Creating a Table
In this section, you’ll create a DynamoDB table calledreview to store product reviews. The table features a simple key schema:
- Partition Key:
product(String) - Sort Key:
user(String)
--attribute-definitions flag to specify data types and the --key-schema flag to denote each key’s role (HASH for partition key and RANGE for sort key). The --provisioned-throughput flag sets the table’s read and write capacity units as shown below.
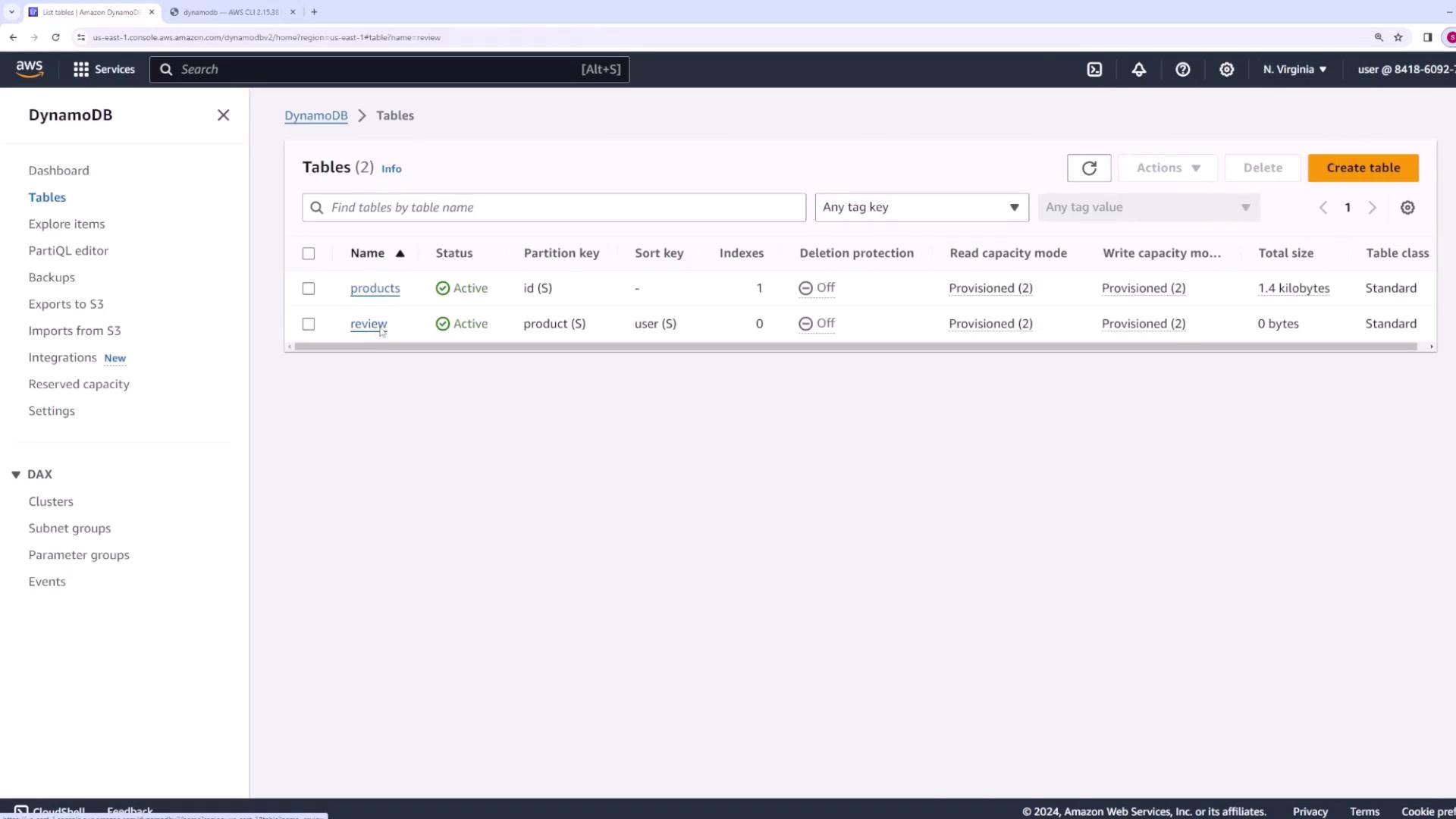
Run the following command to create the table:
products), run:
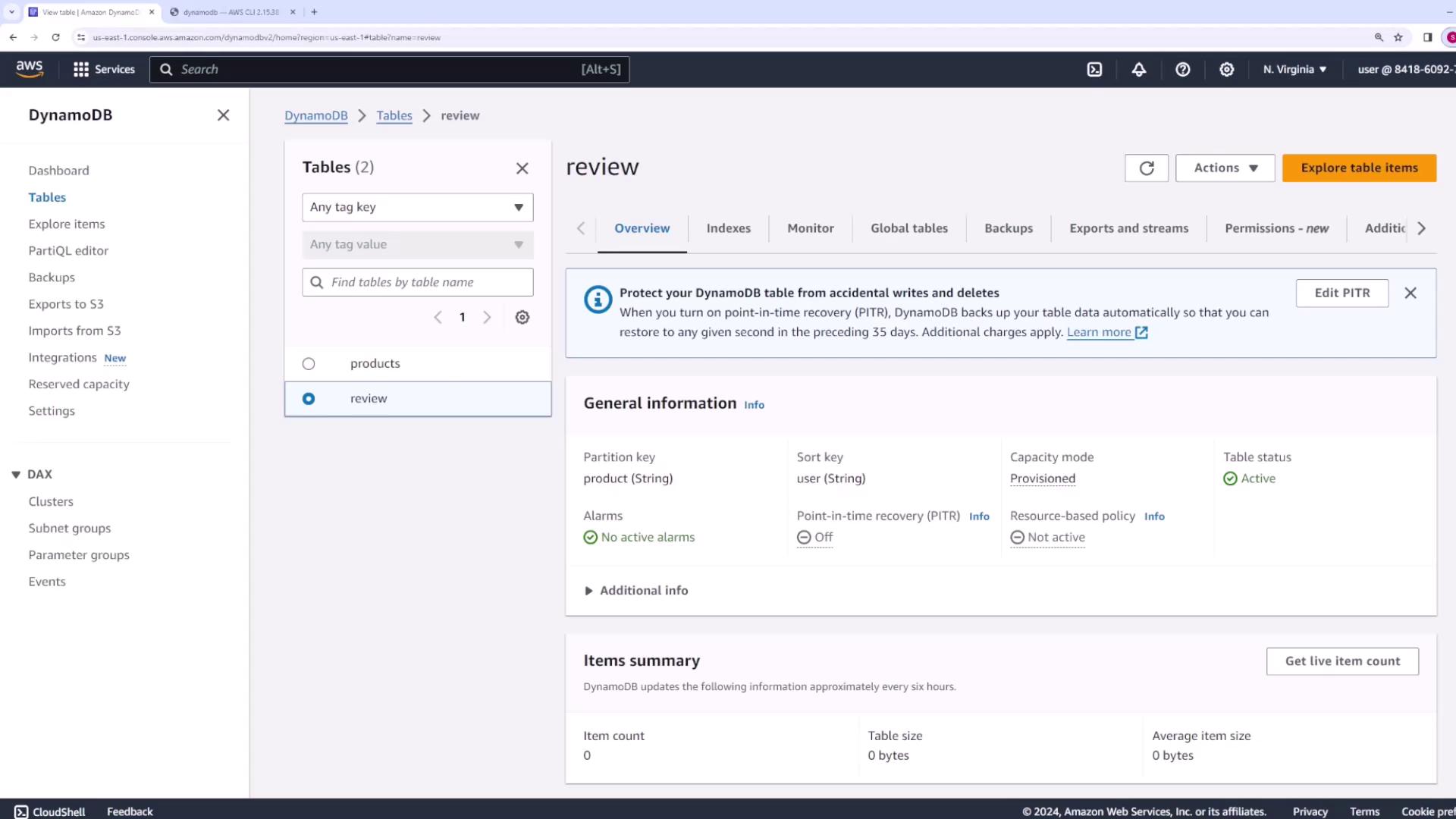
review table is listed with a partition key defined as product (String) and a sort key as user (String).
