS Management Console to control request rates and cache responses for faster performance.
- Security Integration: Integrates seamlessly with AWS IAM and Amazon Cognito to simplify authentication and authorization.
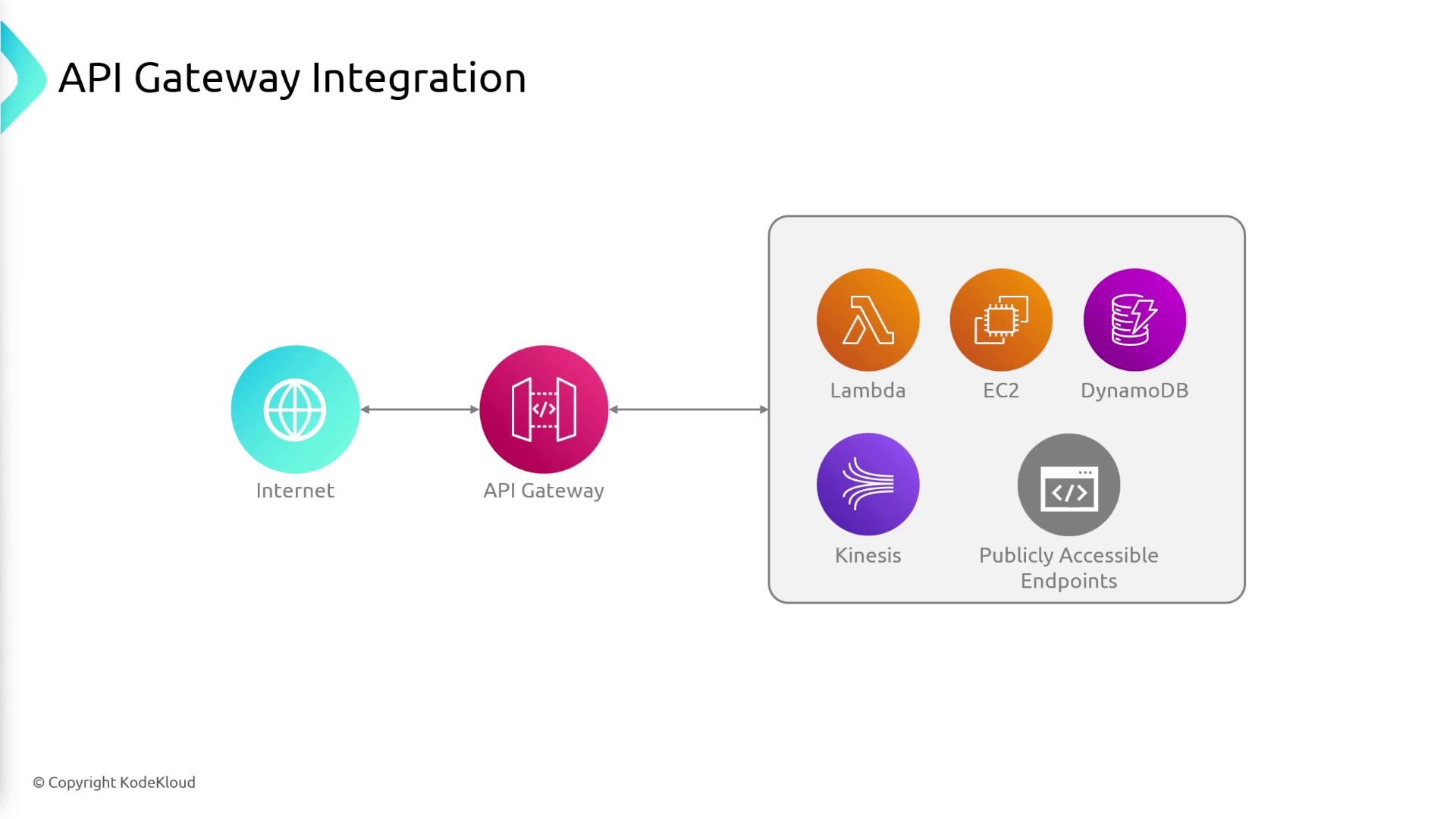
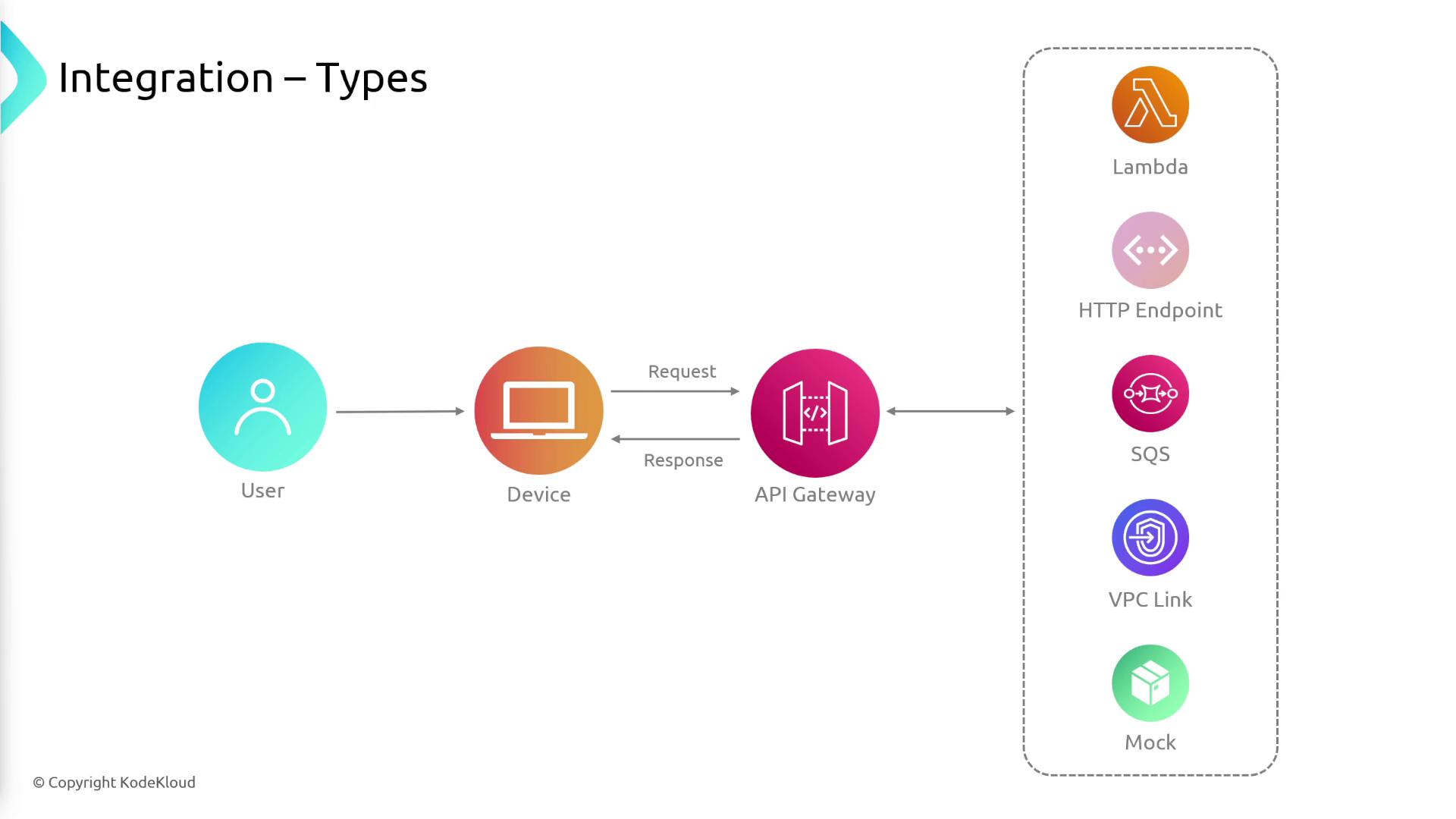
Integration Types
API Gateway supports various integration types, allowing you to connect your API to the appropriate backend with ease:- Lambda Integration: Directly invoke Lambda functions to execute custom backend logic.
- HTTP Integration: Route requests to any existing HTTP endpoint.
- Direct AWS Service Integration: Connect with other AWS services such as SQS, DynamoDB, and S3.
- VPC Link Integration: Securely route requests to resources hosted within your VPC—like EC2 instances or ECS tasks—without exposing them publicly.
