Creating an ECR Repository
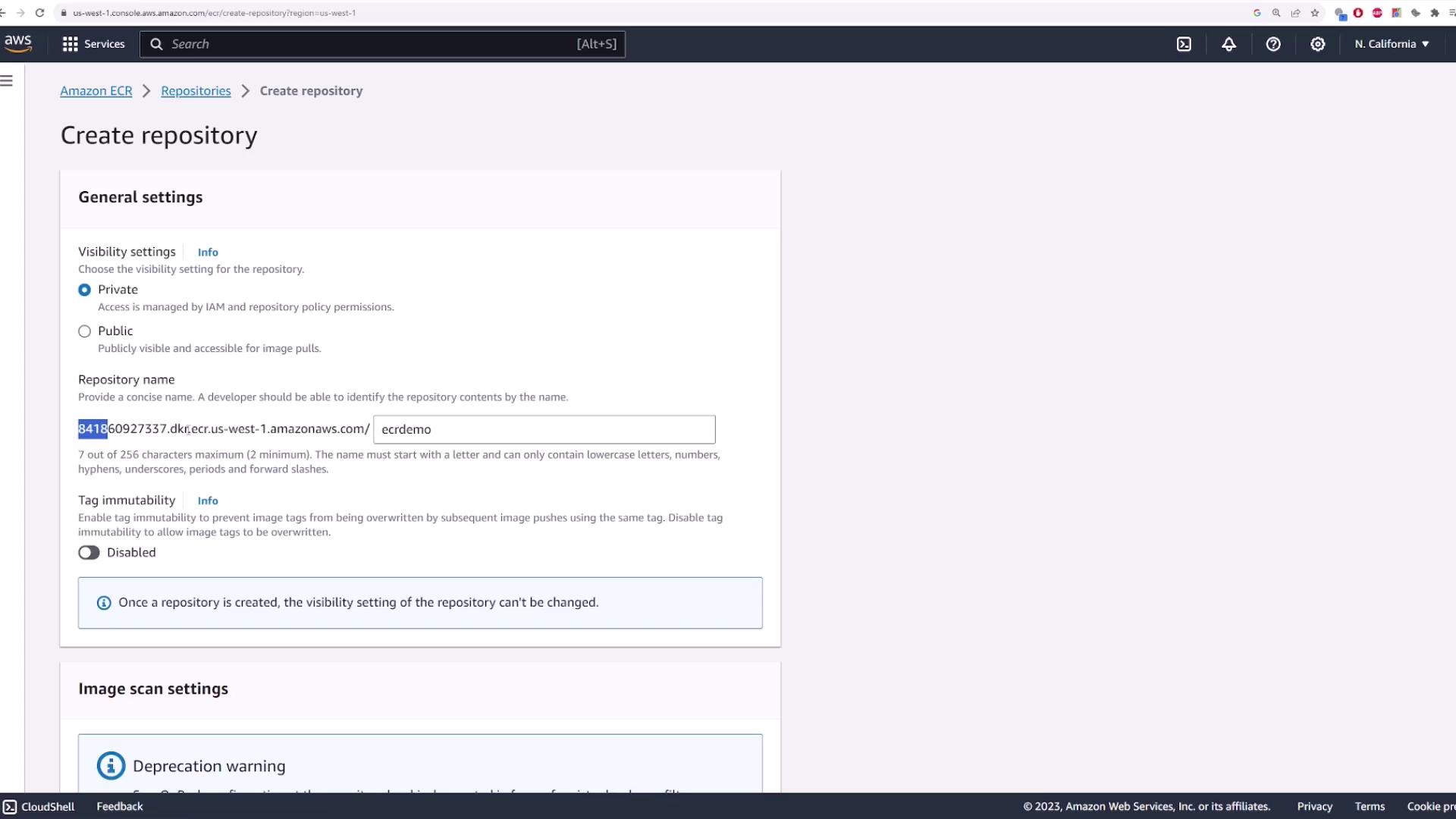
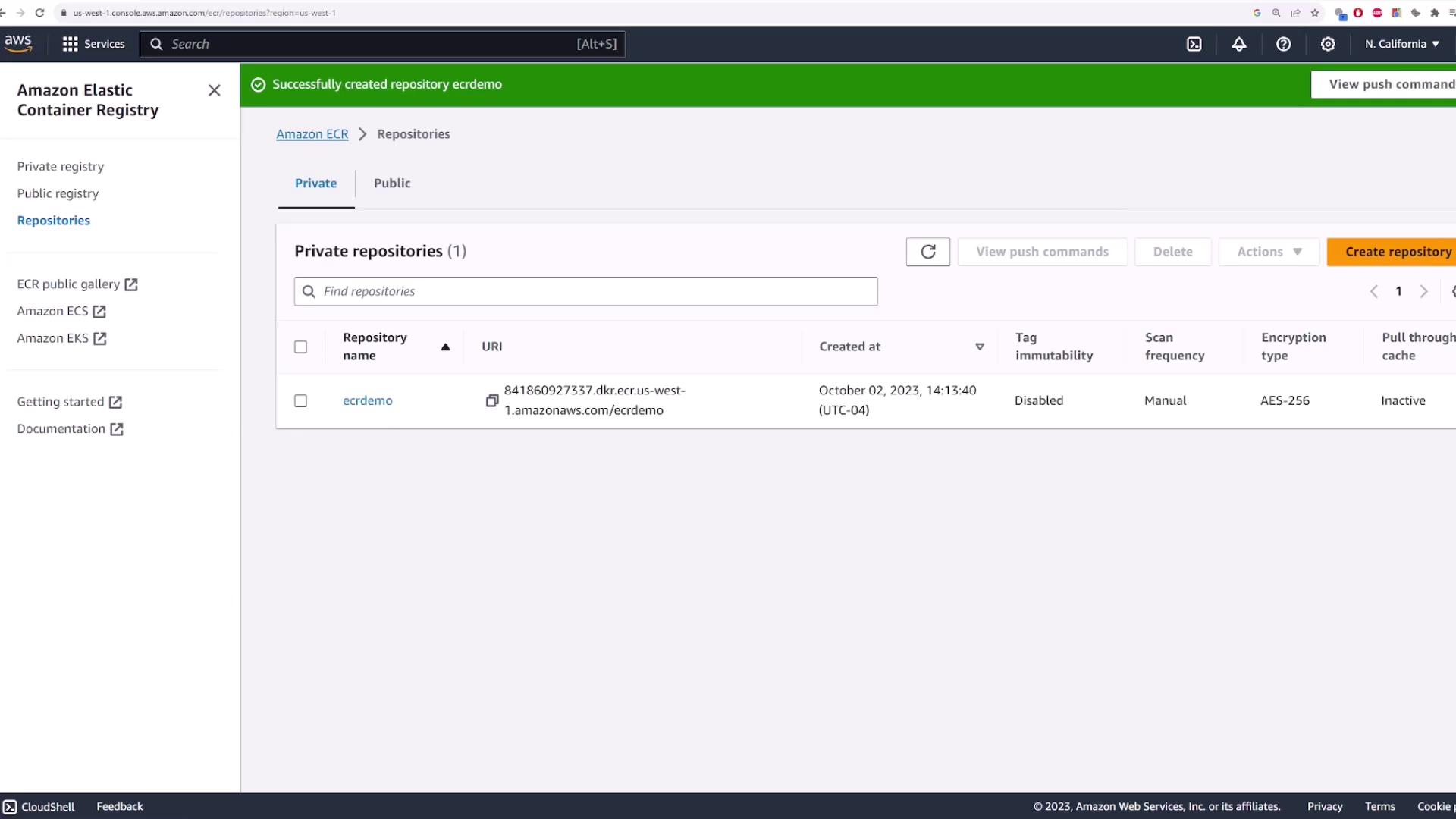
Start by searching for “ECR” in the AWS Management Console. Once you locate the service, choose to create a repository. You can either click the “Create repository” button directly or navigate to “Repositories” and then click “Create repository.”
Pushing a Docker Image to ECR
To push a Docker image to your repository, AWS provides a set of commands. Begin by authenticating Docker with ECR using the AWS CLI, which retrieves a login password and pipes it to Docker. Run the following command:Note: Ensure the AWS CLI is installed and configured with your access keys. If you’re on an EC2 instance, consider assigning an IAM role with the appropriate permissions instead of using static credentials.After authentication, build your Docker image and tag it with your repository URI. Use the commands below to complete the process:
docker image ls will list your image locally. Remember that your image must be tagged in the exact format, including your account ID, region, and repository name, before pushing it to ECR.