Exploring the Products Table
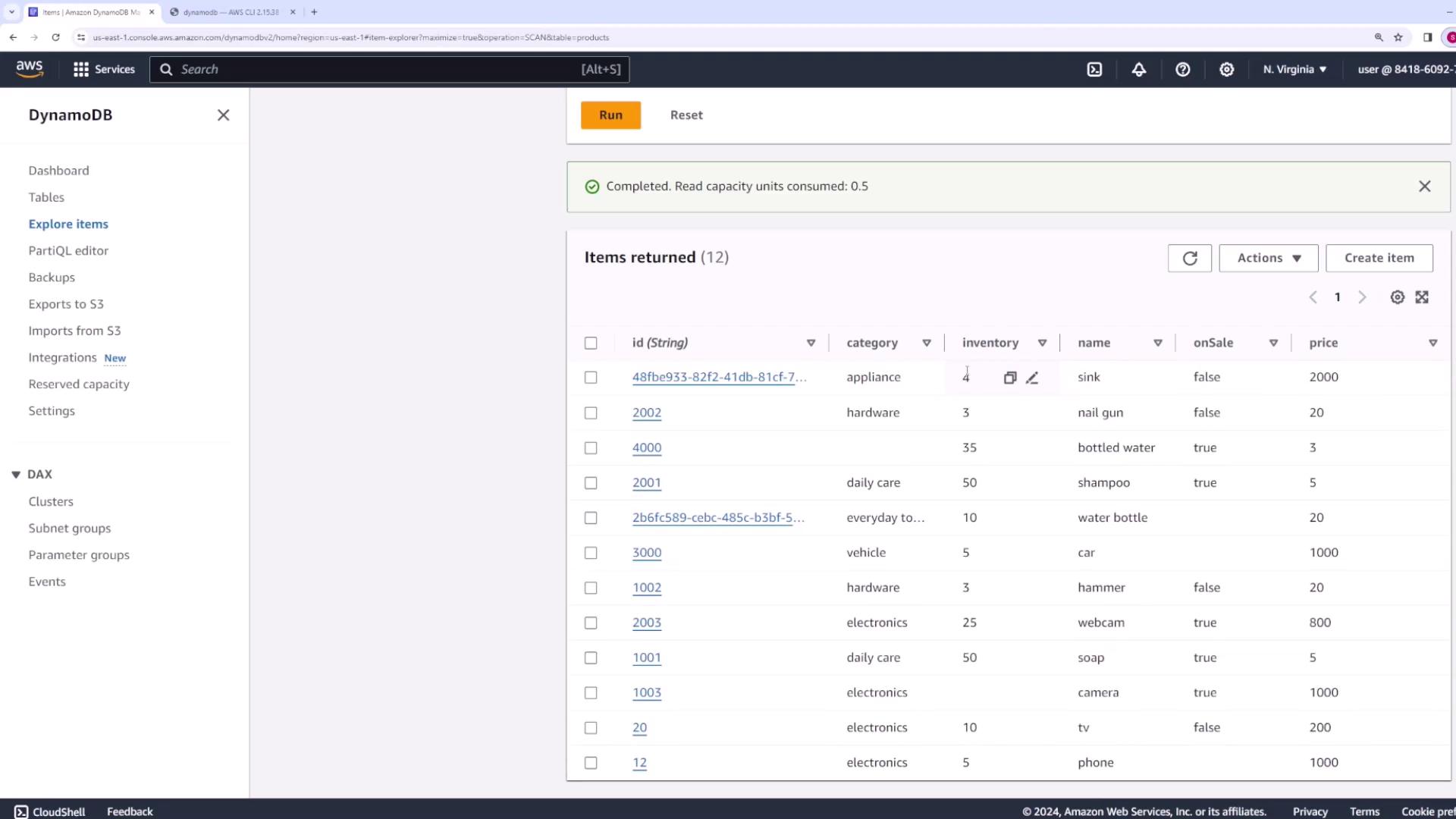
For this demo, we will work with an existing table calledproducts. This table uses a single partition key and includes additional attributes:
id– Unique identifier (String)name– Product namecategory– Type of product (e.g., electronics, appliance, hardware)price– Product price (Number)onSale– Boolean indicating if the product is on saleinventory– Stock quantity (Number)
Scanning a Table
Scanning is the simplest operation to retrieve all items from a table. Although scanning can be resource-intensive for large datasets, it is perfect for demonstrations or small datasets.Basic Scan
Run a basic scan to retrieve items:--max-items flag:
Items, Count, and ScannedCount.