- Mock Integration: Return predefined responses to facilitate testing and reduce backend costs during development.
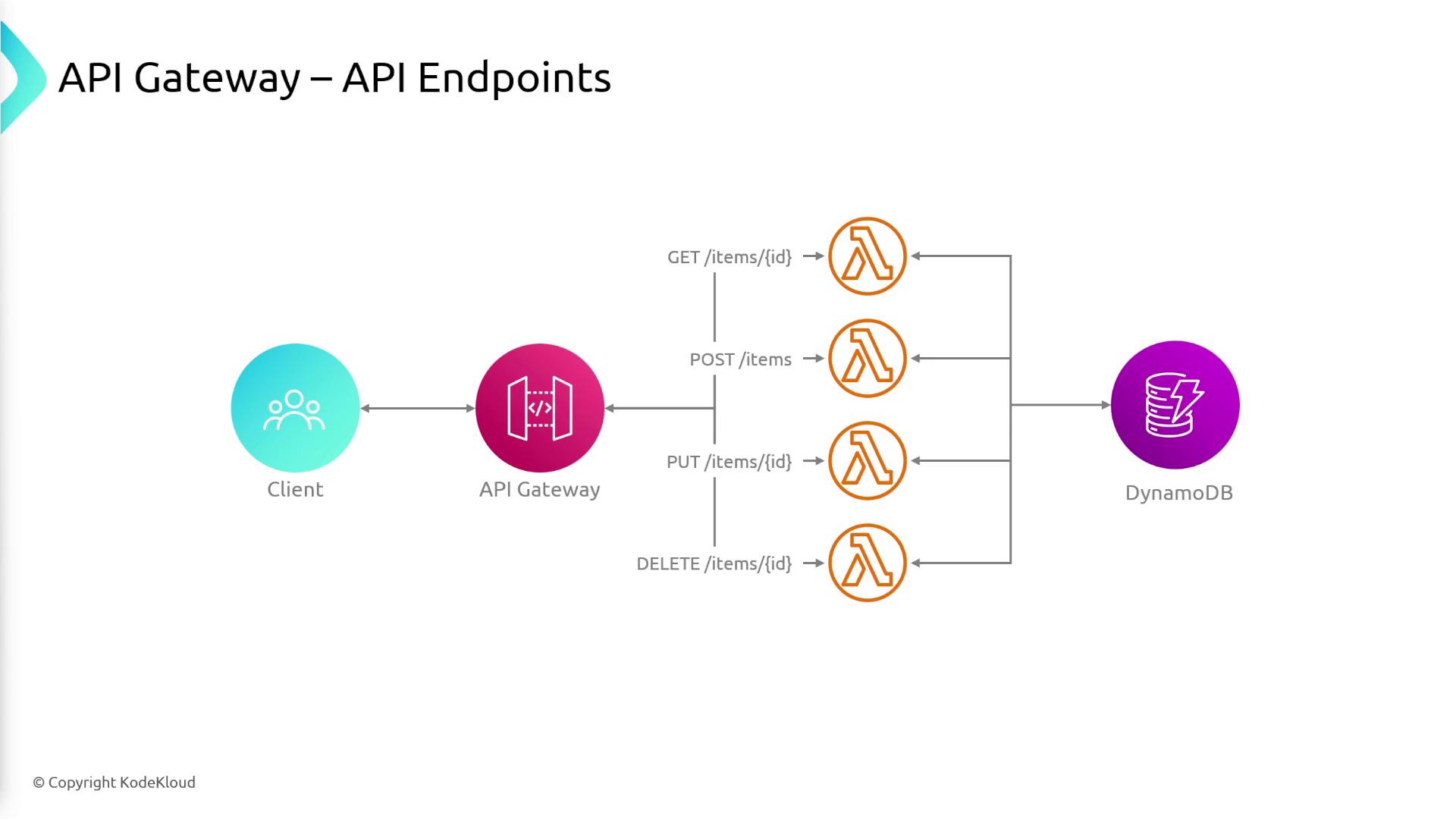
/items could trigger a Lambda function that interacts with a DynamoDB table.