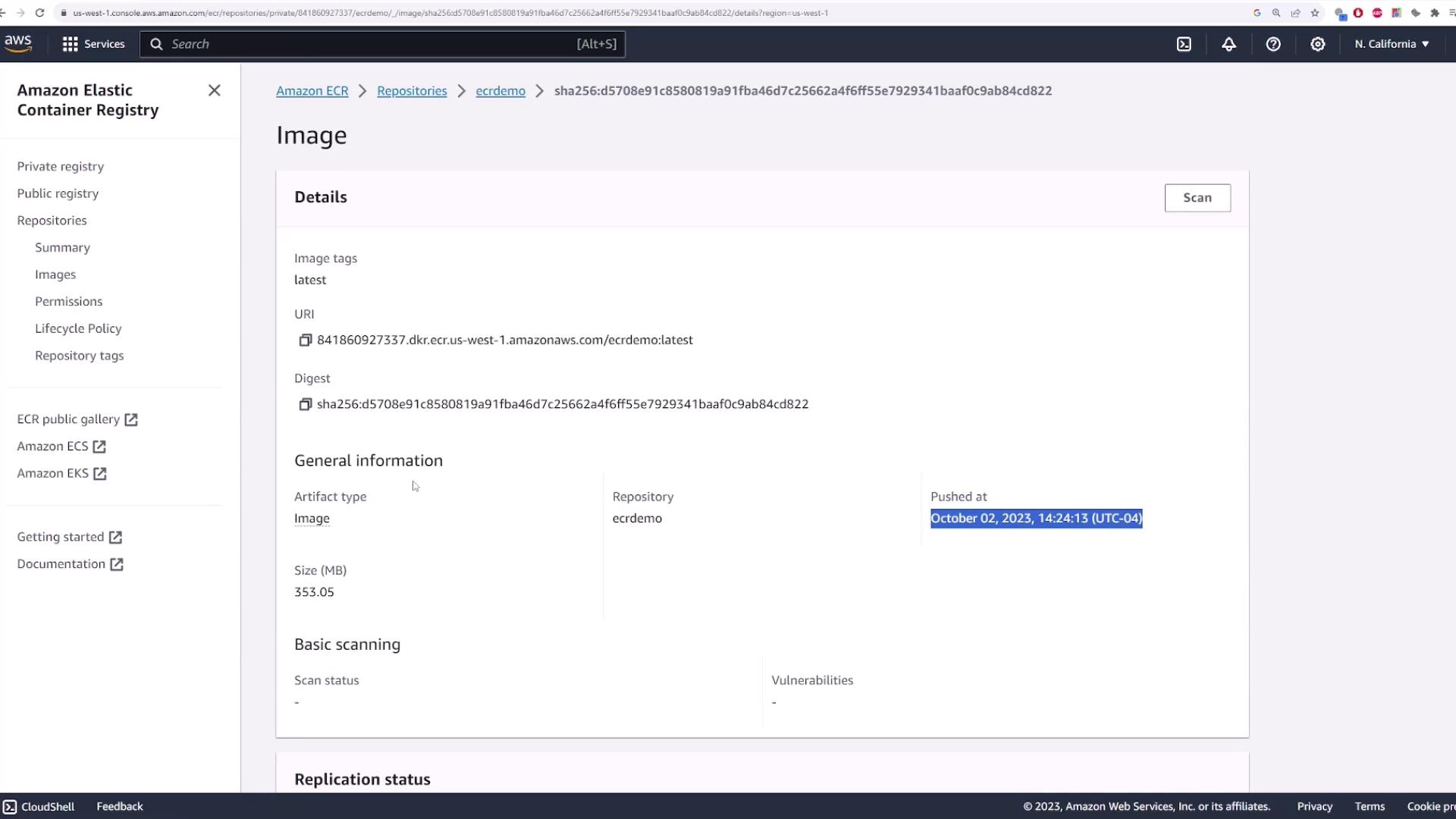
After pushing, the AWS console will show the image details such as tags, URI, digest, and the push date.
Deploying the Image from ECR
To verify that your image is deployable from ECR, try pulling the image on a server. First, remove the local copy of the image to simulate a fresh pull:Tip: Always ensure that you use the full image name (AccountID.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/repository-name) when pushing or running your Docker images. This guarantees that Docker pulls the image from ECR regardless of the deployment platform, be it EC2, Kubernetes, ECS, or another orchestrator.
Summary
This demonstration covered the process of:- Creating an ECR repository with proper configuration.
- Authenticating Docker with ECR using AWS CLI.
- Building, tagging, and pushing a Docker image.
- Verifying the image’s deployability by pulling and running it in a container.