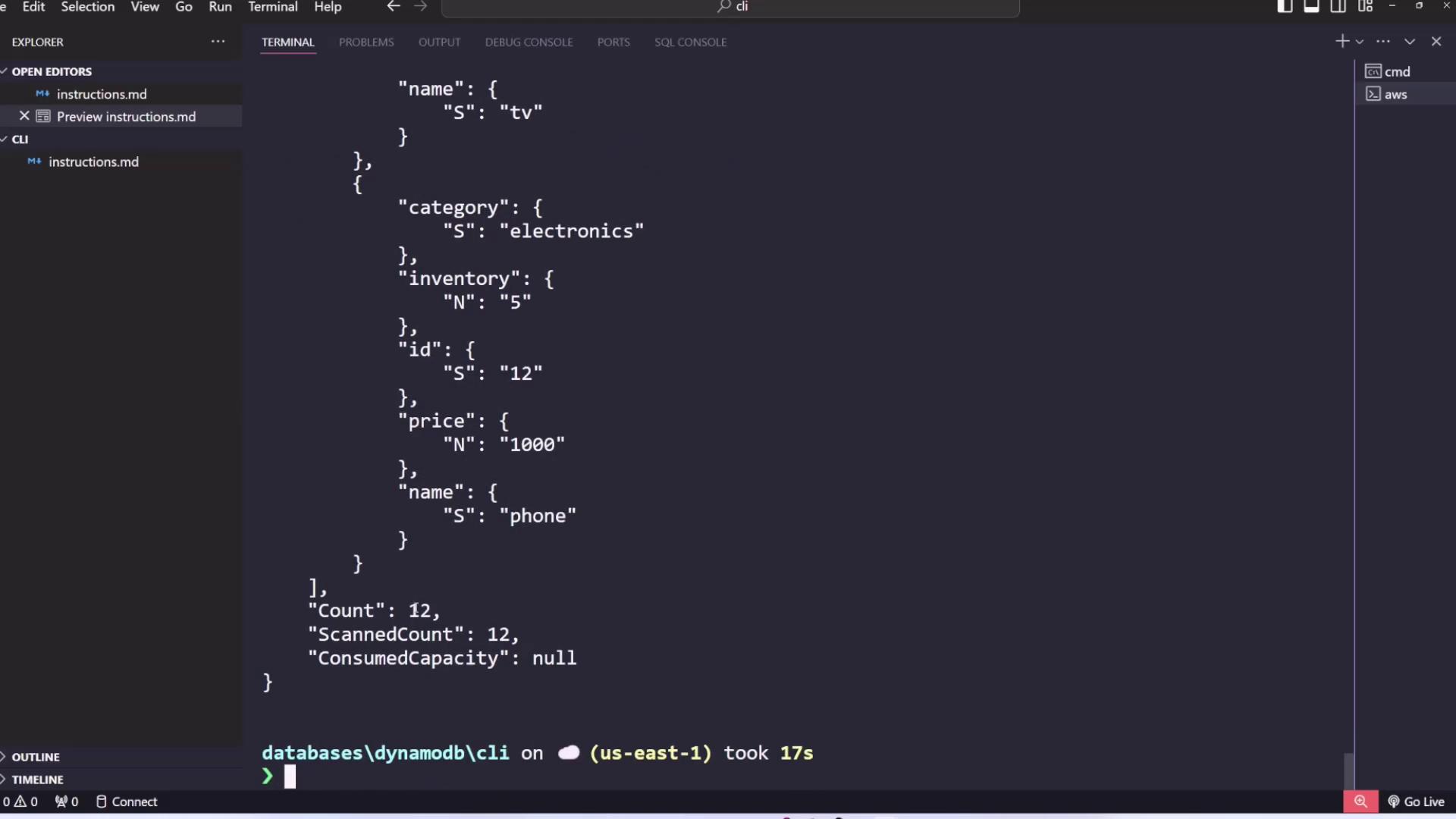
Example JSON output:
id, name, price, inventory, and onSale.
A sample command output might resemble:
Pagination with Scan
For larger datasets, pagination retrieves items in batches. DynamoDB provides aNextToken when additional results are available. Retrieve the next batch with:
<token> with the token returned in the previous scan. Continue paginating until no token is returned.
Using Projection Expressions
To minimize data transfer, you can retrieve only specific attributes. For example, to fetch only theid, price, and category attributes:
Filtering Items with Scan
DynamoDB supports client-side filtering. For instance, to retrieve only products belonging to theelectronics category, use a filter expression. Although filtering reads all items, it returns only those that match the specified condition.
Run the following command:
:category with its value defined in the --expression-attribute-values flag. You can also combine this with projection expressions:
category equals electronics will be displayed.
Querying a Table
For efficient data retrieval when key values are known, use the query operation. In this demo, an index is configured with the partition keycategory to allow efficient queries by product category.
Query the products table for all electronics items using the following command:
id of “20”. If your table uses both a partition and sort key, include both in the command.