Endpoint Types
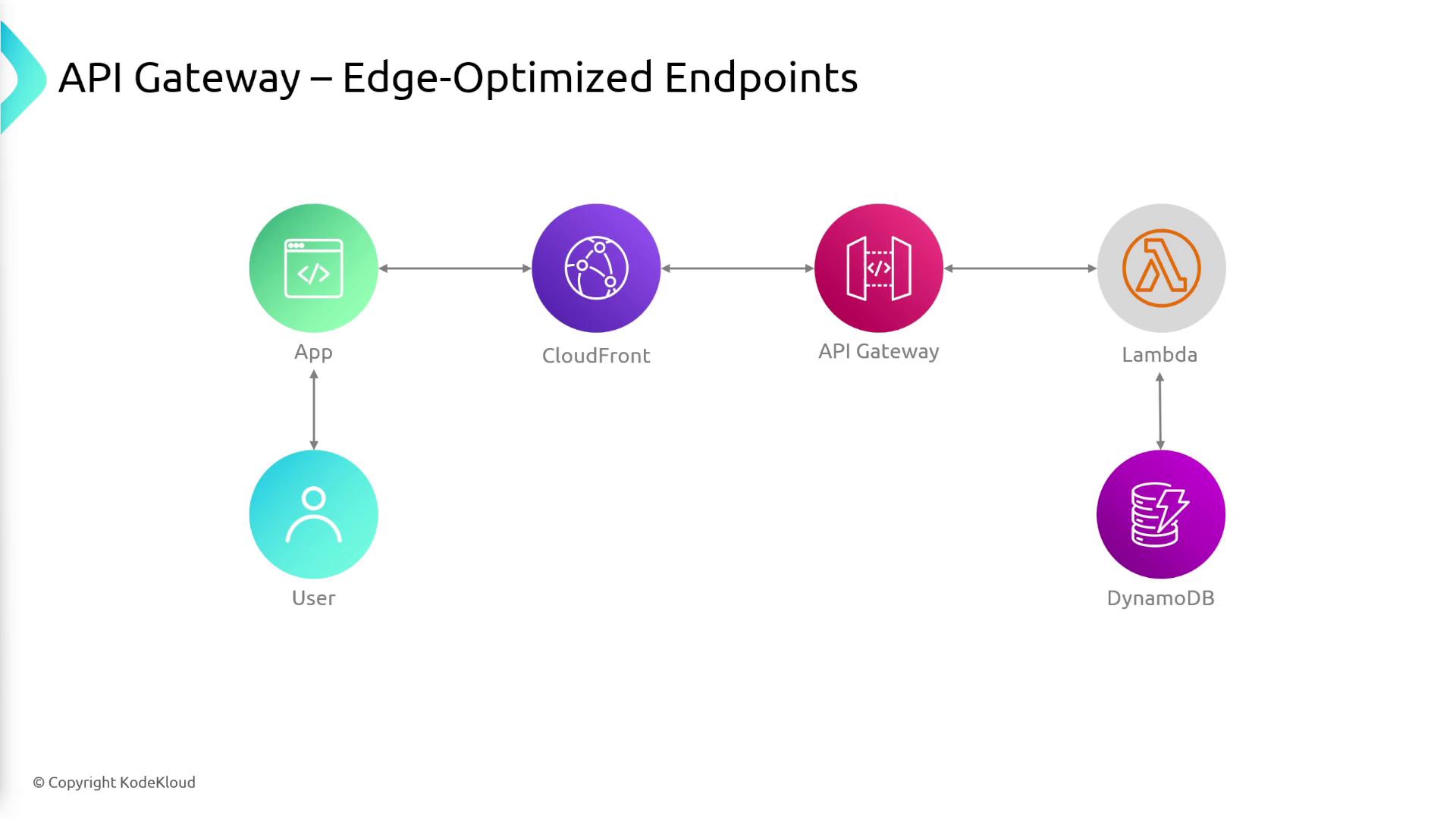
API Gateway offers three different endpoint types to match your deployment needs:- Edge-Optimized:
Best for a global user base, these endpoints leverage Amazon CloudFront’s global edge locations to minimize latency.
