- Restrict public access by selecting specific virtual networks or IP addresses.
- Disable public network access completely.
- Integrate your existing virtual networks or create new ones for communication through service endpoints.
- Add designated IP ranges from your organization to the firewall for precise access control.
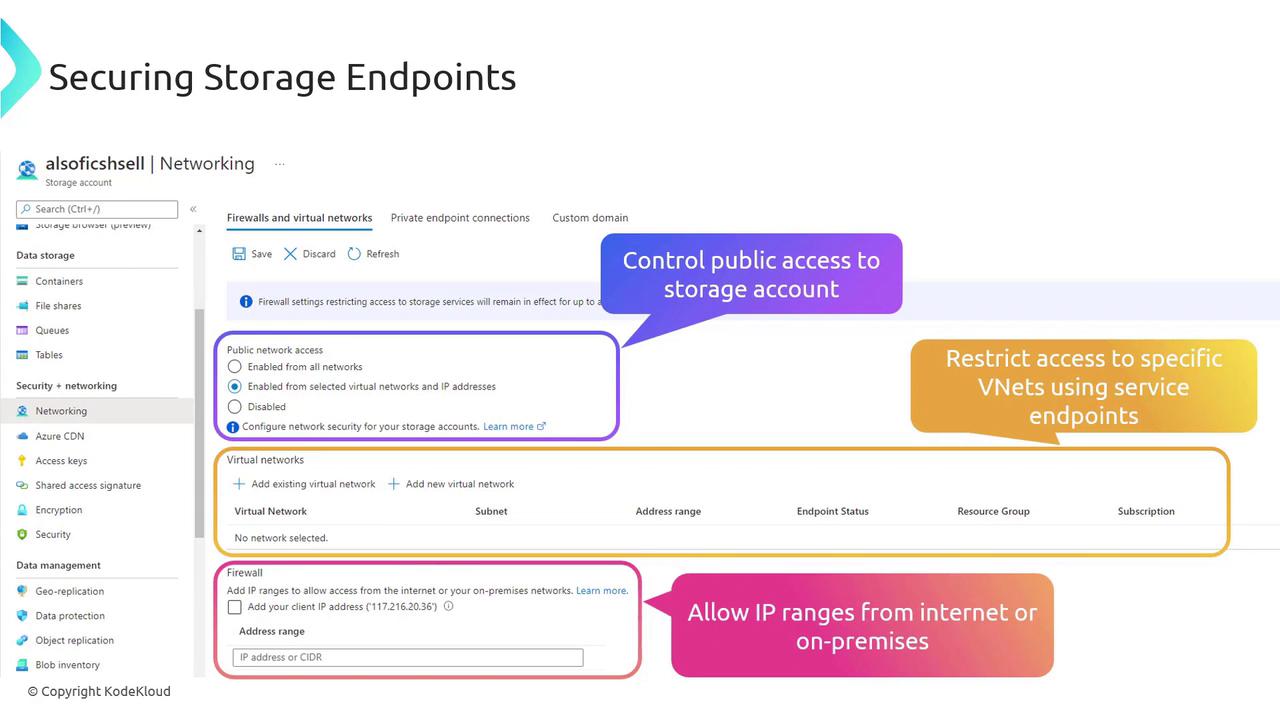
For organizations that prefer to eliminate all public communication, consider disabling public network access and configuring a private endpoint. This approach ensures a fully private connection to your storage accounts.
Key Security Capabilities for Storage Accounts
Storage accounts are equipped with built-in security features that provide comprehensive protection:-
Encryption:
All data stored in your storage account is encrypted by default using Storage Service Encryption (SSE). No additional configuration is required, ensuring data remains secure at rest. -
Authentication:
Leveraging Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), you can authenticate requests and authorize access to your storage accounts with fine-grained control. -
Data in Transit:
Data is protected during transfer through HTTPS, client-side encryption, and protocols such as SMB 3.0. Additionally, Azure Disk Encryption secures the operating system and data disks in both Linux and Windows virtual machines. -
Shared Access Signatures (SAS):
SAS tokens provide granular control by defining which operations can be performed on your storage account, enhancing overall security and access management.
In-Depth Topics Covered
This article will delve into the following areas to help you understand and implement these security features effectively:- Storage Service Encryption (SSE)
- Azure Disk Encryption
- Configuring networking rules for secure access
- Integrating virtual networks and private endpoints