Example output:
Creating, Updating, and Deleting Items
Put Item
To insert a new item into theproducts table, use the put-item command. For example, to add a new product:
If you rerun the put-item command to update an existing item (for example, adjusting the
price), you must include all attributes to avoid unintentionally deleting any attribute. In the example below, the entire item is replaced with the updated attributes:Delete Item
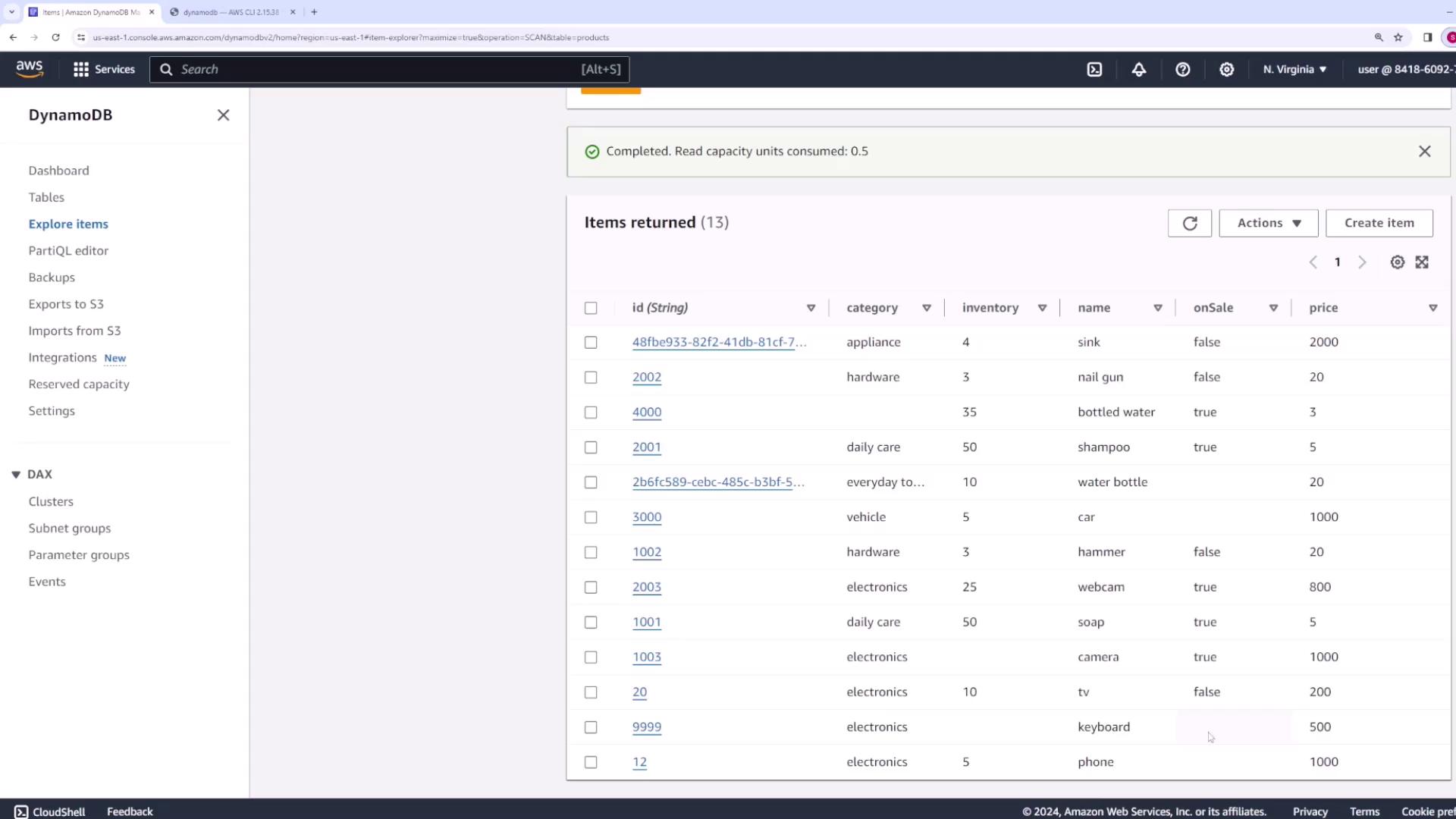
To remove an item from the table, use the delete-item command and specify the primary key. For example:id of “9999” has been removed.
Summary
In this lesson, you learned how to:- Create a DynamoDB table using the AWS CLI with a specified key schema and provisioned throughput.
- Scan a table to retrieve all items, implement pagination, utilize projection expressions, and apply client-side filtering.
- Use the query command for efficient data retrieval when indexes are available.
- Retrieve specific items with the get-item command.
- Insert new items using put-item, update existing items by replacing them, and remove items using delete-item.