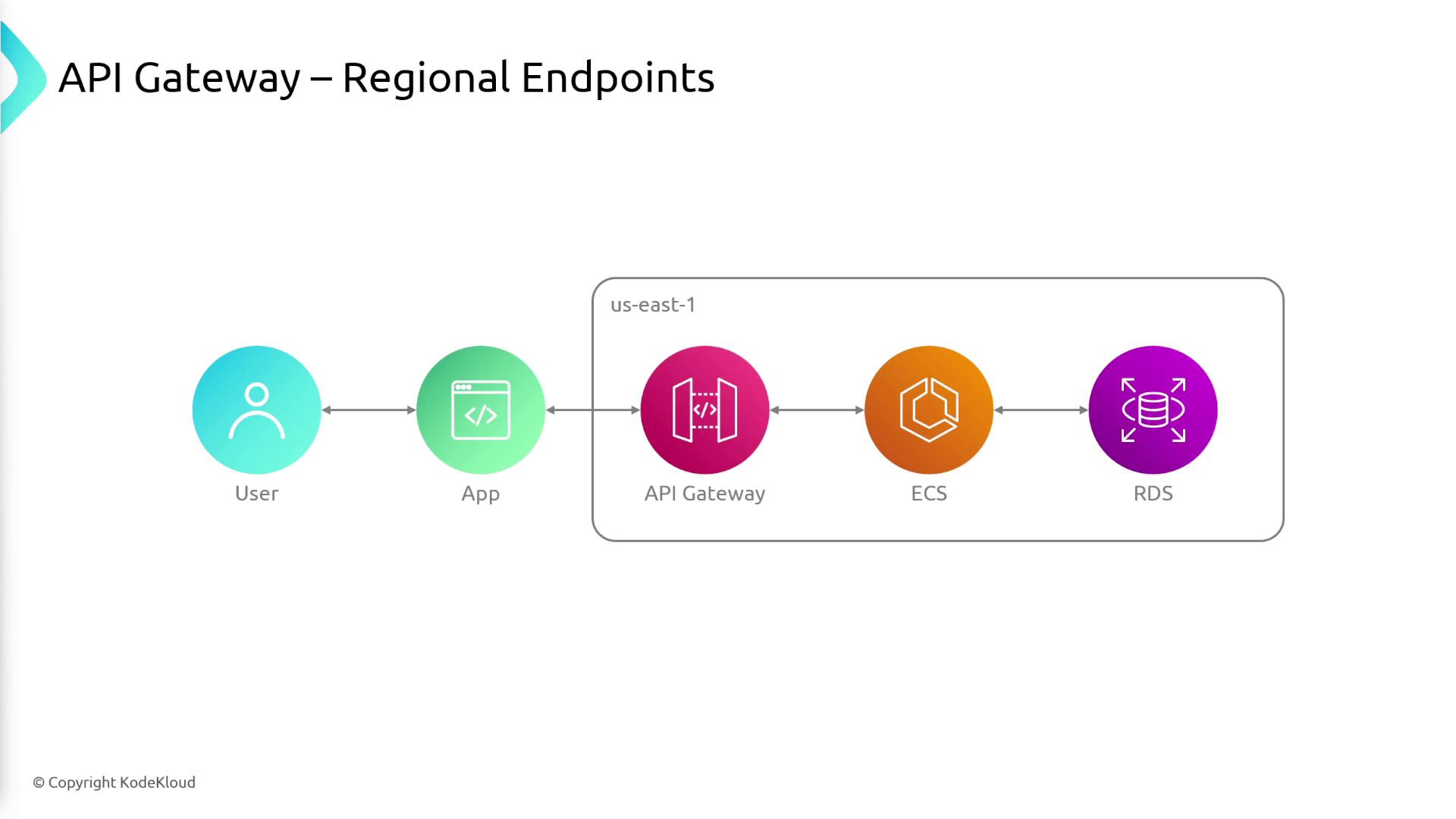
- Regional:
Ideal for clients located in the same geographic area. Although globally accessible, users outside the designated region might experience increased latency.
- Private:
These endpoints are accessible only from within your VPC and are intended for private, internal-use cases.
For edge-optimized endpoints, CloudFront routing directs requests to the nearest edge location, ensuring fast response times for users worldwide.
REST API vs HTTP API vs WebSocket
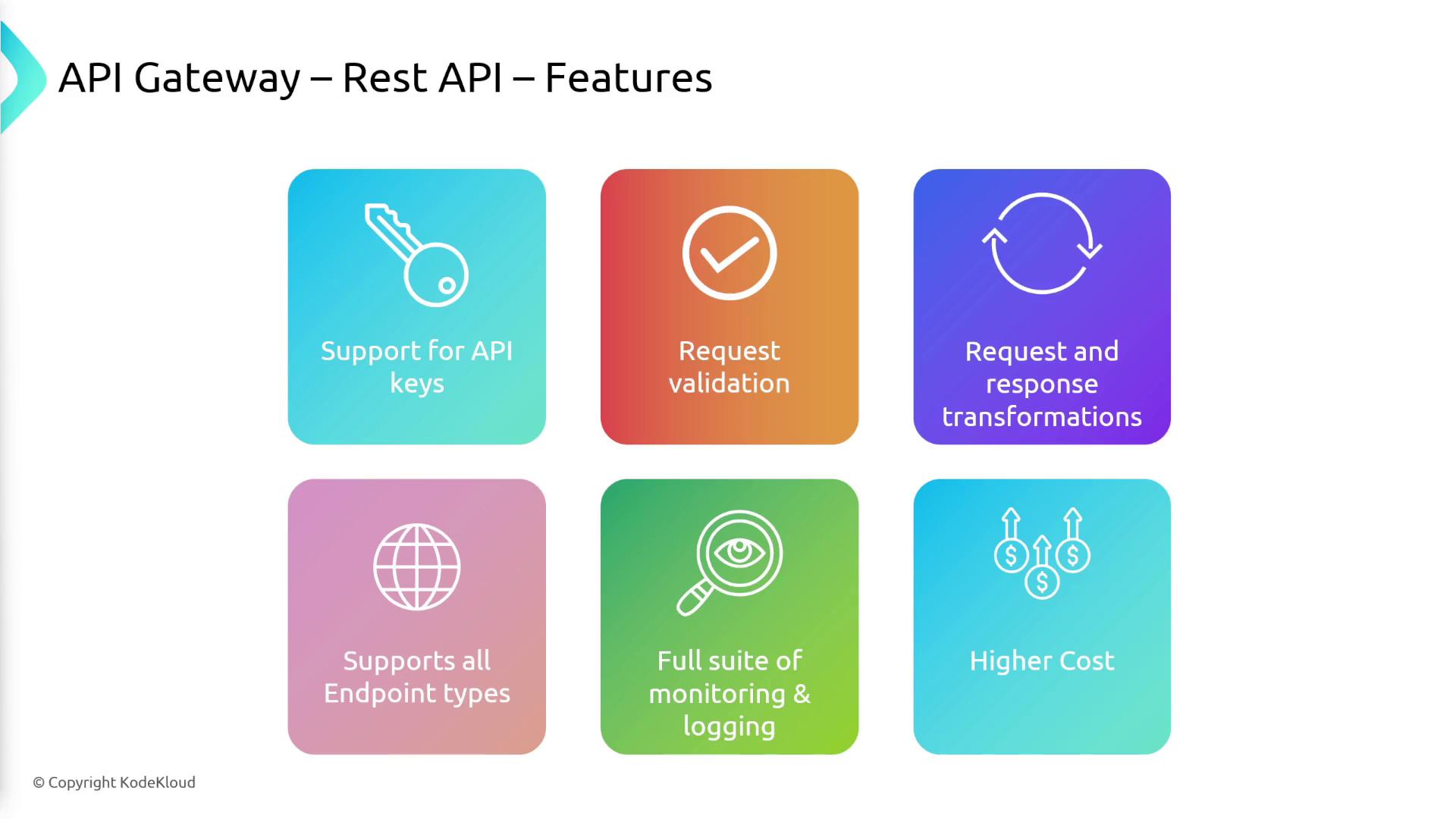
When setting up your API using the API Gateway console, you can choose from three options based on your application’s needs:- REST API:
Provides an extensive feature set, including API keys, request validation, transformation capabilities, and comprehensive monitoring/logging. REST APIs support all endpoint types, though they are priced higher due to their robust functionalities.
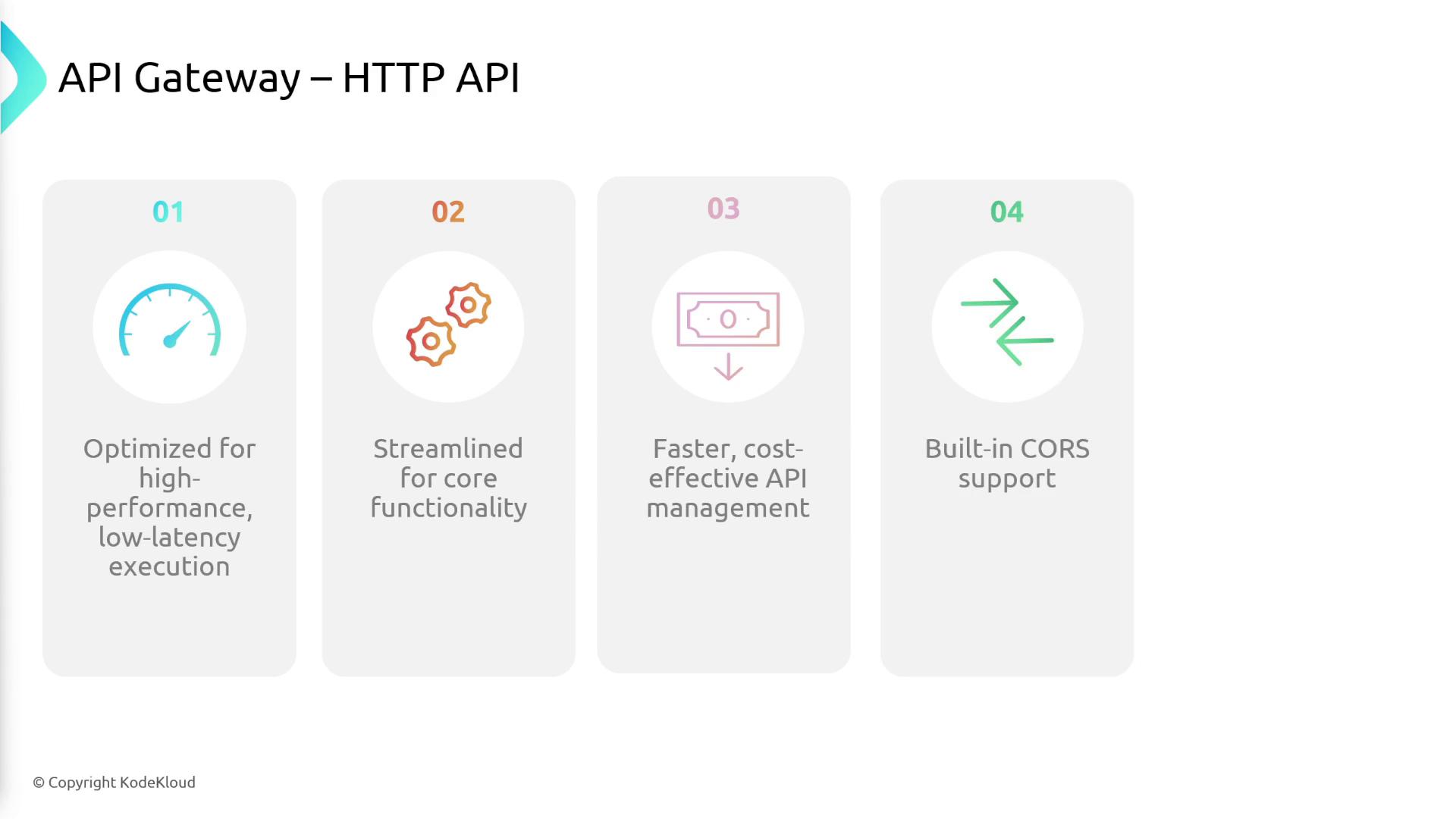
- HTTP API:
Optimized for low-latency, high-performance scenarios with a streamlined feature set. Although HTTP APIs do not offer all advanced features, they provide a cost-effective solution for many common use cases.
- WebSocket:
Designed for applications that need real-time, bi-directional communication.
- Performance: HTTP APIs are optimized for lower latency and faster performance.
- Cost: HTTP APIs are generally more cost-effective due to their streamlined functionality.
- Endpoint Types: While REST APIs support all endpoint types, HTTP APIs primarily support regional endpoints.
- API Management and Monitoring: REST APIs offer extensive features for throttling, API keys, and detailed logging, whereas HTTP APIs provide essential monitoring and basic management capabilities.
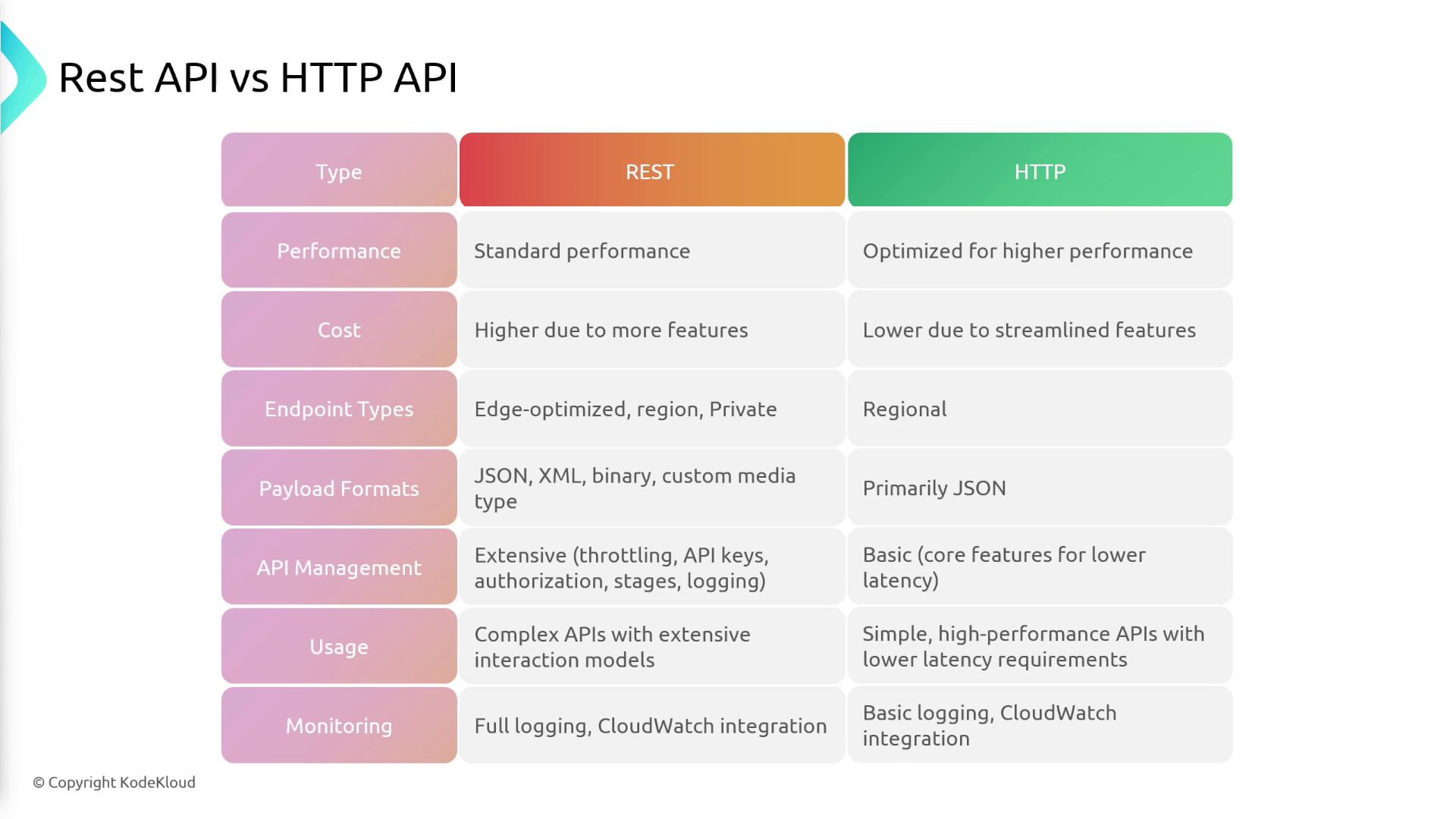
Before selecting the API type, consider your application’s specific requirements. Choosing a REST API might provide extensive features but at a higher cost, while an HTTP API offers better performance and lower cost for simpler use cases.